1. A Deep Dive into Avalanche's Three Blockchains
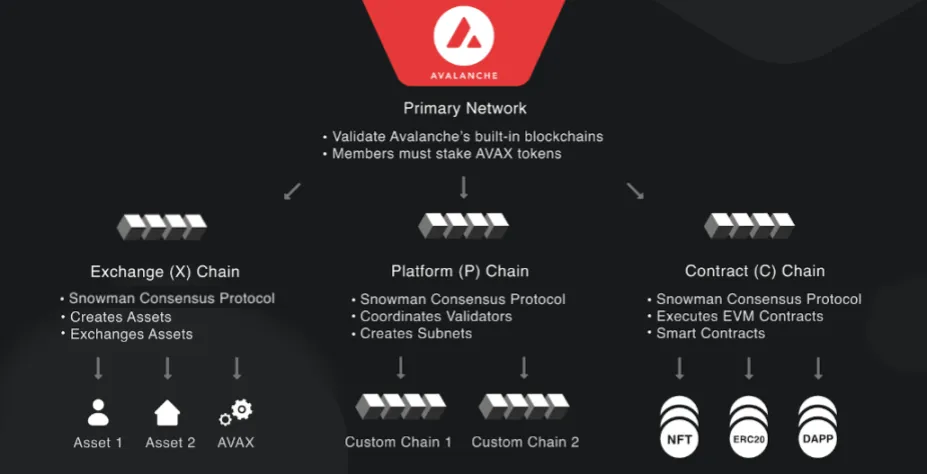
1.1. The X-Chain (Exchange Chain)
The X-Chain, short for Exchange Chain, is Avalanche’s blockchain dedicated to the creation, management, and trading of digital assets. It allows users to issue both fungible tokens (like cryptocurrencies) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), complete with customizable properties such as supply limits, transfer rules, or ownership conditions. This makes it a powerful tool for tokenization projects, such as digitizing real-world assets like art, real estate, or intellectual property.
The X-Chain operates using the Avalanche consensus protocol, a highly efficient mechanism that achieves transaction finality in less than one second—far faster than many traditional blockchains like Bitcoin or Ethereum.
The native AVAX token is used to pay transaction fees on this chain, ensuring smooth and cost-effective operations. Its high throughput and low latency make it an ideal environment for marketplaces, exchanges, and asset-focused dApps.
1.2. The C-Chain (Contract Chain)
The C-Chain, or Contract Chain, serves as Avalanche’s hub for smart contract functionality. It is fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), allowing developers to port Ethereum-based smart contracts and dApps to Avalanche with minimal adjustments.
This interoperability has fueled the growth of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, NFT marketplaces, and blockchain games on the C-Chain, as developers can leverage familiar tools like Solidity and popular wallets like MetaMask.
Beyond its Ethereum compatibility, the C-Chain benefits from Avalanche’s high-performance consensus, enabling it to process thousands of transactions per second with near-instant finality. This scalability addresses common pain points in Ethereum, such as high gas fees and network congestion, making the C-Chain a go-to choice for developers seeking efficiency without sacrificing functionality.
1.3. The P-Chain (Platform Chain)
The P-Chain, or Platform Chain, is the backbone of Avalanche’s network governance and infrastructure. It manages the platform’s validators and oversees the creation and coordination of subnets—custom, independent blockchains that can be tailored to specific use cases.
Validators stake AVAX tokens on the P-Chain to secure the network, participate in consensus, and earn rewards, ensuring the ecosystem remains decentralized and robust.
The P-Chain’s ability to support subnets is a game-changer, as it allows organizations or developers to launch private or public blockchains with unique rules while still benefiting from Avalanche’s overarching security and interoperability. This makes the P-Chain essential for enterprise solutions, cross-chain projects, and large-scale decentralized systems.
2. How They Work Together?

The brilliance of Avalanche lies in how these three blockchains complement each other. By splitting responsibilities, Avalanche avoids the bottlenecks that plague single-chain systems like Ethereum, where all transactions compete for the same resources.
For example, a spike in NFT trading on the X-Chain won’t slow down smart contract execution on the C-Chain, while validator updates on the P-Chain remain isolated from user-facing activities.
This division of labor allows Avalanche to achieve sub-second transaction finality and process over 4,500 transactions per second, far surpassing many competitors. The result is a seamless, high-performance ecosystem that caters to diverse needs without compromise.
3. FAQs
Q1: Why does Avalanche use three blockchains instead of one?
Avalanche’s tri-chain design enhances scalability and efficiency by assigning specific tasks to each blockchain. This separation prevents congestion, improves transaction speeds, and allows for specialized optimization, making the platform more versatile than single-chain alternatives.
Q2: Can I use Ethereum tools on all three blockchains?
No, Ethereum compatibility is limited to the C-Chain, which supports the EVM. The X-Chain and P-Chain have distinct purposes (asset trading and network governance, respectively) and use Avalanche-specific APIs and tools.
Q3: What are subnets, and how do they relate to the P-Chain?
Subnets are custom blockchains created and managed via the P-Chain. They allow developers to build tailored networks with unique rules, such as privacy features or compliance requirements, while still leveraging Avalanche’s security and infrastructure.
4. Conclusion
Avalanche’s three blockchains—the X-Chain, C-Chain, and P-Chain—represent a groundbreaking approach to blockchain design. By dividing responsibilities across specialized chains, Avalanche delivers unparalleled speed, scalability, and customization, making it a top contender in the blockchain space. From enabling rapid asset trading and robust smart contract deployment to supporting custom subnets and secure decentralization, this tri-chain system meets the needs of developers, businesses, and users alike. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, Avalanche’s innovative architecture positions it as a platform to watch in the years ahead.
Read more:

 English
English Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt