1. What is DeFi?
1.1. What is DeFi?
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) is decentralized finance, in which financial services are provided through decentralized platforms, based on blockchain technology and smart contracts. DeFi allows users to perform traditional financial services without having to go through intermediaries, but those transactions will be carried out entirely through smart contracts.
DeFi Features:
- Non-custodial or Self-custody (no entrustment - no custody): Users own and hold their private key, which means the user has full control and management of their assets.
- Permissionless: Users do not need to ask for permission or provide personal information to any intermediary to participate in these financial services.
- Trustless (No need to put trust in intermediaries): Because users are the owners of their private keys and assets, all transactions and financial activities will be handled by smart contracts so there is no need to put trust to any third party.
- Decentralized: Financial services and transactions are performed entirely based on blockchain technology, each transaction will be confirmed and processed by the whole network, from many people in many different places, so Decentralization will be guaranteed.
Advantages of DeFi:
- Decentralization: The biggest problem that DeFi can solve is decentralization. Every transaction in DeFi is validated by a network consisting of many validators from many places and is presented transparently.
- Unlimited user financial access: With DeFi, users have global access and do not need to go through traditional intermediaries, limited by geographical location, national laws .
- Transparency: DeFi uses blockchain technology and smart contracts to record transactions and financial processes, creating a transparent and immutable environment.
- Ownership and control: DeFi allows users to retain ownership and control of their assets through the use of personal wallets and smart contracts.
- Liquidity: DeFi provides liquidity solutions based on liquidity pools or automated trading models (AMM), which enhance the ability to trade quickly and easily.
1.2. What is CeFi?
CeFi (Centralized Finance) is a term for a centralized financial market, where financial services operate through intermediary organizations such as governments, banks, funds or insurance companies,... In particular, these organizations have the right to decide, manage and control all financial activities of users.
In CeFi, users need to trust and depend on the above intermediaries to carry out their financial transactions, such as storing assets, borrowing money or investing in items. These organizations require users to verify their identity (KYC - Know your customer) and will have full control and management rights over users' assets.
Some examples of CeFi include: Traditional banks, centralized exchanges like Binance, Coinbase,... or money lending platforms like BlockFi, Celsius, Nexo,...
CeFi characteristics:
- Custodial (Trust - Custody): Users must entrust their assets to intermediaries and those organizations have the right to custody those types of assets
- Permission: Users need to meet certain requirements of financial institutions to be allowed to participate in that institution's financial activities.
- Trust: Users need to place absolute trust and comply with certain rules of financial institutions because they are the ones who completely control and manage their assets.
- Centralized : Asset control and implementation need to go through financial institutions.
Comparison table of CeFi and DeFi:
| CeFi | DeFi |
|---|---|
| Concentrate | Decentralization |
| Trust - Depository | No entrustment - No custody |
| Put your trust in intermediaries | No need to trust intermediaries |
| Must be licensed | No licensing required |
2. History of DeFi formation
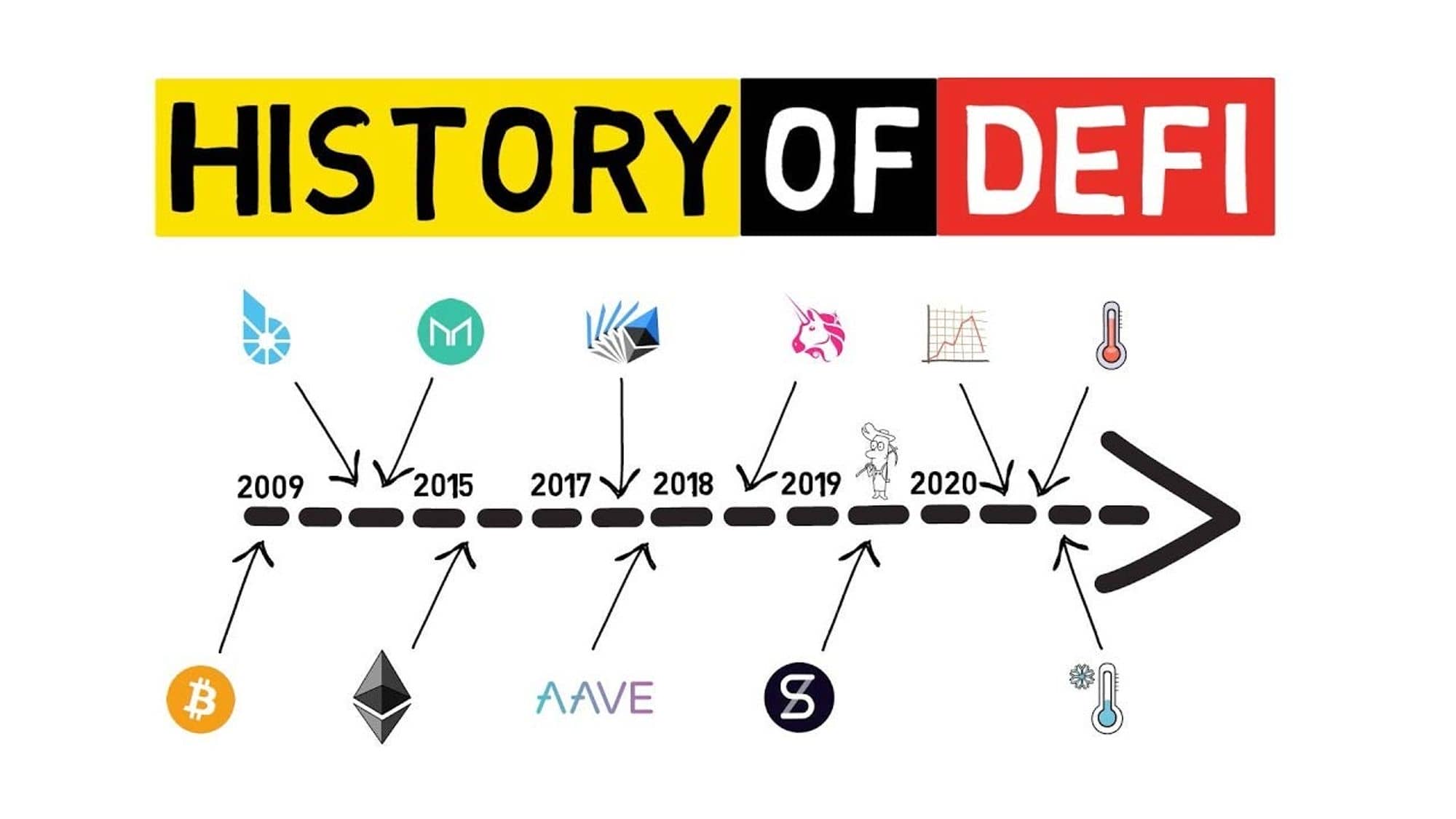
While Bitcoin has been laying the foundations for a peer-to-peer payment solution since its launch in 2009, in 2015, the launch of Ethereum maximized the potential of blockchain in decentralized finance. .
Ethereum is one of the first smart contract application blockchain platforms that allows developers to build decentralized financial applications.
Ideas for decentralized finance have been discussed since before 2015, with early projects and concepts such as Mastercoin (now Omni) or Bitshares. Mastercoin was created as a layer protocol on top of Bitcoin, with the goal of expanding Bitcoin's capabilities by adding more complex financial features. However, after Ethereum was launched in 2015 with the ability to deploy smart contracts, Mastercoin was no longer as famous and developed as expected.
By 2017, the MakerDAO protocol went live, a major turning point for financial applications in the blockchain space. This is a protocol built on Ethereum, allowing users to mortgage digital assets in exchange for DAI - a stablecoin (stable coin issued by MakerDAO, pegged 1:1 to the US dollar). . Users have begun to make more use of their digital assets than just transferring funds between two wallet addresses.
In late 2017 - early 2018, AAVE launched as a lending platform, supporting more diverse asset types and continuously ranking first in DeFi projects with the highest volume of locked assets.
Then, at the end of 2018, Uniswap - the leading decentralized trading platform on Ethereum was born. Using the Automated Market Maker (AMM) mechanism, Uniswap allows buyers and sellers to exchange ERC-20 tokens directly with each other through smart contracts without the need for central government. space of traditional trading floors.
Since this period, other projects have begun to appear in the DeFi space and create an ever-expanding ecosystem. In October 2020, the total value locked (TVL) in DeFi officially exceeded $10 billion, starting the DeFi summer boom .
