1. A few words about Ethereum
1.1. What is Ethereum?
Ethereum is the most developed Layer 1 blockchain platform and the leading cryptocurrency on the market, second only to Bitcoin by capitalization. Founded by Vitalik Buterin in 2013, Ethereum became the first project to expand the capabilities of blockchain through the introduction of smart contracts.

With Ethereum, not only can users own and trade the cryptocurrency Ether (ETH), but developers can also build and deploy decentralized applications (DApps) and Smart Contracts on this blockchain platform.
Ethereum lays the foundation for thousands of technology startups and large companies globally, providing a platform to promote innovation and development in fields such as decentralized finance (DeFi), Blockchain Gaming, NFT and many other fields.
1.2. Who is Vitalik Buterin?
When answering the question what is Ethereum, it is impossible not to mention Vitalik Buterin. He is one of the most important and influential individuals in the cryptocurrency industry.

From an early age, Vitalik showed exceptional mathematical ability and was selected for a class for gifted students. Since then, he has developed more and more abilities in mathematics, programming and economics.
With his analytical ability and extensive knowledge of programming languages, he became famous when he founded Ethereum before he was even 20 years old.
1.3. Formation of Ethereum
Before Ethereum was born
At the age of 17, Vitalik learned about Bitcoin through his father - a computer scientist. At that time, Bitcoin had only been launched for 2 years.
Vitalik was quite skeptical about the value of BTC at that time because this currency was not supported by any party. But the more he learned, the more Vitalik wanted to join this new economy.
However, Vitalik's conditions do not allow him to have full facilities to mine Bitcoin. After that, he decided to find a job related to Bitcoin and became a writer for Bitcoin Weekly with a royalty of 5 BTC/article (equivalent to 3.5 USD at that time).
In 2013, Vitalik delved into crypto projects in different countries and realized: Bitcoin is a great form of digital currency but not suitable for building advanced applications.
When Ethereum was born
In November 2013, Vitalik perfected the idea with the Ethereum whitepaper, which he sent to his friends and received a lot of attention.
On January 26, 2014, Vitalik announced Ethereum at the North American Bitcoin Conference and Ethereum was hailed as the "successor" to Bitcoin.
A few months later, Ethereum held an ICO for ETH and raised 31,000 BTC (equivalent to $18M at the time).
In 2015, Frontier - the first fully functional version of Ethereum was officially launched. The platform's rapid success has attracted the attention of tech giants like IBM and Microsoft.
In 2016: Ethereum's DAO was hacked, causing Ethereum to split into two separate blockchains: Ethereum and Ethereum Classic.
In 2018, Vitalik Buterin and the development team launched a plan to upgrade Ethereum to Ethereum 2.0 version. This decision was made to address several important issues facing Ethereum, including scalability, energy consumption, and improving network performance. However, it will not be until 2022 that this upgrade will be implemented.
Podcast with Vitalik Buterin about crypto and Ethereum
Above is the formation process of Ethereum. So how does Ethereum work? Let's learn more in the next section.
1.4. Differences between Ethereum and Bitcoin – Purpose of Ethereum
Bitcoin and Ethereum are quite similar because they are developed on the Blockchain platform. However, the biggest difference is the purpose of these two currencies. With Ethereum, it was created as a platform for the development of smart contracts and Dapps - decentralized applications.
As for Bitcoin, its purpose is to become a currency, a payment method and a place to store value. In addition, the Ethereum platform also has advantages over Bitcoin such as: faster transaction speed than Bitcoin and cheaper transaction fees than Bitcoin.
1.5. What is an Ethereum Wallet?
If I explain this term in a technical way, it will probably be very complicated. So I will explain it briefly as follows:
ERC20 is a standard used for all tokens running on the Ethereum Blockchain platform. And the truth is that you can create your own ERC20 token in an extremely simple way.
Where to store Ethereum?
Currently, there are many options for you to safely store Ethereum from online wallets to offline wallets. Below are some of the most popular types of ETH storage wallets: Metamask Wallet; Blockchain Wallet; Ledger Nano S cold wallet.
So which of the 3 wallets above should you use to store Ethereum?
The answer depends on each person's goals. If you want to store Ethereum for a very long time and don't care about it, you can use the Ledger Nano S cold wallet. It is a safe wallet. If you want to move quickly and regularly transfer ETH for transactions, you should use the other two wallets.
