1. What Is Interchain Security?
Interchain Security is a technology developed and introduced by Cosmos, allowing chains to build and develop on Cosmos, with the option to use the same $ATOM security layer of Cosmos Hub without having to build the network themselves its own security net.
This is one of the services provided by Cosmos Hub - the central blockchain of the entire Cosmos ecosystem. In which Cosmos Hub is called the provider chain and chains using Interchain Security are called consumer chains.

Lợi ích và hạn chế của Interchain Security
2. Interchain Security and Replicated Security
Interchain Security is a broader term used for a group of blockchains with shared security. In particular, there will be many versions designed with different setups to use for each blockchain.
The first and simplest is “Replicated Security”, where identical validators on the provider chain (Cosmos Hub) are used to validate new blocks on the consumer chain. This allows consumer chains to fully inherit the security of Cosmos Hub. Or you can see that each validator is lending its shares to consumer chains.
But as a separate module, this Replicated Security works through IBC. IBC will act as a data relay between chains, periodically updating the Cosmos Hub's data and validators. The consumer chain will then update its own set of validators and replicate the Cosmos Hub setup data on its chain.
Validators on Cosmos Hub can validate multiple consumer chains at the same time, and will receive back both transaction fees from Cosmos and the native tokens of those chains.
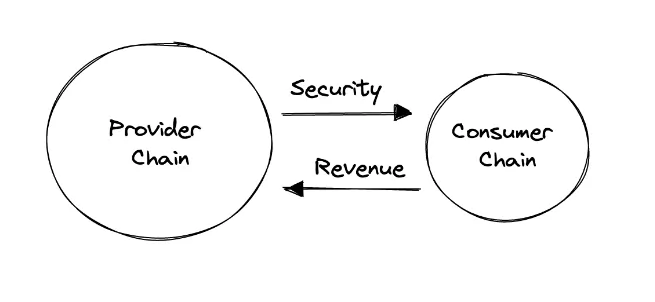
How Provider chain and Consumer chain work
One of the special points is that at any time the consumer chain can return to building an independent chain with its own validator system without having to use the security layer from Cosmos's $ATOM. Hubs too.
3. Benefits Interchain Security brings
3.1. Be fully secured with Cosmos Hub authenticators
Blockchains using Interchain Security powered by Cosmos will not need to bother building their own initial security layer and will benefit entirely from the security layer of Cosmos Hub. This also means that those blockchains will use the security provided by ATOM stakers, Cosmos validators will also directly participate in the process of validating transactions on the chain. consumer chain.
Currently, the number of validators on Cosmos has reached more than 180 validators, these validators will validate transactions in parallel on both Cosmos Hub and chains using Interchain Security. This significantly reduces the resources projects need to launch securely, as the cost of a potential attack on this emerging platform on the network is equivalent to the cost of attacking the Cosmos Hub itself—a of the largest and safest chains by market capitalization, backed by billions of ATOM staked.
3.2. Cost savings
Interchain Security removes a significant barrier to creating efficient and secure consumer chains by allowing them to rent security from Cosmos Hub. Building a security framework for any blockchain always costs a large amount of money, which has helped remove the initial barrier for chains wanting to build on Cosmos.
Developers can completely use Cosmos's security layer without worrying about building from scratch and just focus on developing the ecosystem.
3.3. Profit sharing, beneficial for both chains
Consumer chains using Cosmos security will be required to share a portion of the profits earned from their projects such as MEV, revenue, transaction fees (including trading fee and transaction fee) to the provider chain. . Currently, this level is being set at 25%.
3.4. Increase value for $ATOM and develop a sustainable ecosystem
Because $ATOM is used as a security layer for both Cosmos Hub and consumer chains, the need to use and utility of ATOM will always increase continuously.
This means that the implementation of the Interchain Security feature will provide a boost to $ATOM adoption. In the long term, it will help increase the value of $ATOM as well as help the ecosystem develop sustainably.
4. Limitations of Interchain Security
4.1. Limited scalability
Replicated Security is one of the significant milestones in the Cosmos ecosystem, however this technology will also limit the number of chains that Cosmos Hub can support.
Supporting blockchains that integrate Replicated Security will require close support. This will need to get faster as more chains launch with this technology. Cosmos Hub can support about 5 to 10 chains this year using Replicated Security. It is unlikely that validators will be able to run more chains in the short term as they need to run a separate server for each chain.
4.2. High costs for small chains
One weakness of Interchain Security is that it can be expensive for smaller consumer chains to rent security from the provider chain, as well as it can be difficult for validators on the provider chain to run nodes for both chains in parallel.
A recent example is Neutron, which pays Cosmos Hub 25% in transaction fees. Meanwhile, validators must invest an additional 400 USD per month to run a node for Neutron. This poses a risk in case Neutron does not generate enough revenue or ATOM price does not increase as much as expected.
4.3. Increased likelihood of centralization
For smaller validators, node operation may not be enough to cover costs due to the two factors mentioned above, which can easily lead to centralization. Transactions will largely be processed by top validators. Additionally, scalability will also be an issue if too many consumer chains rent security from the same provider chain validator at a given time.
5. Conclusion
Above are some reviews and analyzes of Interchain Security technology - used to share security for new chains on Cosmos. This is considered one of the core technologies, helping the Cosmos ecosystem to easily expand and develop more sustainably in the future.
Hopefully the above article provides useful information for users about the project. The content is for informational purposes only, not investment advice. Investors need to DYOR themselves and make their own assessments before deciding to invest in any project.

 English
English Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt


.jpg)

.jpg)











