1. What is DePIN and How does it work?
DePIN utilizes blockchain technology to create and maintain physical infrastructure networks in a decentralized way. Traditionally, infrastructure like telecommunications, energy grids, and transportation systems have been centralized, controlled by governments or large corporations. DePIN changes this model by allowing individuals and communities to manage and maintain these networks.
At its core, DePIN operates on the principle of decentralization. Instead of relying on a central authority, control and responsibility for infrastructure are distributed among a network of participants. These participants can include anyone from individuals to businesses who contribute resources, services, or maintenance to the network.
Key Technologies Behind DePIN
-
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain ensures a transparent and immutable ledger for recording all transactions and activities within the network. This provides security and trust, as every action is verifiable and tamper-proof.
-
Smart Contracts: Smart contracts automate agreements and actions within the network. For example, when certain conditions are met—like providing energy or computing power—smart contracts automatically trigger payments or rewards without the need for intermediaries.
-
Tokens: Tokens act as incentives, rewarding participants for their contributions to the network. These digital assets can be earned through actions like providing coverage for decentralized networks, contributing renewable energy, or offering computing resources. Tokens also add a layer of economic activity, as they can be traded or used within the ecosystem.
2. Use Cases of DePIN

DePIN has the potential to revolutionize several sectors by decentralizing infrastructure. Here are some prominent use cases:
| Field | How DePIN Benefits | Real-Life Use Case | Use Case Description |
| Telecommunications | Decentralized wireless networks built by community hardware | Helium Network | Individuals provide antennas to create a decentralized IoT network |
| Energy Grids | Decentralized renewable energy grids powered by community contributions | LO3 Energy | People contribute solar energy to local grids and earn tokens |
| Transportation | Tokenized rewards for decentralized ride-sharing and logistics | DOVU | Participants share transportation data for improved logistics |
| Healthcare | Secure, decentralized health data access | Medicalchain | Blockchain provides secure access to health records |
3. Benefits of DePIN
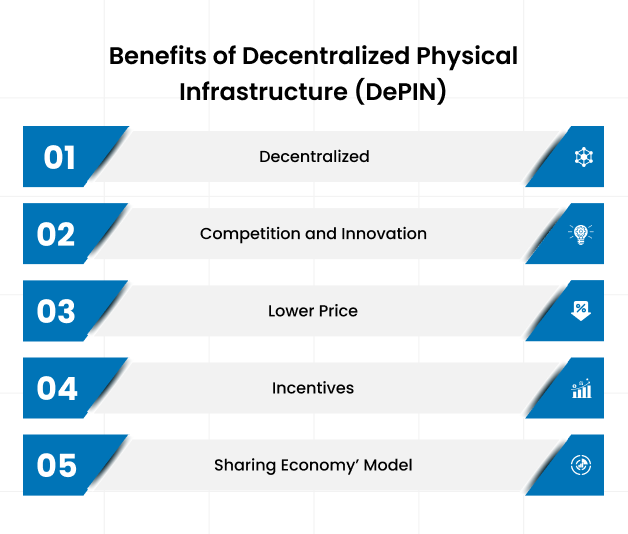
DePIN offers numerous advantages over traditional centralized infrastructure systems:
-
Decentralization: Control and responsibility are spread across a network, reducing single points of failure. This ensures greater system resilience. For example, in decentralized energy grids, failures in one part of the network don't bring down the entire system.
-
Incentivization: Participants are rewarded with tokens, creating an economic ecosystem. By contributing resources or services, individuals earn tokens, which can be traded or reinvested, promoting continuous engagement and growth.
-
Transparency: Blockchain ensures that all activities and transactions are recorded on an immutable ledger, which reduces fraud and errors. This transparency enhances trust among participants.
-
Efficiency: Smart contracts automate processes, reducing the need for intermediaries and administrative overhead. For instance, in decentralized energy grids, smart contracts automatically handle energy distribution and billing.
-
Resilience: With a distributed network, DePIN systems are more resilient to failures. For example, a decentralized network of servers or energy producers continues operating even if some nodes go offline.
4. Types of DePINs: PRNs and DRNs
.png)
DePINs (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks) can be divided into two primary categories: Physical Resource Networks (PRNs) and Digital Resource Networks (DRNs). These two types differ in the types of resources they use—tangible physical assets versus digital resources—but both rely on community participation and decentralization to deliver their services.
4.1 Physical Resource Networks (PRNs)
PRNs are decentralized networks that rely on physical assets to provide services. These assets can include hardware, infrastructure, and tangible goods. The idea is to encourage community members to contribute their physical resources, often in exchange for cryptocurrency or other incentives.
Example: Helium Network
-
Description: The Helium Network is a decentralized wireless network that uses community-owned hardware to offer Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity.
-
