1. What is flash loan?
Flash loans are unsecured loans without borrowing limits, where users borrow money and pay it back in the same transaction. If the user cannot repay the loan before the transaction is completed, smart contract will cancel the transaction and return the money to the lender.
1.1. Why do Flash loans exist?
To understand why Flash loans were created, consider existing lending systems in centralized and decentralized finance.
1.1.1 Centralized financial lending system (CeFi)
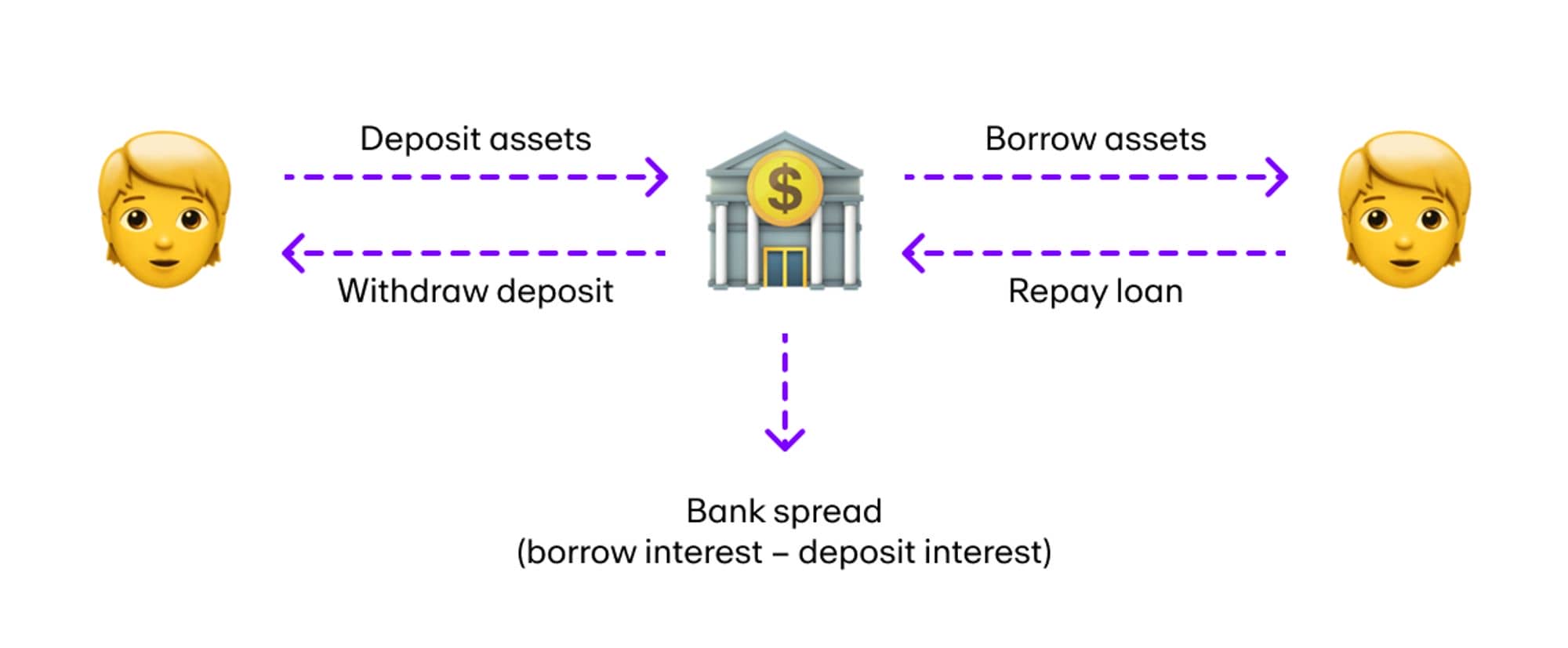
A secured loan requires the borrower to pledge assets to the lender. Liens are often placed on large sums of money and help lenders recoup their losses by selling the property if the borrower cannot repay the loan.
For example, if you have a mortgage, your house becomes collateral and the lender will sell it to cover the mortgage if you default.