3. The pieces that make up the DeFi ecosystem
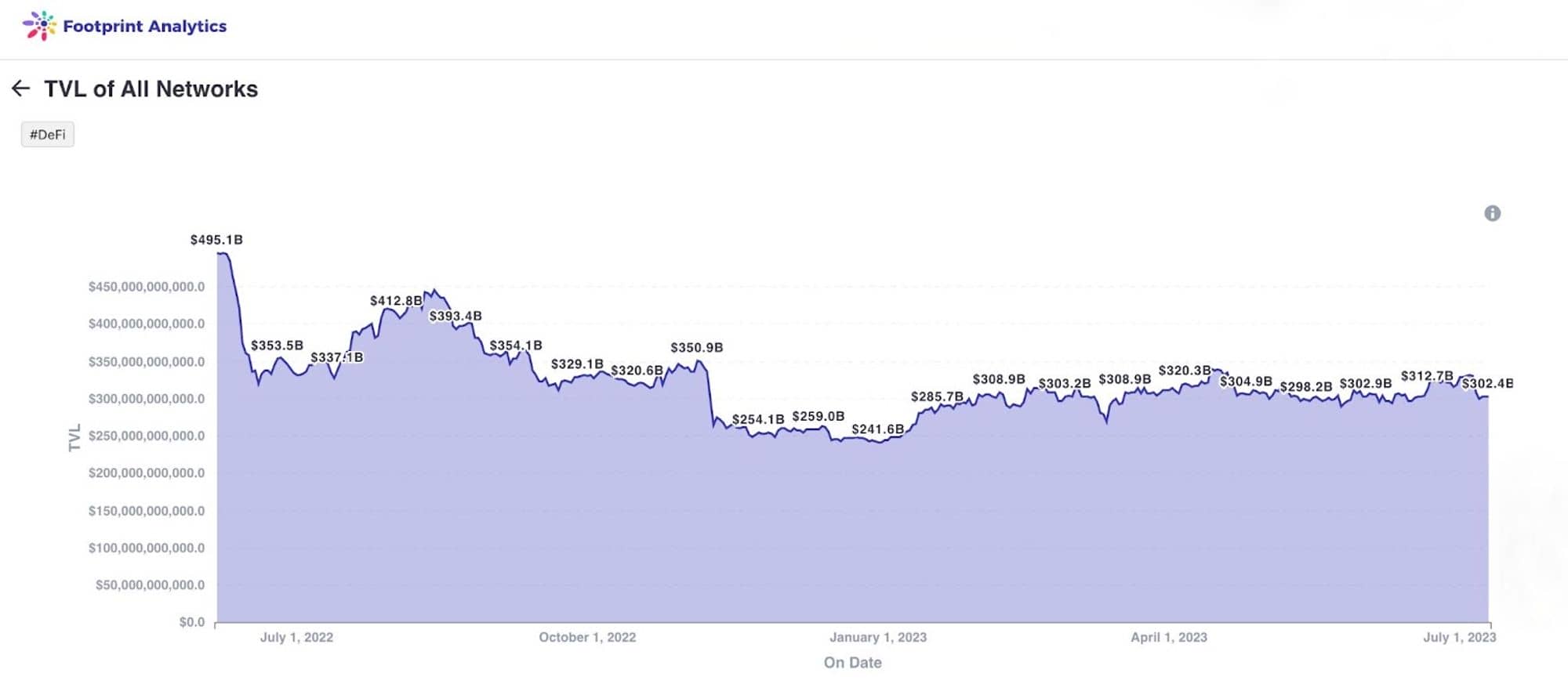
In today's article, we will provide an overview of the top DeFi applications on Ethereum and explore why these applications are so successful. How have these apps gained market share?
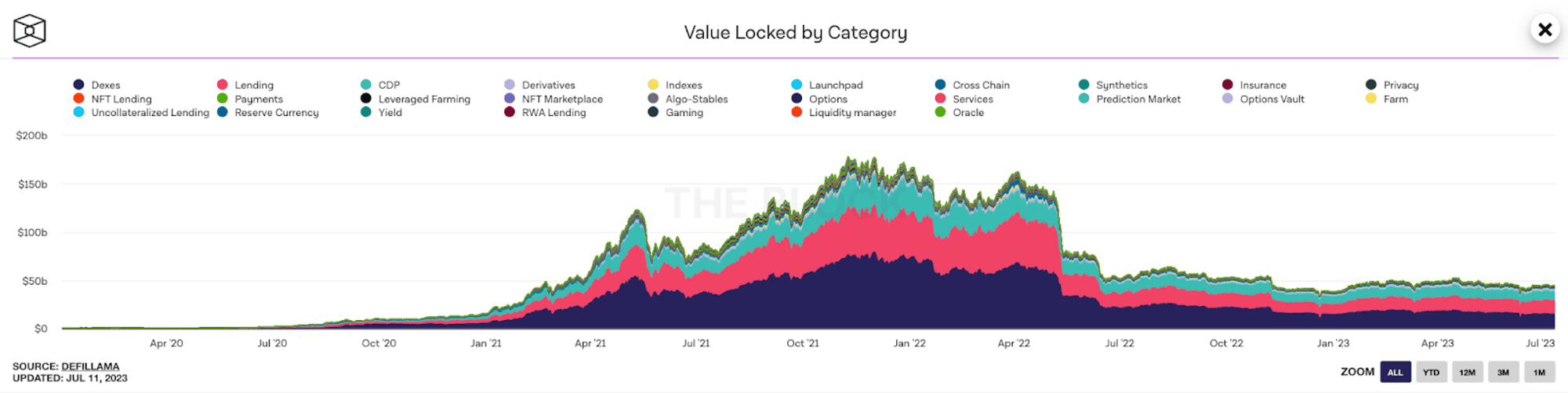
Based on the above data, it can be seen that currently the pieces in DeFi are being classified into the following main niches:
- Decentralized exchange (DEX)
- Lending/Borrowing protocols
- Liquid Staking
- Yield Farming
- Derivatives
- Launchpad
- Wallets
- Stablecoins
3.1. Decentralized Exchanges (DEX - Decentralized Exchanges)
A decentralized exchange (DEX) is a type of cryptocurrency exchange, using blockchain technology, smart contracts and liquidity pools, allowing users to trade directly with each other without going through any any third party.
