1. What is a Multi-Party Computation (MPC) Wallet?

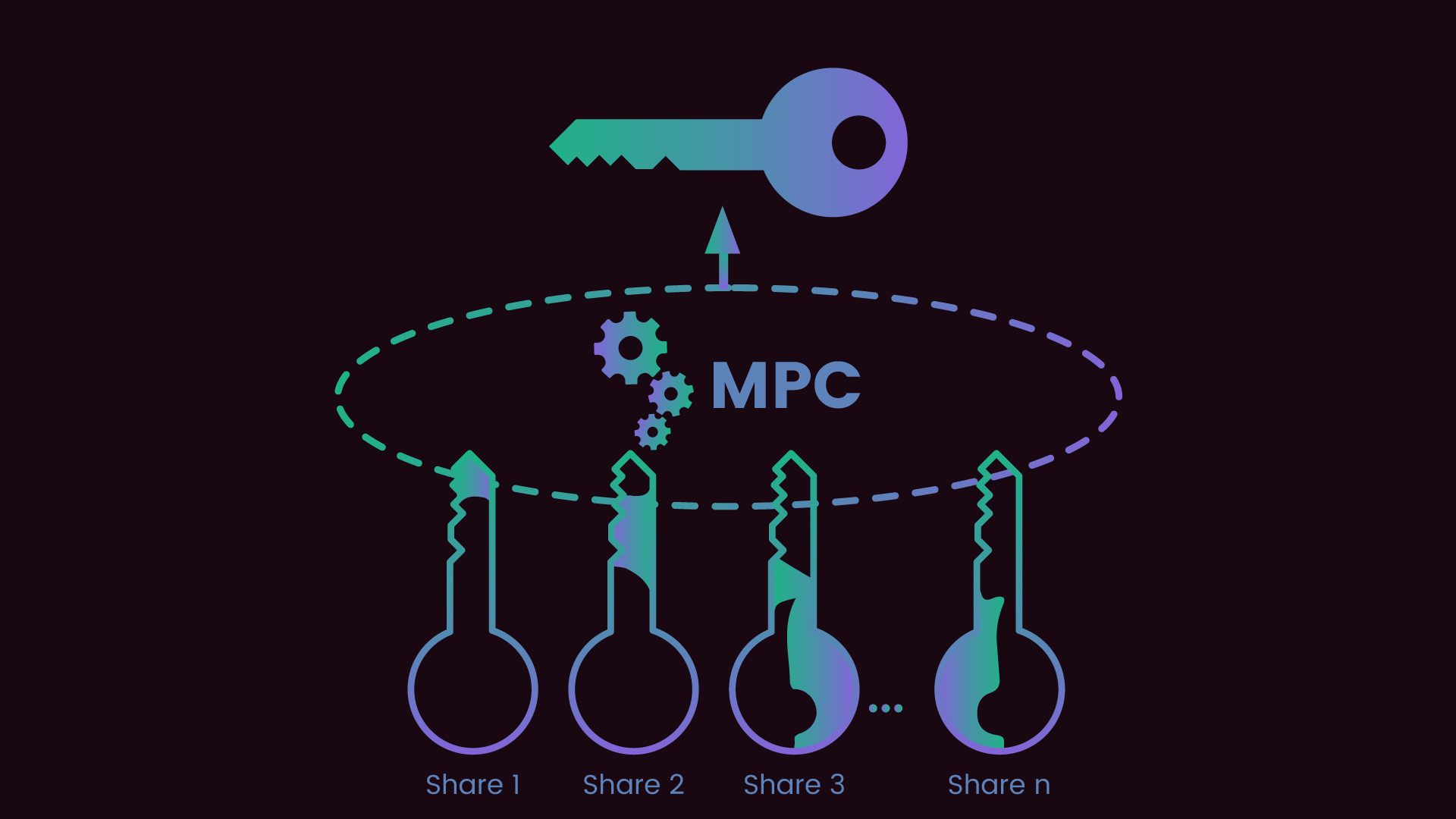
Multi-Party Computation (MPC) refers to a class of cryptographic protocols that enable multiple parties to jointly compute a function without revealing their private inputs to each other. In the context of cryptocurrency, MPC is primarily used to enhance the security and privacy of digital asset transactions by collaboratively signing them. Instead of a single party holding the entire private key, an MPC wallet splits the private key into multiple shares, each held by different participants. The beauty of this approach is that no individual party ever has access to the complete private key, effectively mitigating single points of failure and reducing risks of unauthorized access.
MPC wallets are designed to increase the security of cryptocurrencies by distributing the private key shares across multiple parties. This decentralized structure ensures that the private key is never exposed or stored in one location, further safeguarding digital assets from hacks or breaches.
2. How MPC Wallets differ from Traditional wallets?

