1. Understanding Blockchain Layers
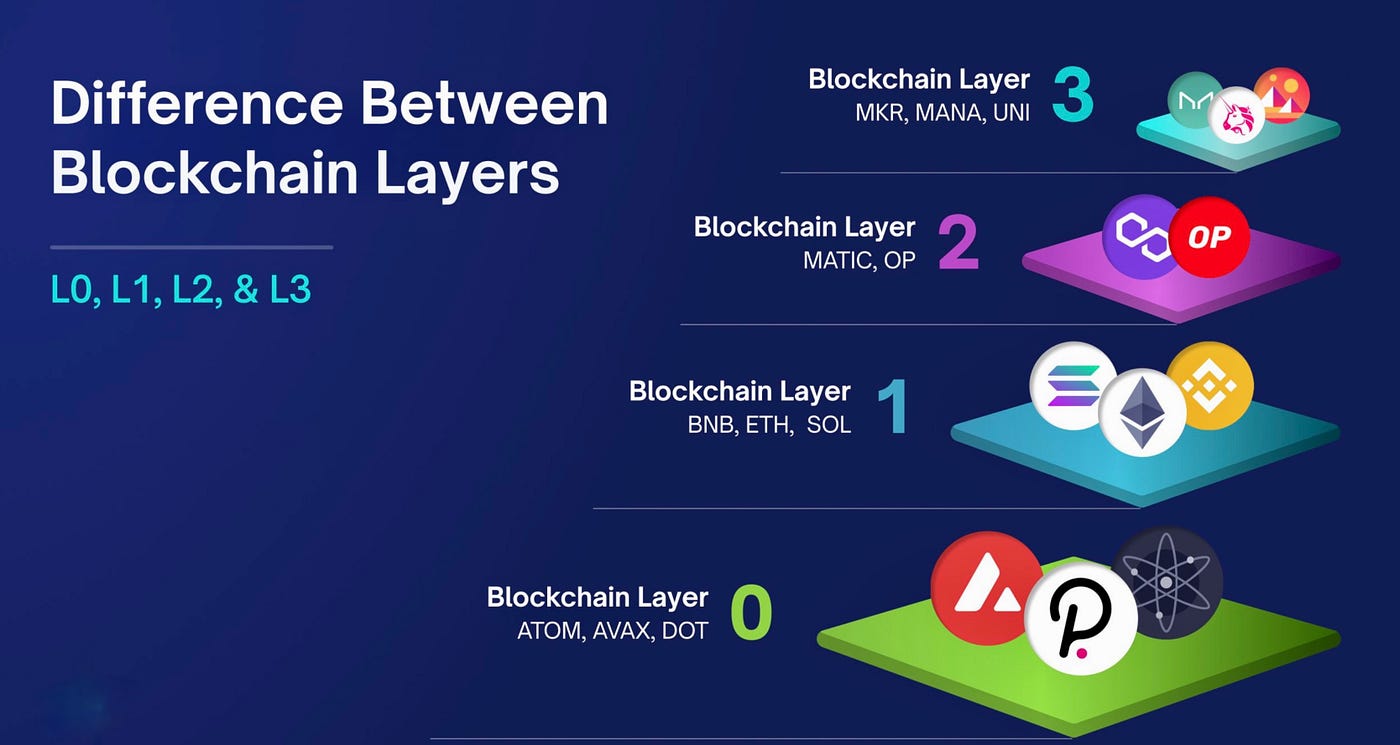
To comprehend Layer 3 solutions, it’s crucial to first understand the layers that form a blockchain ecosystem. Blockchain networks can be thought of as a stack of technologies, each layer addressing different needs within the infrastructure. Let’s break them down:
Layer 1 Blockchains
Layer 1 is the foundation of the blockchain ecosystem. It includes well-known blockchains like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Solana, which are responsible for maintaining security and achieving consensus. However, Layer 1 networks face scalability challenges, as they prioritize decentralization and security, often leading to high transaction fees and slower processing times. This problem is at the core of the "blockchain trilemma," which highlights the trade-offs between decentralization, security, and scalability.
Layer 2 Solutions
Layer 2 solutions build on top of Layer 1 and aim to address scalability by processing transactions off-chain and posting the results back to the main chain. Examples include the Lightning Network (for Bitcoin) and Optimism (for Ethereum). Layer 2 solutions are designed to reduce fees and increase transaction speeds, but they still face limitations in terms of interoperability—i.e., the ability to work across different blockchains.