The first thing to do to buy Ethereum is to create a wallet address (Wallet) to store your Ethereum coins. You can use an "Online" or "Offline" wallet or a cold wallet depending on your needs. If you often buy and sell, you should use an Online wallet. If you plan to store it for a long time, about a few months, a year or a few years, you can use it. You can use cold wallets.
+ With Online wallets, web wallet platforms include some of the most popular and widely used wallets such as Blockchain.info, CoinBase or MyEtherWallet.
+ With Offline wallets or cold wallets, there are software wallets or USB wallets (shaped like a USB), such as Ledger Nano S or Trezor.
2. How does Ethereum work?
2.1. Ethereum's operating mechanism
Technology
Ethereum operates on a public blockchain network and uses a virtual machine called the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) to carry out transactions and run smart contracts.
A smart contract is an automated and self-executing computer program, written in a programming language and deployed on a blockchain network. It is used to execute the terms and conditions of an agreement automatically and reliably, without the need for third-party intervention.
For example:
Suppose person A rents a house from person B, person A can pay rent to person B in crypto through blockchain. The receipt will then be included in the smart contract for processing and storage.
Person B promises to give person A the code to open the door to the house at 8:00 am the next morning. If at 8am the next morning, person A does not receive the code on time to enter the house, the blockchain system will automatically return the money to person A because B did not comply with the agreement.
If B sends the code to A before 8:00 a.m. (before the deadline), the smart contract system will retain both the money and the key code until exactly 8:00 a.m.; Then the system will automatically send the code to A and send money to B.
Therefore, smart contracts provide a trustless system where neither A nor B need to worry about potential risks. This also eliminates the need for a middleman. Here, A and B do not need to pay any additional fees for any intermediary services before they can make purchase and exchange agreements.
Ethereum's operating process (when applying the POW mechanism)
Ethereum's POW mechanism includes the following 6 steps:
a. Transaction: here refers to users creating and sending transactions on the Ethereum network. This transaction could be transferring funds from one Ethereum address to another or performing other operations such as deploying a smart contract.
b. Transaction confirmation: The transaction is sent to the Ethereum network and is confirmed by nodes on the network, contributing to the verification process and added to a block in the blockchain.
c. Block Mining: The block mining process is performed by miners on the Ethereum network. Miners compete to solve a difficult problem, and when they solve it, they are allowed to add new blocks to the blockchain and receive rewards in Ether (ETH).
d. Confirmation by the network: When a new block is added to the blockchain, it is confirmed by nodes on the Ethereum network. This process ensures the integrity of data and transactions on the network.
e. Running smart contracts: The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is an environment that runs smart contracts on Ethereum. EVM ensures secure and consistent execution of smart contracts across the Ethereum network.
f. Gas fee: When making transactions or running smart contracts on Ethereum, users have to pay a fee called gas fee. Gas fee represents the amount of computational work and network resources required by a transaction or contract.
2.2. EVM and its role in the Ethereum network
EVM is a solution to help DApps on Ethereum integrate and be compatible on many different blockchain platforms. EVM is understood as Ethereum virtual machine.

In its blockchain platform, EVM will act as an intermediary in executing smart contracts on the Ethereum network.
Each node on Ethereum will be its own EVM to ensure transparency and decentralization of the network. Thanks to that, EVM will provide an environment that allows many applications to access and run in many different ways.
This is the premise for EVM blockchains to develop more easily in integrating infrastructure applications from the Ethereum ecosystem.
The birth of the EVM blockchain
If later platforms want to take advantage of Dapps on Ethereum, they must build platforms that are compatible with the Ethereum virtual machine or EVM blockchain.
Developers, whether new or experienced, spend time researching and getting familiar with a new programming language. For EVM blockchain, builders only need to customize a little to help Ethereum smart contracts or Dapps run on their blockchain platforms.
Examples of some prominent blockchain EVMs: Avalanche, Fantom,…
3. Ethereum update phases
3.1. What is POW Ethereum? Mechanism of action
So what is POW on Ethereum?
Proof of Work (POW) translated into Vietnamese is Proof of Work. This is the first consensus mechanism created on the blockchain to verify and confirm transactions, create consensus, and secure the network.

In the POW system, miners compete with each other to solve complex computational problems. This process is called "mining". To find the correct answer, miners must spend a large amount of energy and computational work.
When a miner finds the correct answer, they have the right to add a new block to the blockchain and receive a reward of that network's currency.