On the other hand, an unsecured loan is a loan where the borrower does not have to provide collateral to borrow money. If the borrower defaults, the lender will sell the collateral to get back the loan money.
Why do Flash loans exist?
Centralized lending process: In both cases, the borrower has to pay interest. And in both cases, if the borrower defaults, the lending agency bears the brunt of the loss.
1.1.2 Decentralized financial lending system (DeFi)
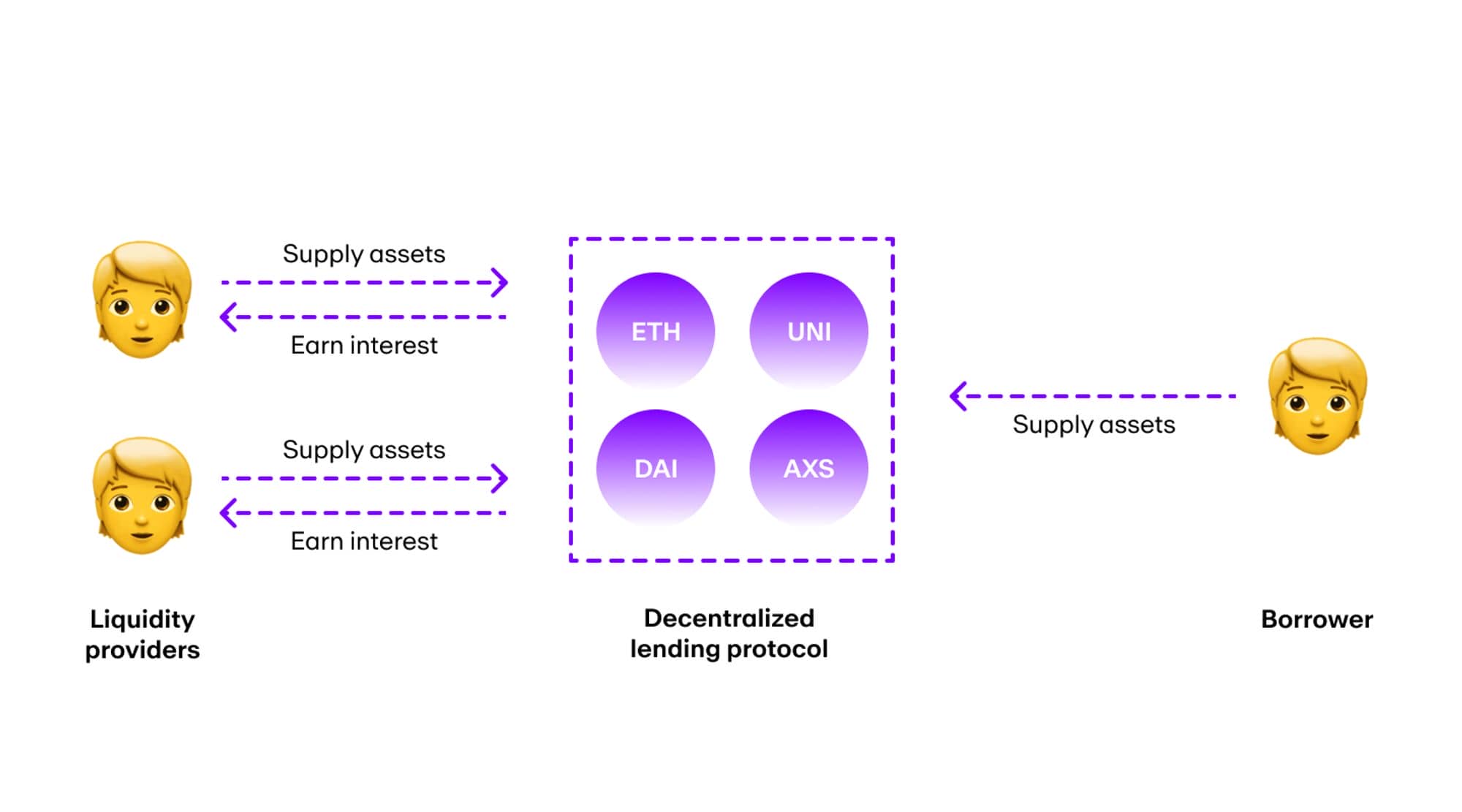
DeFi lending systems operate differently from their traditional centralized counterparts. They pool capital from depositors into a “liquidity pool” to provide mortgage loans to borrowers.