Decentralized exchanges (DEX) often use an automatic price determination trading model (AMM - Automated Market Maker) or an order book model similar to current CEX exchanges.
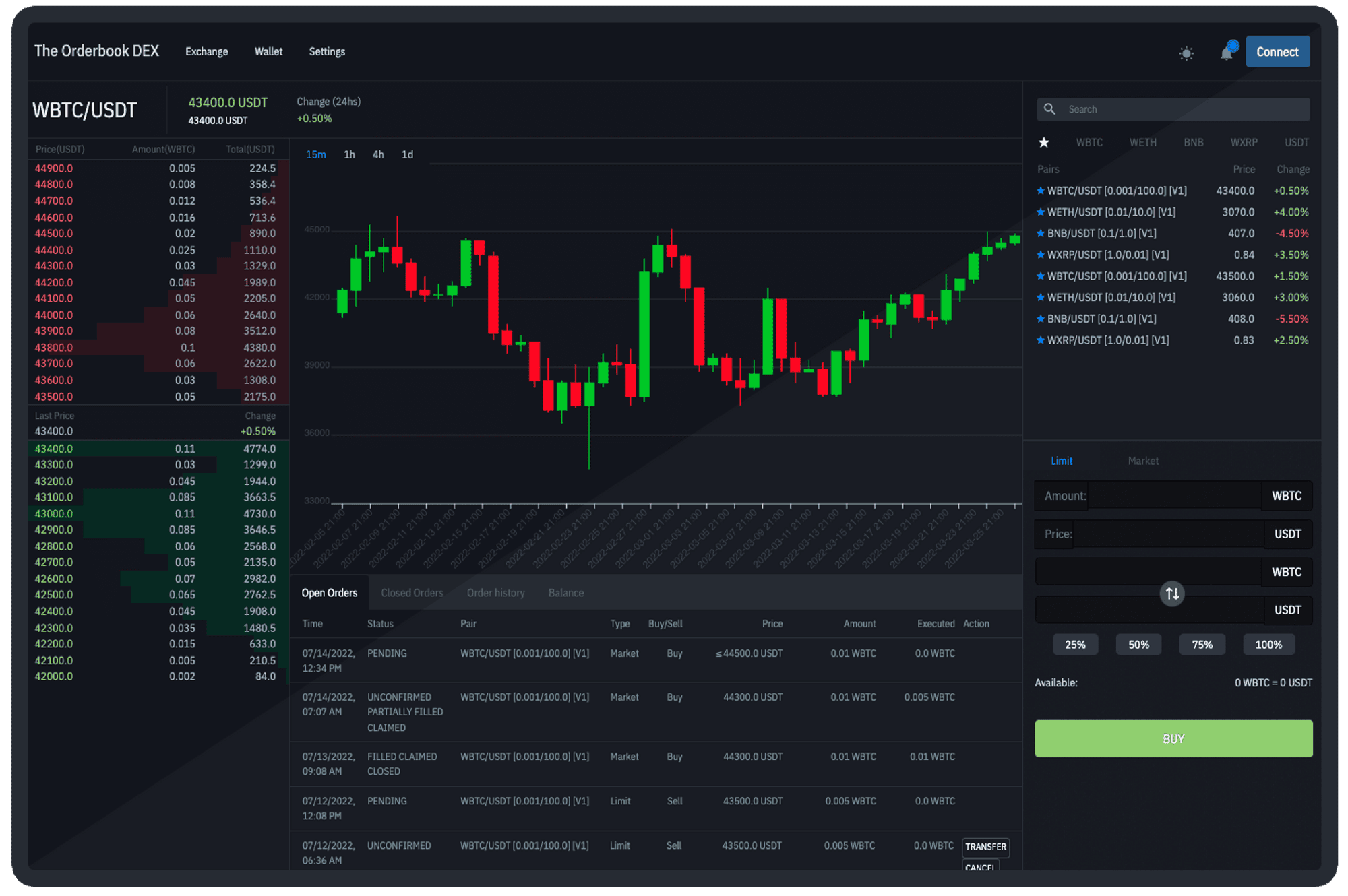
AMM determines the value of assets through automatic supply and demand based on liquidity pools. Users can participate in liquidity pools by providing their assets and receiving reward tokens in return. The AMM model is more popular than order book due to low market liquidity, thin order walls making it difficult to set price walls.
Uniswap is the leading decentralized exchange on Ethereum, always leading in trading volume and total locked assets. At present, the total amount locked in DeFi is more than $45 billion, of which DEX accounts for $15 billion of that share and Uniswap is holding more than $8 billion of it (Based on data from Theblock and DefiLlama).
Some other prominent exchanges: Curve Finance, Balancer,...