How It Works: Participants, known as "Hotspot Hosts," set up physical devices called Hotspots that provide network coverage and relay data. In return, they earn Helium tokens (HNT), which are awarded based on network coverage and service quality.
-
Impact: This network offers an alternative to traditional telecom networks by creating a global decentralized wireless infrastructure. The incentive structure encourages widespread participation, ensuring broad coverage and reliability.
Example: Filecoin
-
Description: Filecoin is a decentralized data storage network that enables users to rent out their unused storage space.
-
How It Works: Individuals, known as "Storage Providers," offer their spare storage capacity to the network. In exchange, they earn Filecoin (FIL) tokens, which are awarded for providing storage space and enabling data retrieval services.
-
Impact: Filecoin helps decentralize data storage, reducing dependence on centralized data centers. It also democratizes the market, allowing anyone with spare storage to contribute and earn rewards.
4.2. Digital Resource Networks (DRNs)
DRNs focus on digital resources such as computational power, data, and digital services. These networks incentivize individuals to contribute their digital assets or services to support decentralized operations.
Example: Golem Network
-
Description: Golem is a decentralized marketplace that allows users to rent out unused computing power.
-
How It Works: Participants, known as "Providers," offer their computational resources to the network. They earn Golem tokens (GLM) for providing computational power to users who need it for tasks like rendering, scientific calculations, or machine learning.
-
Impact: Golem enables access to powerful computational resources, offering users a decentralized supercomputer. This reduces costs and makes high-performance computing more accessible to a wider audience.
Example: Livepeer
-
Description: Livepeer is a decentralized video streaming network that provides video transcoding services through community-provided computational power.
-
How It Works: "Transcoders" contribute their computational resources to process and transcode video streams. In return, they receive Livepeer tokens (LPT).
-
Impact: Livepeer helps decentralize the video streaming infrastructure, making it more efficient and scalable. It also reduces the costs of video streaming by utilizing the collective computational power of participants.
4.3. Key Differences Between PRNs and DRNs
| Feature | Physical Resource Networks (PRNs) | Digital Resource Networks (DRNs) |
| Resource Type | Physical assets (hardware, infrastructure) | Digital assets (computational power, data) |
| Contribution Mode | Participants contribute physical resources | Participants contribute digital assets/services |
| Examples | Helium Network, Filecoin | Golem Network, Livepeer |
5.Opportunities and Challenges
While DePIN offers numerous opportunities, it also faces challenges:
5.1 Opportunities
-
Innovation: DePINs enable the creation of cutting-edge infrastructure with blockchain and smart contracts.
-
Community Empowerment: Local communities can directly contribute to infrastructure development, making solutions more sustainable and tailored.
-
Economic Growth: The token-based incentive model stimulates economic activity, promoting financial inclusion.
-
Environmental Sustainability: DePINs can help integrate renewable energy solutions into various sectors, supporting global efforts to combat climate change.
5.2 Challenges
-
Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating legal frameworks for decentralized energy, data privacy, and distribution is complex.
-
Scalability: As DePIN networks grow, maintaining performance and security becomes more challenging.
-
Security: Protecting decentralized networks from threats like 51% attacks requires robust security measures.
-
Interoperability: Ensuring seamless communication between different DePIN projects and centralized systems is crucial for widespread adoption.
6. Conclusion
DePINs represent a major shift in how we build and maintain infrastructure, harnessing the power of blockchain and decentralization to create more resilient, transparent, and efficient systems. These networks empower communities, drive innovation, and support sustainable practices, particularly in the fields of telecommunications, energy, and transportation.
Despite the challenges, DePINs offer significant opportunities for economic growth, environmental sustainability, and technological advancement. With continued innovation and collaboration, DePINs are poised to play a vital role in the future of infrastructure development.
Read more:

 English
English Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt.png)
.jpg)






.jpg)



.jpg)