This mechanism has been successfully applied to Ethereum in the past and Bitcoin until now. However, this mechanism consumes too much energy and requires investment in hardware, so some blockchain platforms have switched to Proof of Stake (POS) mechanism to reduce energy consumption as well as increase efficiency. network capacity. And Ethereum is one of those blockchains.
3.2. Transition from POW to POS on Ethereum
On September 15 2022, at 06:42:42 UTC, at block 15537393, The Merge upgrade was completed, moving Ethereum from Proof of Work (POW) to Proof of Stake (POS), causing quite a big change.
Instead of requiring mining nodes to run expensive equipment to discover new blocks, the new POS system requires users to deposit and lock up 32 ETH to become network validators.
The Merge upgrades Ethereum consensus from POW to POS by merging the Ethereum Mainnet with the Beacon Chain Proof of Stake system.
This upgrade improved Ethereum's sustainability by reducing energy consumption and is part of the ongoing upgrade of the Ethereum platform to improve scalability, security, and sustainability.
3.3. Benefits and challenges of POS
Benefits of POS
-
Shard chains: Ethereum's new POS blockchain supports the implementation of new “shard chains”. These will be 64 smaller blockchains, each of which will process their own batches of data, allowing Ethereum to process significantly more transactions per second.
-
Less energy: The new Ethereum blockchain uses 99.95% less energy than the proof-of-work version.
-
Reduced barriers: Because validators do not need to purchase and operate expensive mining equipment, this lowers the barrier to entry for everyone participating in the network; In addition, it supports improving decentralization and network security.
Challenges of POS
Although the POS mechanism brings many benefits, it also has certain challenges, specifically:
-
Centralization: POS can create the phenomenon of asset concentration where validators with more assets to stake will have more opportunities to validate the next block. Then, the more money validators accumulate, the more money they can stake and earn. This also means that people with more tokens will have more power; causing injustice and imbalance in network decision making.
-
Consensus and security: In POS, achieving consensus and ensuring network security depends on miners having an economic interest in following the rules. However, if a large number of miners have bad intentions, 51% attacks can occur.
3.4. Ethereum Update Phases
The initial development of Ethereum is divided into 5 main stages: Frontier, Homestead, Metropolis, Serenity/Ethereum 2.0, Beacon Chain
Frontier phase
This is the period that marks the official launch of Ethereum and is also the period when EVM is introduced, allowing developers to build and deploy decentralized applications (Dapps) on the Ethereum blockchain.
Homestead Phase
This phase provides security and stability improvements to Ethereum; Enhances signature checking, optimizes performance, and fixes bugs in the Frontier version.
Metropolis phase
The Metropolis period is divided into two parts: Byzantium and Constantinople.
-
Byzantium is a software update of Ethereum, deployed on October 16, 2017. This phase brought many improvements to the development of Ethereum; including enhancing security and scalability. Byzantium also paves the way for the implementation of new functionalities, such as “zk-SNARKs” smart contracts, which allow transactions to be conducted with greater privacy.
-
Constantinople is a continuation of the Metropolis phase launched on February 28, 2019 to improve performance and reduce transaction costs.
Serenity/Ethereum 2.0 phase
Ethereum 2.0 is an important improvement, aiming to increase Ethereum's scalability and move from Proof of Work (POW) to Proof of Stake (POS). Serenity introduces Beacon Chain, Shard Chains and Ethereum Docking (identical to Ethereum 1.0).
Beacon Chain Phase
Beacon Chain was activated on December 1, 2020 and is the first phase in the implementation of Ethereum 2.0. Beacon Chain's mission is to manage validator evaluation, shard chain management, and create a trusted environment for Ethereum 2.0.
4. What is Ethereum gas fee?
4.1. What is Ethereum gas fee?
You've heard the phrase Gas fee a lot, so do you know what the gas fee on Ethereum is?
Gas fee is understood as the cost required to perform each transaction on Ethereum.
Ethereum has been developing more and more applications. One of the applications that has made waves on the Ethereum network is Crypto Kitties - an electronic cat breeding application.

Crypto Kitties attracted special attention from the crypto community at that time. When Crypto Kitties became popular, the Ethereum network experienced complete congestion for about 2 days. During that time, gas fees (transaction fees) have increased dramatically, reaching hundreds of gwei.
4.2. Why do users need to pay gas fees?
Suppose person A transacts using Ethereum, signs and sends that transaction to another e-wallet, all of those transactions will be pushed into the mempool.