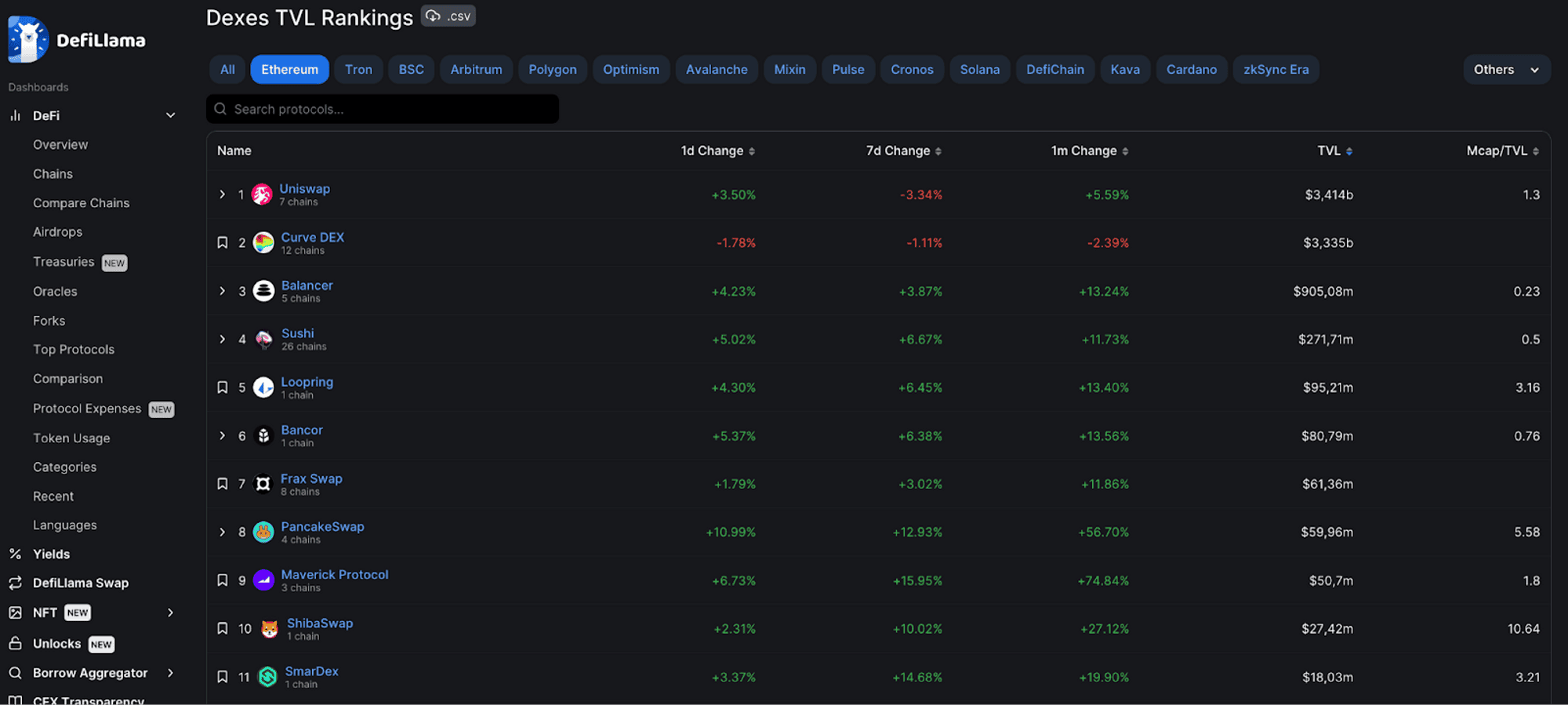
3.2. Lending and Borrowing
Lending protocols are divided into 2 main groups:
- Lending platforms allow users to mortgage their assets to borrow another type of asset. There are two main participating components:
- Lender (lender): deposits assets into the pool of lending platforms to lend to borrowers, and receives interest in return.
- Borrower (borrower): borrows money from the pools for a certain period of time and is responsible for repaying the interest and loan.
- Right after decentralized exchanges, lending platforms account for the second highest market share in terms of locked asset volume, accounting for more than $14 billion out of $45 billion. Launched in 2017, MakerDAO is one of the pioneering DeFi protocols on Ethereum, specifically in the lending segment. These platforms provide a decentralized borrowing system, allowing users to mortgage their digital assets (coins, tokens) in exchange for another type of asset (stablecoins issued by the project itself). project or the project's native token).
- One of the outstanding projects in the lending niche can be mentioned as Compound (2.6 billion TVL), AAVE (8.7 billion TVL),...
Collateralized Debt Positions (CDP)
- CDP protocols allow users to collateralize their digital assets and borrow stablecoins issued by the protocol. These platforms will allow the creation of stablecoins, pegged to the value of a certain asset, such as the US dollar, euro, gold,...
- When creating a CDP, users need to stake digital assets of corresponding value such as ETH into the smart contract. The ratio between the value of the deposited assets and the amount that can be borrowed (debt volume) is determined by a specific ratio called the collateralization ratio. If the value of the deposited assets decreases to a level that is not enough to secure the debt volume, the CDP owner may lose part or all of the deposited assets.