Most of these loans are overcollateralized, meaning the borrower must provide crypto collateral of a higher value than the asset borrowed. This is to account for fluctuations in cryptocurrency prices and ensure that assets are not undercollateralized.
Decentralized Lending: In other words, if the value of the collateral can no longer repay the debt, the platform will sell the collateral at a discount to partially repay the loan. This process is called liquidation.
1.2. Flash lending solves the limitations of CeFi and DeFi lending
Flash loans not only bring many benefits but also overcome the disadvantages of loans in centralized financial systems (CeFi) and decentralized finance (DeFi). In a traditional CeFi system, the loan approval process can take months, while with Flash loans, the smart contract processes and approves instantly.
Additionally, in case the borrower defaults, responsibility for the debt lies with the lending agencies. However, with Flash loan, if the borrower fails to repay the loan, the smart contract will automatically cancel the transaction and return the money to the lender. In the DeFi system, users must provide collateral to receive a crypto loan, while Flash loans do not require collateral, making borrowing more accessible and creating more opportunities. money making association.
2. How does flash loan work?
There are two main entities in a Flash loan: the lender and the borrower.
To interact with a flash loan lender, the borrower must develop a smart contract consisting of three parts:
- Borrow loans from flash lenders (Aave, dYdX and Uniswap)
- Interact with smart contracts for other activities
- Pay back loans
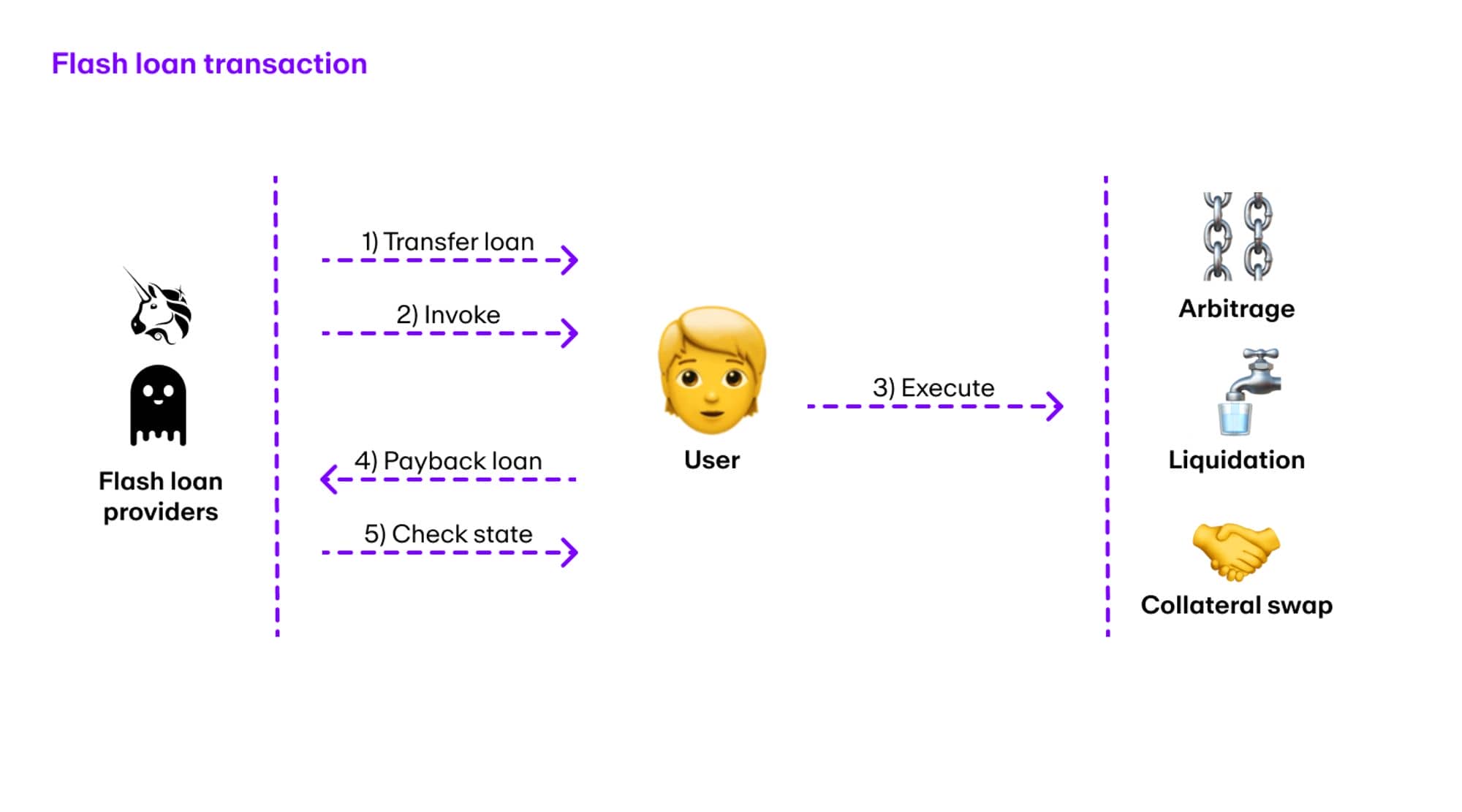
The entire workflow includes 5 steps:
- Loan Transfer: The flash loan provider transfers the required assets to the borrower.
- Invoke: User invokes pre-designed operations.
- Running Operations: Users interact with various smart contracts to perform operations (arbitrage, liquidation, etc.) with borrowed assets.
- Repayment: When the operations are completed, the user will return the assets to the quick loan provider with or without the borrowed assets.
- Check status: Finally, quick loan providers will check their balance. If the user has deposited insufficient funds, the providers will reverse the transaction immediately.
3. The most common use of flash loans
Flash loans have a wide variety of applications, from paying off debt to making profits from trading. Here, we discuss the three most common use cases.
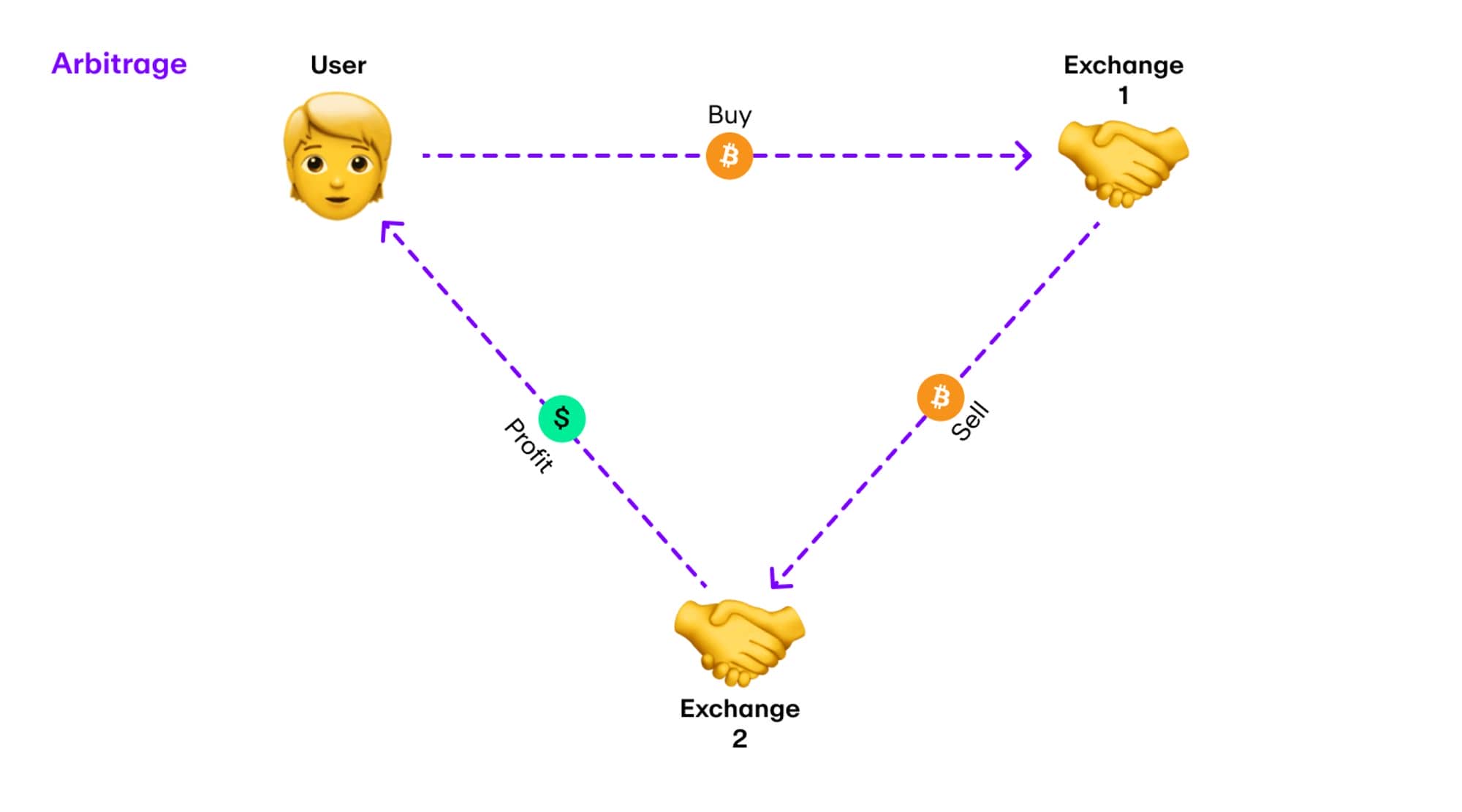
3.1. Arbitrage
Arbitrage is a strategy that takes advantage of price differences for the same asset in different currency markets to make a profit.