2. What are layer 3 blockchain solutions?
.jpg)
Layer 3 solutions are emerging technologies that build on Layer 2 to address the next significant challenge in blockchain: interoperability. Unlike Layer 1 and Layer 2, which focus on enhancing security and scalability, Layer 3 is all about connecting different blockchains to allow them to “talk” to each other. This enables cross-chain communication, making it easier for assets and data to flow between various blockchain ecosystems.
Layer 3 is often referred to as the "application layer" because it focuses on providing specialized services that enhance user experience and blockchain functionality across different networks. It provides the infrastructure for decentralized applications (dApps) to operate seamlessly on multiple blockchains, creating a unified ecosystem.
3. Key features of Layer 3 Solutions

-
Interoperability: Layer 3 focuses on enabling different Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchains to communicate and work together. It’s designed to solve the challenge of cross-chain compatibility, making it easier for users to interact with multiple blockchains from a single platform.
-
Specialized Services: Layer 3 provides tools and services that enhance the functionality of decentralized applications, simplifying the user experience across various blockchain networks.
-
User-Friendly Experience: While Layer 1 and Layer 2 are technical in nature, Layer 3 solutions focus on creating a more accessible environment for end-users. This includes making it easier for users to interact with different blockchain applications without needing to understand the technical complexities.
-
Cross-Chain Transactions: Layer 3 makes it possible to transfer assets, data, and applications across different blockchains. This is essential for the growing trend of multi-chain ecosystems, where users need to manage assets spread across several blockchains.
4. Examples of Layer 3 Blockchain Projects
.png)
As the concept of Layer 3 blockchains gains traction in the crypto world, a few standout projects are already demonstrating its potential. Here are some key examples to explore:
Orbs
Designed to complement existing Layer 1 and Layer 2 protocols, Orbs positions itself as a Layer 3 blockchain addressing scalability challenges on platforms like Ethereum. The project describes its approach as "Enhanced Execution," enabling developers to build smart contracts using a decentralized, serverless cloud infrastructure.
By operating on Orbs’ decentralized network, developers can deploy their smart contracts without the need to manage physical servers or underlying infrastructure. Orbs is currently integrated with several prominent Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchains, including Ethereum, BNB Chain, Avalanche, and Polygon.
- Arbitrum Orbit
In 2023, the Arbitrum Foundation introduced Arbitrum Orbit, a Layer 3 solution built on the Arbitrum Nitro platform. This innovative feature enhances scalability and reduces transaction costs, while giving developers the ability to create self-managed, specialized blockchains tailored to their specific needs.
With Arbitrum Orbit, projects can leverage the flexibility of custom blockchains while benefiting from the robust performance and efficiency of the Arbitrum Nitro ecosystem.
- zkSync Hyperchains
The zkSync team has unveiled zkSync Hyperchains, a Layer 3 framework designed to leverage Layer 2 solutions for settlement. Powered by the zkEVM engine from the ZK Stack, these hyperchains inherit the security of their underlying Layer 1 blockchain.
A unique advantage of zkSync Hyperchains is their seamless communication and interoperability within the broader ecosystem. Layer 3s built on the same Layer 2 can exchange messages more quickly, fostering an interconnected and efficient network of blockchains.
5. Key Differences Between Layer 3 and Layer 2

The key differences between Layer 2 and Layer 3 solutions focus on their core functionalities, benefits, and how they contribute to the overall scalability and usability of blockchain systems.
5.1 Primary Objective
-
Layer 2 Solutions
- Speed and Cost Optimization The primary goal of Layer 2 solutions is to improve scalability by enhancing transaction speed and reducing transaction costs. This layer operates on top of the Layer 1 blockchain (the base layer), leveraging techniques like state channels, rollups, and sidechains to handle transactions off-chain or in parallel, and then posting the final results back to the Layer 1 chain.
- Layer 2 helps reduce the burden on the main blockchain, which typically faces bottlenecks when handling large volumes of transactions. By processing transactions off-chain, Layer 2 can significantly speed up transactions and lower costs without compromising the security and decentralization of Layer 1. Popular Layer 2 solutions include the Lightning Network for Bitcoin and Optimism for Ethereum.
-
Layer 3 Solutions
- Interoperability and User Experience Layer 3 focuses primarily on interoperability — the ability for different blockchains (whether they are Layer 1 or Layer 2 networks) to interact and communicate seamlessly. The goal of Layer 3 is not just to improve the performance of individual networks but to create a unified, interconnected blockchain ecosystem.
- Layer 3 aims to make transactions, data, and assets transferable and accessible across different blockchain networks. This layer operates on top of Layer 2, enabling decentralized applications (dApps) and users to work across multiple blockchains without being restricted to a single network.
For instance, a user on Ethereum can transact with assets or data hosted on Polkadot or Cosmos without friction, all thanks to Layer 3 solutions.