- Currently, the total key value in CDP protocols is accounting for $9 billion out of a total of 45 billion key value in DeFi, proving the development potential of these platforms. Some prominent CDP protocols are: MakerDAO, Angle Protocol, mStable,...
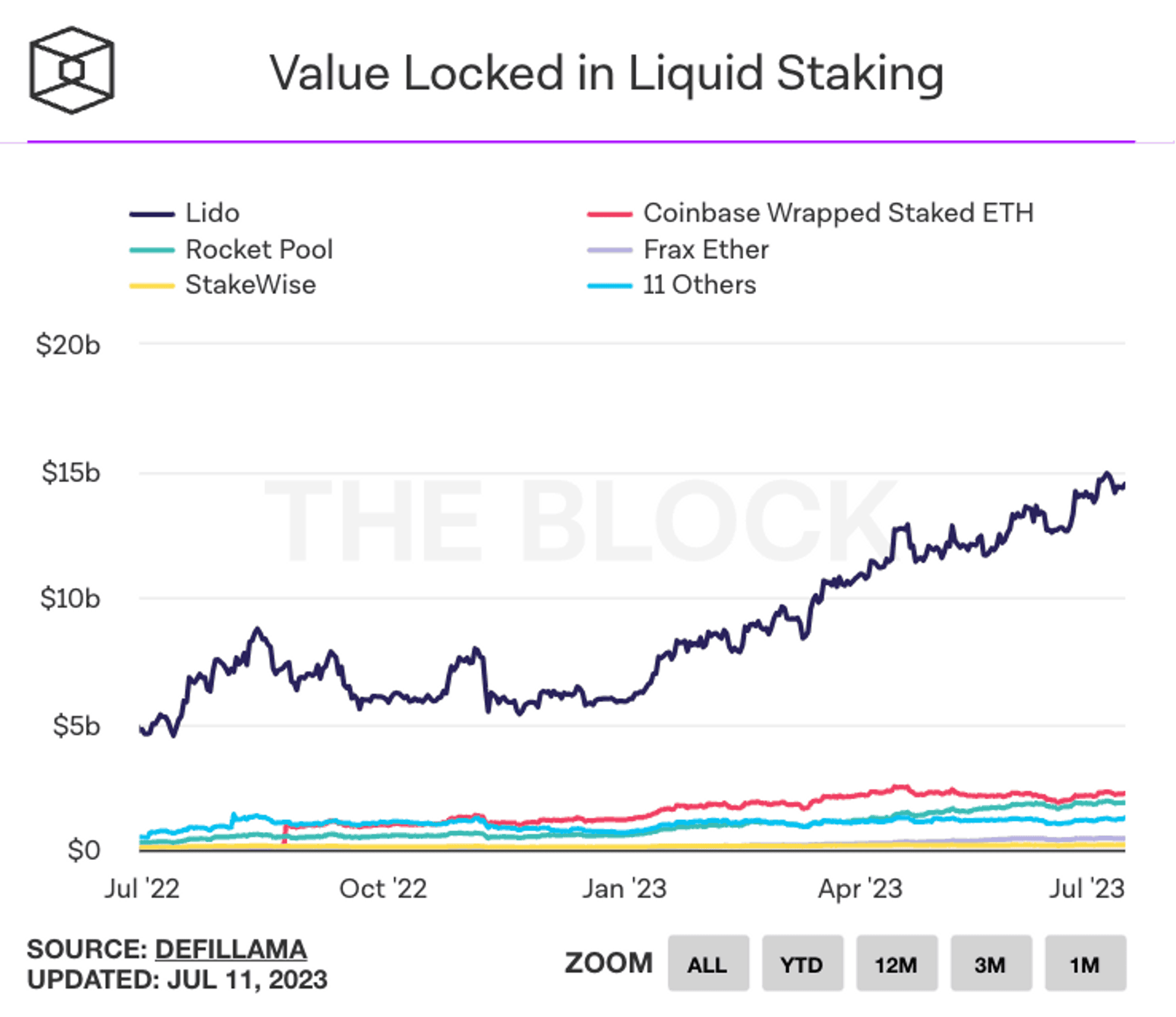
3.3. Liquid Staking
Liquid staking is a concept in the blockchain and cryptocurrency field that refers to the conversion of Staking-like tokens (custodial rights) into a more tradable and flexible version. During the staking process, assets Assets are locked for a certain period of time, and during this time, users cannot use or transfer that asset until the staking process ends.
Therefore, liquid staking platforms were born, allowing users to leverage assets staked in the staking system to create wrapped tokens that can be traded and used in other activities. At the same time, the original asset is still being staked and continues to receive staking rewards.
Prominent projects in this niche are Lido Finance, Rocket Pool, StakeWise,....
3.4. Yield Farming
Yield Farming is a method that involves users providing liquidity to DeFi protocols by locking up digital assets in exchange for rewards that are typically distributed automatically through contracts smart.