Mempool is understood as a virtual waiting room, where transactions are pushed into the pool waiting to be processed. Miners will choose transactions to close into blocks, then they will use mining speed to resolve transactions on that block.
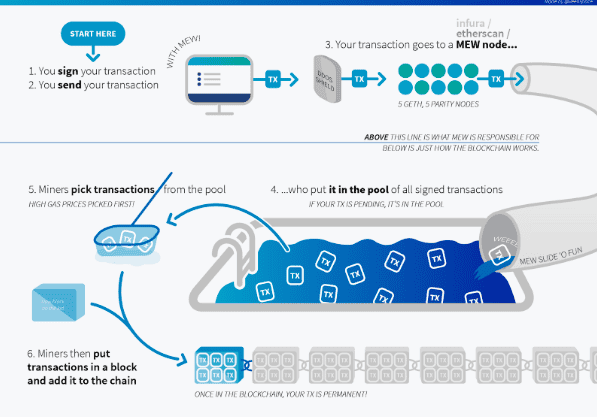
If the mempool is too full, miners cannot put all transactions into the block, they are forced to choose transactions to continue solving.
At that time, miners will choose transactions with high fees to process first because the higher the transaction fee, the more rewards the miner will receive.
4.3. Gas limit and gas price
When talking about gas, there are two terms to pay attention to: gas limit and gas price.
-
“Gas limit” is the maximum amount of gas a user needs to pay for a transaction. For example, if you drive a car, the maximum number of liters your fuel tank can hold is the "Gas limit".
-
“Gas price” is the fee payable per unit of gas used. For example, when filling up with gas, how much does each liter of gas cost? That is the gas price.
4.4. How to calculate gas fees
How to calculate transaction fees on the Ethereum network: Take the highest gas fee you can pay and multiply it by the gas price you want to pay:
-
Transaction cost = gas limit * gas price
For example, if the gas limit is 20,000 and the price per unit is 200 gwei, the calculation would be:
20,000 * 200 = 4,000,000 gwei is equivalent to 0.004 ETH.

Looking at the chart on the left, it can be seen that the base fee (the portion of the transaction fee burned) since The Merge event reached ATH in May 2023. This is the time when the narrative about meme coins took over, causing gas fees. boom.
4.5. Why are gas fees on Ethereum not fixed?
Gas fees on Ethereum are not fixed and can change depending on the following factors:
-
Competition on the network: When more people are making transactions at the same time on Ethereum, the competition to be processed quickly and included in new blocks increases. Users will then need to pay more to increase the chances of their transactions being prioritized. We see this clearly in uptrend market periods.
-
Changing gas prices: Ethereum users can freely set gas prices for their transactions. When the network is not congested, users can set low gas prices to save costs. However, as transaction load increases, users can increase gas prices to ensure their transactions are prioritized for faster processing.
-
Changes from the network: Changes to the Ethereum network rules can occur through improvements or upgrades. These changes may affect how gas fees are calculated and change how high or low gas fees are.
5. Improvements and new features on Ethereum
5.1. Ethereum 2.0 and the transition to POS
Ethereum 2.0 is an outstanding upgraded version of Ethereum. One of the key improvements with Ethereum 2.0 is the move from POW to POS.
When switching to POS, Ethereum users can become validators by locking an amount of ETH as a deposit and participating in transaction verification.
Instead of mining coins like the POW mechanism, POS allows users to earn profits by verifying transactions on the network. The transition to POS significantly reduces energy usage and increases transaction processing speeds on Ethereum.
5.2. Shard and scalability improvements
Shards are a key feature of Ethereum 2.0, signifying the splitting of the network into smaller shards.
Each shard operates as an independent network, capable of processing transactions and storing data separately; helps enhance Ethereum's scalability, allowing the network to process more transactions and decentralized applications simultaneously.
After The Merge is completed, the next upgrade, Shard Chains, is expected to launch this year 2023.
Once this upgrade is complete, the network is expected to be able to scale flexibly according to demand and accommodate the growing number of users and applications on Ethereum.
6. Cryptocurrencies and tokens on Ethereum
6.1. Tokenomics
Basic information about ETH
- Ticker: ETH
- Blockchain: Ethereum
- Token Standard: ERC-20
- Token type: Utility & Governance
- Max Supply: unlimited
- Total Supply: 120,224,090
- Circulating Supply: 120,224,090
How was ETH initially allocated?