Buyers and traders can buy cryptocurrency at a low price and run it through different exchanges to acquire a little more cryptocurrency than before. Although this way of exploiting prices may sound disastrous, it contributes to market efficiency.
When multiple cryptocurrency traders seek to exploit the same price spread, the prices of these assets on different exchanges will converge, leading to the homogenization of the cryptocurrency market.
If you are new to crypto arbitrage, you probably don't have enough assets to make a significant profit.
But flash loans give you the ability to borrow as much as you want, so you can make a decent profit if you find a property with a significant price difference. Here is a trade from Etherscan that shows how you can use flash loans to profit from price arbitrage:
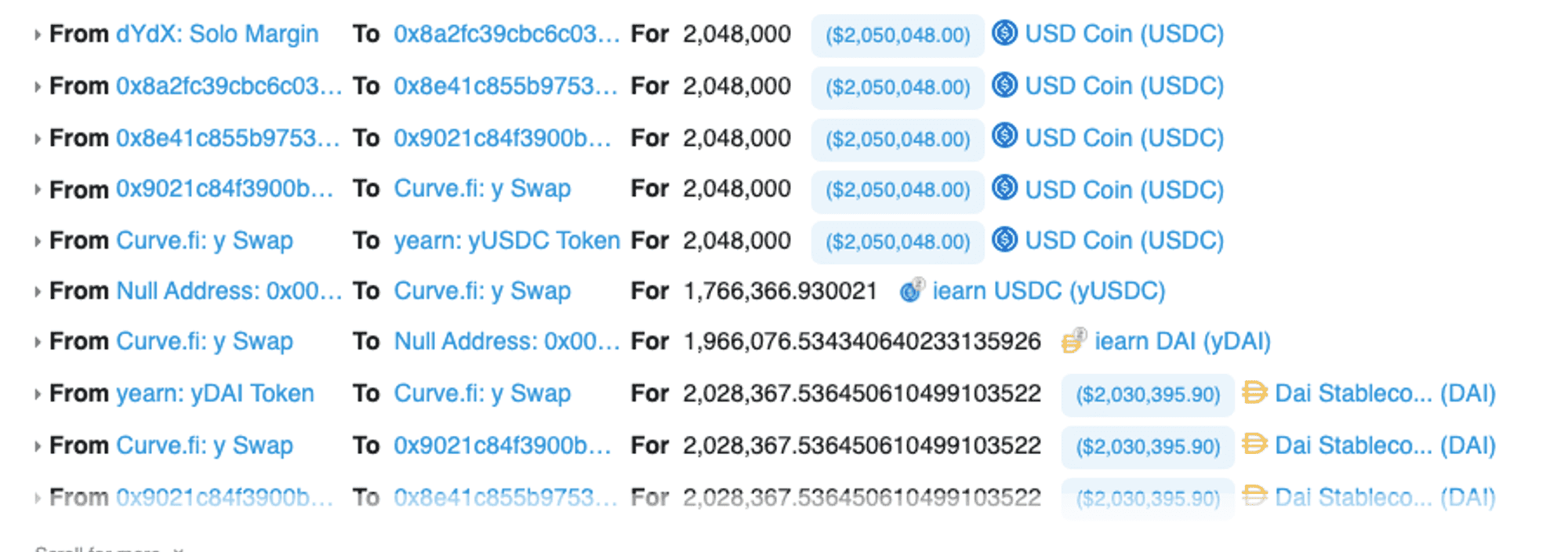
*A cryptocurrency arbitrage trade brings a profit of $16,000* First, users borrowed 2,048,000 USDC using dYdX flash loan. They then exchanged the amount for 2,028,367 DAI on the Curve y pool.
Next, they used 2,028,367 DAI to buy 2,064,182 USDC on Curve's SUSD pool, after which they paid back the loan quickly and kept the difference worth $16,182.
3.2. Wash trading
Like any other financial technology, flash loans can also be used to scam users. Wash trading is one such use case.
Wash trading is the process of using a group of trades to create the illusion of higher trading volume. It fools investors and other users into thinking that a cryptocurrency or NFT is in high demand when in fact it is not.
Some countries like the United States have banned the practice of wash trading, but the practice has seen a resurgence in the cryptocurrency market due to the lack of centralized institutions and regulations.
Now, with the advent of flash loans, wash trading has become more rampant as traders can hold large amounts of cryptocurrency to manipulate the market.
Here is a trade from Etherscan that will help you understand wash trad better

First, users borrow 0.01 Wrapped Ether (WETH) from dYdX. They then exchange it on Uniswap for ~122.189 LOOM, which is converted back to ~0.0099 WETH.
After this step, the user returns the flash loan to dYdX. What differentiates this transaction from arbitrage or other types of legal transactions is that there is a loss during the token swap.
This shows that the user's main intention is to increase trading volume and not to profit from the transaction, making it an illegal transaction conducted solely to manipulate the market and create demand false property.
3.3. Close the mortgage debt position
Collateralized Debt Position (CDP) is simply a cryptocurrency loan backed by collateralized assets. After a user borrows money, the platform locks the collateral until the loan is repaid.
During this period, if the currency of the loan decreases in value relative to the currency of the collateral, the user cannot repay the loan.