The yield farming process typically begins by providing assets such as stablecoins or tokens into a liquidity pool in a DeFi protocol. Users receive reward tokens in return based on the amount of assets they provided. These reward tokens can be traded or used in other activities.
Yield farming brings profits to users through two main ways:
- Yield from liquidity provision: Users receive profits from providing liquidity into liquidity pools in DeFi. This return is usually calculated based on the amount of assets and the time the user has provided liquidity.
- Yield from other activities in DeFi: In addition to providing liquidity, users can also participate in other activities such as leverage, trading, borrowing, and exchange in DeFi to generate profits from price fluctuations and other trading opportunities.
Prominent yield farming projects are Yearn Finance, AAVE, Compound, InstaDapp,...
3.5. Derivatives
Derivatives are trading contracts based on predicting the future value of a certain type of asset (oil, gold, silver, stocks, bonds, tokens, coins,...) that does not require direct ownership of that property. Therefore, these transactions have no intrinsic value. Derivative projects allow users to create investment opportunities from price fluctuations of the above mentioned underlying assets.
There are 4 common types of derivative transactions :
- Options: is the process of buying and selling options contracts. An option is a type of financial instrument that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a fixed price within a certain period of time. The seller of the contract is obligated to execute the transaction when the contract holder chooses to exercise the right. Options contracts include buy options and sell options.
- Futures contract: is a commitment between two parties to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price and time in the future. Futures contracts must be executed and settled according to the previously agreed price and conditions.
- Swap: is an agreement between two parties to exchange benefits or cash flows for a specific period of time. In a swap, the parties agree on the exchange of cash flows, interest rates, exchange rates or other financial factors. The contract will clearly stipulate the time of cash flow swap and specific calculation method.
- Forwards: is an agreement between two parties to buy or sell an underlying asset at a future time, at a fixed price agreed upon at the present time. This contract is not a publicly traded financial instrument, but a custom agreement and is usually executed in a decentralized environment.
In addition, leverage is considered one of the factors that attract investors to derivatives trading. Leverage in derivatives trading is the use of borrowed capital to increase participants' access and transaction size in the derivatives market. By using leverage, participants will have to control a larger amount of capital than their actual capital. Leverage is often expressed by the leverage ratio, which represents the level of borrowed capital compared to equity. For example, a leverage ratio of 1:10 means that a participant can open a trading position with a value equivalent to 10 times his equity.
Some prominent derivatives projects are Synthetix, DYDX,...
3.6. Launchpad
Launchpad is a platform or model that supports blockchain and crypto projects in their fundraising and project development. It provides a mechanism for users to buy and hold tokens of new projects through two forms of token sale (token sale) or fair launch (token price depends on the purchasing power of the community).
Through launchpad, users can purchase tokens with stablecoins or other cryptocurrencies. Fundraising through these platforms helps the project reach a larger community and these platforms are also seen as an initial filter for projects, helping users avoid scam risks. , rug pool when the project sells directly on its website.
Some notable launchpad platforms are: Binance Launchpad, Dao Maker, Polkastarter,....
3.7. Wallets
Web3 Wallet (Web3 wallet) plays a role as a connection door, helping users store and trade cryptocurrencies. Web3 wallet is a type of electronic wallet developed based on blockchain technology. It offers users complete control of their digital assets and the ability to interact with decentralized applications (dApps) on blockchain platforms.
The web3 wallet plays an important role in the blockchain network because it allows users to interact directly with the blockchain and dApps without having to trust a third party intermediary. Web3 wallets provide personal security and control, allowing users to retain complete control of their assets and data.
Some of the most prominent web3 wallets are Metamask, Trust Wallet, Coin98,...