Ethereum started with a supply of 72 million Ether (ETH). 83% of them (60 million ETH) were distributed to those who purchased ETH during the token sale conducted in July and August 2014.
Of the remaining 12 million ETH distributed at the network's launch in 2015, half was divided among the 83 original contributors to the protocol primarily based on contribution time. The remaining half is reserved for the Ethereum Foundation.
What is the use case of ETH?
- Pay gas fees on the Ethereum network.
- In addition, ETH is also used as gas fees for activities on Ethereum's Layer-2 platform such as Arbitrum, Optimism,...
- Stake to become a validator: users can stake ETH to become a validator and earn more profits
- Payment currency: ETH is used to pay for NFTs on some NFT marketplaces such as OpenSea, Blur,...
6.2. Introduction to ERC-20 and ERC-721
What is ERC-20?
ERC-20 is a technical standard used to issue and deploy tokens on the Ethereum network.
This is considered a form of Fungible token - a replaceable token. ERC-20 has become an industry standard for tokens on Ethereum, creating uniformity in token processing and trading on the platform.
What is ERC-721 (or NFT)?
ERC-721 is a decentralized token trading standard on the Ethereum platform. Different from ERC-20, ERC-721 defines tokens as unique and non-fungible, also known as NFTs.
Each NFT represents a unique asset or digital object, such as a painting, a sports match or real estate. NFTs can be used in many cases:
- Digital Art: Use NFTs to collect and trade works from famous artists.
- Games and entertainment: NFTs are used in blockchain games, allowing players to own and trade game items such as costumes, weapons,... and game elements with unique value .
- Virtual real estate: NFT provides the ability to own and trade virtual real estate, such as land and apartments on the blockchain. This creates a new virtual real estate market and opens up investment and business opportunities in the field.
- Digital versions of traditional assets: NFTs are used to create digital versions of traditional assets such as images, ownership certificates, certificates, etc. providing data integrity and digitally own traditional assets and facilitate their trading and sharing on the blockchain platform.
6.3. Ethereum deflation rate after The Merge event
According to Ultrasound.money, ETH supply has dropped sharply due to ETH being burned after the EIP1559 proposal was updated. This shows that the ETH supply has decreased by nearly 300k since The Merge event.
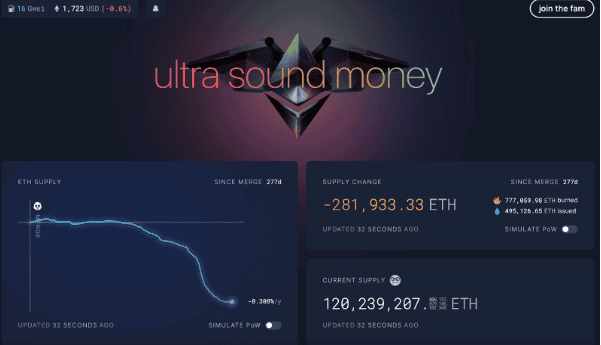
When creating Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto guaranteed that there would only be a finite supply of 21 million BTC. Once all 21 million Bitcoins are mined, no new BTC can be created.
In contrast, Ethereum had an inflationary supply at its inception. Ether supply is growing at an annual rate of 4.5%.
However, after The Merge event, ETH has become a non-inflationary asset because the burn rate is higher than the ETH issuance rate according to the annual inflation rate. The amount of Ether burned to keep the network running is more than the amount of Ether put into circulation.
The implementation of the EIP-1559 protocol changed the economic nature of Ethereum by incorporating the burning of a portion of gas fees for each transaction.
The portion of the transaction fee that is burned is called the Base fee. Base fee is used as the “market rate” to put into transactions. In each transaction, users can add a tip to the Base fee to encourage miners to receive their transactions first.
Advantage:
-
More consistent UX for users: when “market rate” is known, app developers can estimate gas fees for transactions more accurately and help users avoid overpaying.
-
Eliminate gas fee manipulation: for example, bad actors filling blocks with empty transactions to increase gas fees (EIP-1559 suggests BASE FEE will be burned).
-
Reduced inflation on ETH: in addition to paying less fees, ETH holders will also directly benefit from reduced inflation as some fees paid in ETH are burned.
-
Reduced network congestion: Because block sizes can be increased to meet demand (although only up to a certain limit).
-
Potentially lower fees: Since each block can now fit more transactions, transaction fees could drop to lower and more reasonable levels.