MPC wallets stand apart from conventional wallet types, such as single-key, multi-signature, and hardware wallets. Here’s how they compare:
-
Single-Key Wallets: Traditional wallets rely on a single private key that can easily be lost or stolen. This centralization makes them more vulnerable to security threats.
-
Multi-Signature Wallets: Multi-signature wallets require multiple signers to approve a transaction. While this provides additional security, the process can be cumbersome and may delay urgent transactions. Moreover, multi-signature wallets may expose private information to the signers.
-
Hardware Wallets: Hardware wallets store private keys on physical devices. Though they are secure, hardware wallets are susceptible to physical damage or theft and are not ideal when multiple parties need to authorize transactions simultaneously.
MPC wallets, in contrast, allow for a protocol-agnostic, privacy-preserving solution that requires only one transaction signature, making them more efficient and secure in comparison to the above wallet types.
3. Benefits of MPC Wallets

MPC wallets offer several advantages:
-
Decentralization: Private keys are distributed across multiple parties, eliminating the need for a central authority to store or manage the keys. This reduces the risks associated with centralized control, corruption, or collusion.
-
Data Privacy: Since the private key shares are never fully revealed, MPC wallets ensure that no party has complete access to users’ sensitive data, enhancing privacy and security.
-
High Accuracy: MPC wallets are powered by cryptographic techniques that ensure high accuracy in operations, such as address generation, transaction signing, and signature verification.
-
Eliminates Single Points of Failure: MPC wallets mitigate the risks of losing access to a wallet due to a lost private key or device malfunction. Since the private key is divided, the failure or compromise of one participant does not lead to the loss of assets.
-
Scalability: Users can scale their security by adding or removing participants from the MPC protocol as needed. This allows for greater flexibility and adaptability in managing assets.
-
Flexibility: MPC wallets support dynamic transaction policies, allowing users to set thresholds based on criteria like transaction size, frequency, or destination. These thresholds can be adjusted without affecting ongoing transactions.
-
Compliance: MPC wallets can support regulatory requirements such as Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC). They provide transparent records for auditing purposes and ensure that security and governance practices align with industry standards.
4. Risks of MPC Wallets
Despite the advantages, MPC wallets do have some inherent risks:
-
High Communication Costs: MPC protocols require continuous communication between parties, which may increase bandwidth consumption and introduce network latency. This also makes the system vulnerable to attacks like Denial-of-Service (DoS) or Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks.
-
Technical Complexity: The implementation of MPC relies on advanced cryptography and distributed computing. This can lead to coding errors, bugs, or vulnerabilities that may compromise the wallet’s security or functionality if not properly executed.
-
Lack of Standardization and Open-Source Solutions: Unlike traditional wallets like Ledger or Trezor, MPC wallets lack widespread compatibility with existing infrastructure. Additionally, many MPC wallet solutions are not open-source, limiting accessibility and transparency for users.
5. Popular MPC Wallets

Several MPC wallets have gained recognition for their security features and functionality. Below are some of the top MPC wallets in the market:
-
ZenGo: Known for its user-friendly interface, ZenGo is one of the most popular MPC wallets for individuals and small teams. It supports over 70 cryptocurrencies and offers features like biometric authentication, backup and recovery options, and seamless integration with decentralized applications (DApps) via Wallet Connect.
-
Fireblocks: Fireblocks is a highly trusted MPC wallet, especially for institutional investors. It supports over 40 blockchain protocols and integrates with major exchanges. Fireblocks offers enterprise-grade security features like multi-factor authentication, insurance coverage up to $150 million, and detailed audit logs.
-
Coinbase: Coinbase, one of the largest centralized exchanges, also provides an MPC wallet solution for institutional clients. It supports over 90 cryptocurrencies and integrates with the Coinbase Pro trading platform, allowing users to manage assets securely.
-
Qredo: A newer entrant in the MPC wallet space, Qredo offers cross-chain liquidity for institutional investors. It supports over 20 blockchain protocols and features advanced security like decentralized governance and atomic settlement, enabling users to transfer assets across different blockchains seamlessly.
6. Conclusion
Multi-Party Computation (MPC) wallets represent a significant leap forward in securing digital assets. By decentralizing the management of private keys, they reduce the risk of theft, loss, and attacks, offering greater flexibility, privacy, and scalability compared to traditional wallet systems.
For both individuals and institutions, adopting MPC wallets can help achieve a higher level of security and regulatory compliance while reducing the vulnerabilities associated with traditional wallet models. As the crypto space continues to evolve, MPC wallets are poised to become an integral part of the digital asset management ecosystem.
Read more:

 English
English Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt.png)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)