Flash loans allow you to repay the loan and release the collateral so you can use it for other purposes. Here's a trade that explains the concept better:

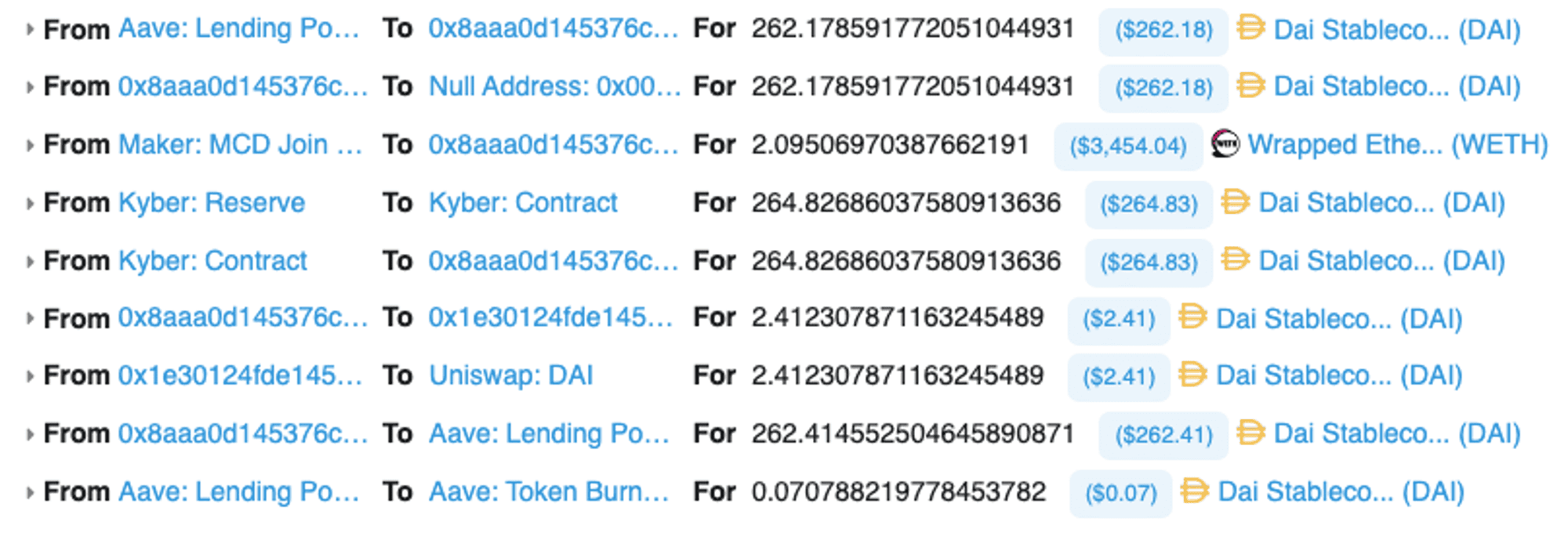
First, users receive a flash loan equivalent to the debt (~262.17 DAI.) from Aave. Next, they repay the loan on Maker and their collateral release platform (2.09 WETH).
They then go to the Kyber reserve to convert their WETH to DAI and transfer the surplus (~2 DAI) to Uniswap for other purposes. Finally, the user returns the loan to Aave, which burns a portion of its tokens for 0.07 DAI to increase the value of the tokens in circulation.
4. Can you make money with flash loans?
When a debt becomes undercollateralized, a group of users called liquidators trigger a liquidation event to purchase the undercollateralized asset at a discount.
With flash loans, anyone can become a liquidator and profit from discounted assets. For example, take a look at this transaction:

First, the user borrowed 12,940 DAI from dYdX and exchanged it for 13,046 USDT. This USDT is then used to purchase collateral at a discounted price on Compound.
After exchanging the assets they purchased, the liquidator received 13,450 DAI. And after they pay back the flash loan, 510 DAI is still profit, larger than the gas fee (~$172).
5. What are flash loan attacks?
Protocols that use centralized on-chain price predictions, such as a single DEX, are vulnerable to attacks using flash loan vulnerabilities.
When a single online exchange is used as a price feed, the asset's data is extremely limited as it only reflects the market conditions of that one exchange.
However, an oracle like Chainlink is powered by a decentralized network of oracles, so even though an attacker can execute a single flash loan transaction, it still has no impact. to the price feed where the exchange gets price data from multiple sources.
7. Summary
Flash Loan has created a fever in the decentralized finance community by allowing users to instantly borrow assets without collateral. However, this flexibility comes with potential risks and could have adverse consequences for the cryptocurrency ecosystem, depending on how they are used.
Many cryptocurrency investors are now exploiting Flash Loan to optimize profits and protect their assets from liquidation risks. However, potential perpetrators are also leveraging this technology to conduct attacks on smart contracts and hijack assets.
The risk of these attacks could be reduced in the future if DeFi platforms increase their source code auditing. At the same time, Flash Loan is also new to the DeFi space, so the potential for future innovation is endless.
Read more:

 English
English Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
