Defect:
- 20 - 35% of miner's income will be directly affected when Base fee is burned. (Miners still earn from tips and block rewards).
- Ethereum could be more overloaded: with a block size of up to 25 million gas, node operators will have to scale/prepare their infrastructure accordingly to handle it.
7. Decentralized applications (Dapps) on Ethereum
7.1. What are Dapps? Benefits of decentralized applications
What are Dapps?
Dapps is an acronym for Decentralized Applications - decentralized applications. Built and deployed on the blockchain platform, these applications do not have any intermediaries or control agencies to manage or operate.

Benefits of decentralized applications
Decentralized applications bring many benefits to users: from financial applications such as e-wallets, trading and borrowing to non-financial applications such as games, NFT markets, etc. ..
In addition, because it is a decentralized application, it will help save people time and money because there is no need for the intervention of a third party intermediary.
7.2. Examples of successful Dapps on Ethereum
-
Crypto Kitties: this is considered the first decentralized application on Ethereum. With Crypto Kitties, users can raise, trade and play with unique virtual cats.
-
Uniswap: Uniswap is a DEX and automated decentralized exchange (AMM) protocol built on Ethereum, allowing users to swap any ERC-20 standard token. Uniswap is considered the largest DEX on the Ethereum network.
-
Aave: Aave is considered the big brother in the DeFi village. This is a decentralized borrowing and lending platform on Ethereum; allows users to deposit money and create loan contracts with interest rates determined through smart contracts.
-
Decentraland: is a decentralized virtual world where users can buy, own and exchange land and virtual assets using MANA tokens.
-
Chainlink: decentralized Oracle protocol on Ethereum. Chainlink acts as a connection between smart contracts and external data sources; allowing smart contracts to securely access off-chain data feeds.
7.3. DeFi (Decentralized Finance)
DeFi is understood as decentralized finance. This is considered the most practical application of blockchain. Some prominent DeFi projects on Ethereum include:
-
Uniswap: Number 1 DEX on Ethereum
-
Aave: Lending platform on Ethereum
-
DYDX: DEX on Ethereum
7.4. NFT (Non-Fungible Token) and NFT market on Ethereum
NFT or Non-Fungible Token is a non-fungible token. It represents digital assets that are irreplaceable, unique, and have distinct value.
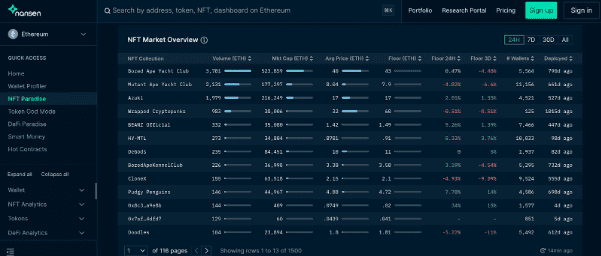
Up to now, it can be said that the NFT niche is the fastest growing on Ethereum. With top NFT collections such as: BAYC, AZUKI, DEGODS, CAPTAINZ, CRYPTO PUNK, PUDGY PENGUINS...
8. Conclusion: What is the future of Ethereum?
Ethereum has existed for 10 years and is still constantly developing its ecosystem. Below are 3 trends and development potential of Ethereum in the near future:
-
DeFi Platform: Ethereum has become the first platform for decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. Therefore, the potential for growth in the DeFi sector is huge, including the expansion and diversification of financial services, improved liquidity and enhanced security. This will create many new opportunities for asset management and trading in the DeFi ecosystem.
-
NFT: NFT has become a prominent growing trend on Ethereum. The growth of NFTs is likely to continue in art, sports, entertainment, real estate, and more. With its high liquidity, Ethereum will continue to provide a powerful platform for the development and trading of NFTs, creating new opportunities for artists, creators, collectors and mainstream users in the future. .
-
Scaling Innovations: Ethereum is continuing to research and develop scaling solutions to increase transaction processing capacity and reduce costs. The two ETH expansion solutions that are currently popular are Optimistic Rollup and ZK Rollup; helps the Ethereum platform handle a larger volume of transactions and supports the development of complex applications on the network.
Although Ethereum has certain development potential, it should be noted that Ethereum's future development will depend on many factors such as the legal environment, competition from other blockchain platforms and the development of blockchain technology in general.
Above is the entire content explaining what Ethereum is and information related to Ethereum. Hope the article is useful to you!
Read more


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt