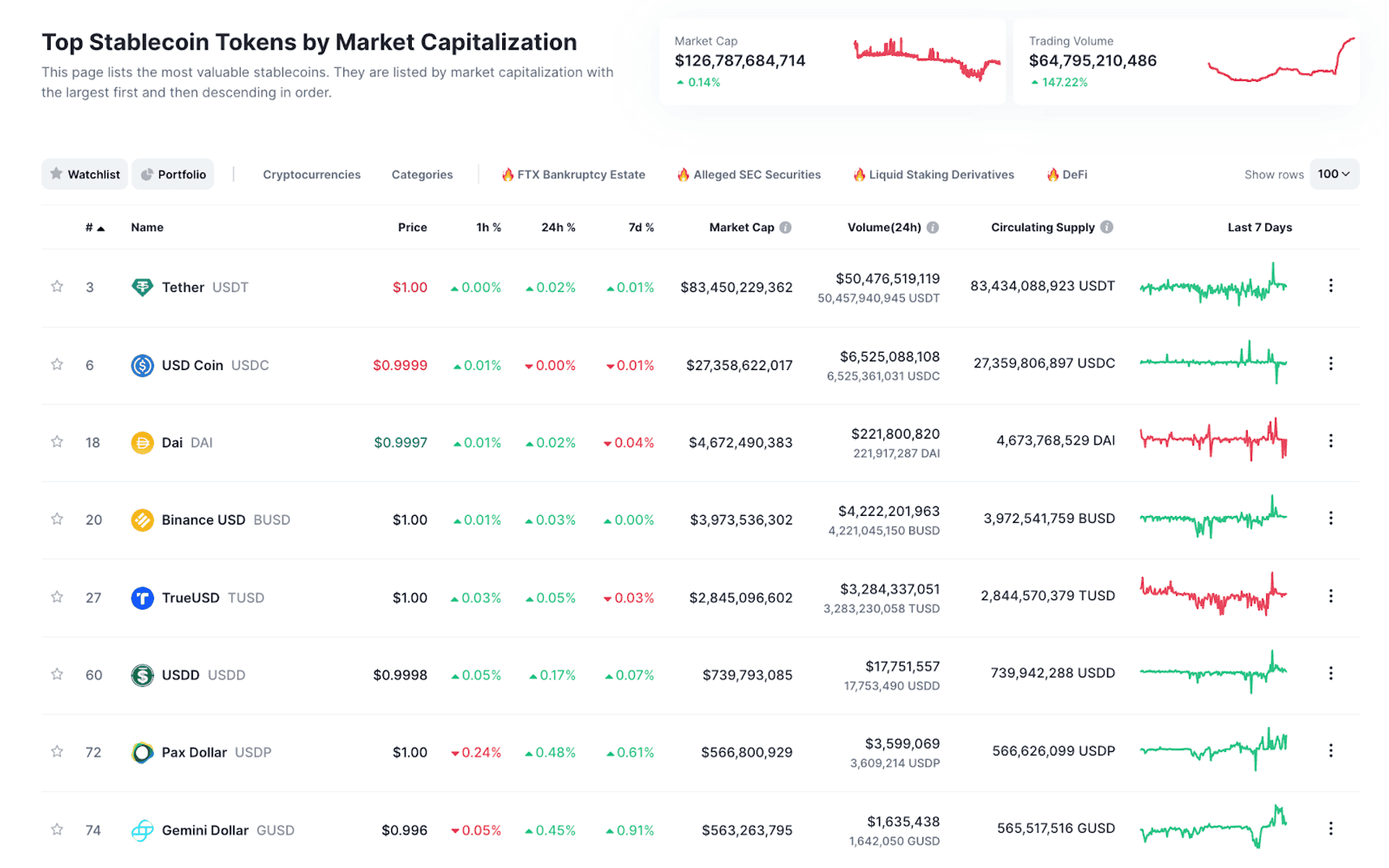
3.8. Stablecoins
Stablecoins are a type of cryptocurrency designed to keep their value stable and less volatile compared to traditional currencies such as USD, EUR or JPY. The goal of stablecoins is to provide a stable means of payment and store of value within the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Popular types of stablecoins:
- Tethered/Backed Stablecoin: This type of stablecoin is backed by traditional assets such as cash or gold. Each stablecoin unit has an asset behind it that ensures stable value. The most popular example of this type of stablecoin is Tether (USDT), each USDT coin is backed by US dollars.
- Algorithmic Stablecoin: This type of stablecoin is not based on traditional assets but uses algorithms and adjustment mechanisms to ensure stable value. This may include increasing or decreasing cryptocurrency supply based on supply and demand and other metrics.
- Hybrid Stablecoin: This type of stablecoin combines both guaranteed and algorithmic elements. An example of this type of stablecoin is USD Coin (USDC), a stablecoin linked to USD and verified by independent audits and bank accounts.
4. FAQs
Q1: How to get started in DeFi?
To get started in DeFi, you need a cryptocurrency wallet, like MetaMask or Trust Wallet, to connect to DeFi applications. You can then purchase and store the corresponding tokens and participate in trading, lending, or liquidity creation as desired.
Q2: What are the popular DeFi applications?
Popular DeFi applications include lending protocols like Compound and Aave, decentralized exchanges like Uniswap and SushiSwap, auto-trading platforms like Yearn.Finance, and liquidity generation platforms like Curve Finance.
Q3: How to learn more about DeFi?
To learn more about DeFi, you can refer to information sources such as blogs, books, online forums, and instructional videos on the internet. At the same time, join the Bigcoin Vietnam community to exchange ideas and learn from experienced people.
5. Conclusion
DeFi has become one of the important pieces of the puzzle that most clearly demonstrates the applicability of blockchain to finance. Although the DeFi summer is over, the volume of locked assets and transaction volume in the DeFi niche has partly proven its importance.
DeFi is the backbone to expand the further development potential of other niches in blockchain, such as the application of DeFi to the NFT market, social,... Hopefully, the above article will help everyone. You can have a more general overview of DeFi and its future applications !

 English
English Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt







.jpg)