5.2. Functionality and Approach
-
Layer 2 Solutions
- Off-chain Transaction Processing Layer 2 solutions work by processing transactions off the main chain, relieving the primary blockchain (Layer 1) from handling every single transaction. This is achieved through several techniques:
- State Channels: These allow users to conduct multiple transactions off-chain in a private setting, only submitting the final state to the main blockchain.
- Rollups: Rollups bundle many transactions into a single one and execute them off-chain, reducing the load on Layer 1 while maintaining security through Layer 1.
- Sidechains: These are independent blockchains connected to a main blockchain, where transactions are processed on the sidechain and then settled on the main chain.
- The Layer 2 approach is predominantly about optimizing blockchain performance at the transaction level, reducing fees, and increasing throughput.
-
Layer 3 Solutions
- Cross-Chain Communication and Enhanced User Tools Layer 3 solutions, on the other hand, go beyond transaction speed and cost. These solutions are centered around enhancing cross-chain interoperability and improving the overall user experience. Layer 3 is like a middleware that bridges Layer 1 and Layer 2 solutions, allowing applications to span multiple blockchains.
=> While Layer 2 helps optimize the performance of a single blockchain, Layer 3 aims to optimize the user’s experience across multiple chains.
5.3. Scalability Focus
-
Layer 2 Solutions
Localized Scalability Layer 2 directly addresses the scalability of a single blockchain. By moving transactions off-chain and reducing the load on Layer 1, Layer 2 can increase the transaction throughput of that specific network. However, its scalability improvements are local to the Layer 1 blockchain it is built on. It doesn’t inherently solve problems related to cross-chain scalability or communication.
In other words, Layer 2 scalability focuses on optimizing the performance of one blockchain (e.g., Ethereum) but doesn’t aim to create a broader, cross-chain scalable environment.
-
Layer 3 Solutions
Global Scalability and Interoperability Layer 3 solutions, however, are designed for scalable interaction across chains. By creating an interoperable ecosystem, Layer 3 allows users to manage assets, data, and applications across multiple blockchains. This opens the door to scaling not just a single network but the entire blockchain ecosystem, enabling users to interact with a variety of chains without worrying about their underlying architecture.
In essence, Layer 3 solutions aim to facilitate the global scalability of blockchain networks by enabling cross-chain collaboration.
5.4. Use Cases and Applications
-
Layer 2 Use Cases:
- Speeding up DeFi Transactions: In decentralized finance (DeFi), Layer 2 solutions reduce transaction latency and costs, making trading, lending, and borrowing faster and more affordable.
- Micropayments: With Layer 2 technologies like the Lightning Network, Bitcoin becomes viable for small-scale transactions, which would otherwise be too expensive on the main blockchain due to high fees.
- Gaming: Layer 2 can significantly improve gaming applications by reducing the fees and latency associated with in-game transactions and assets.
-
Layer 3 Use Cases:
- Cross-Chain DeFi: Layer 3 enhances the interoperability of DeFi applications across multiple blockchains, allowing users to move assets between networks like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Solana without friction.
- NFT Interoperability: Layer 3 solutions allow NFTs from different ecosystems to be transferred and traded across various marketplaces, increasing liquidity and creating a more seamless user experience for collectors and creators.
- Cross-Chain Bridges: Layer 3 enables the creation of bridges that allow assets to flow between different blockchains, simplifying complex decentralized applications (dApps) that operate across several networks.
5.5. Integration and Complexity
-
Layer 2 Complexity: While Layer 2 solutions are crucial for improving transaction efficiency on a single chain, integrating them can be relatively complex. Developers need to implement additional infrastructure and deal with complexities such as state finality, fraud proofs, and security when processing transactions off-chain. While Layer 2 solves speed and cost issues, it still relies heavily on the security and consensus mechanisms of the underlying Layer 1 blockchain.
-
Layer 3 Complexity: Layer 3 solutions introduce another level of complexity by needing to integrate multiple blockchains. The challenge is ensuring that various Layer 1 and Layer 2 networks can interact efficiently, without sacrificing security, privacy, or performance. However, Layer 3 also simplifies user interaction by offering user-friendly tools and making it easier to transfer data and assets between various ecosystems.
6. Conclusion
Ultimately, both Layer 2 and Layer 3 are complementary in nature. While Layer 2 solves scalability issues within a single blockchain, Layer 3 connects different blockchains and enables seamless cross-chain interactions, paving the way for a more connected and scalable blockchain ecosystem. Together, these solutions will shape the future of decentralized applications and the blockchain industry as a whole.
Read more:

 English
English Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt.png)
















