
6 fundamental criteria to consider before purchasing an NFT
1. NFT Contract
A smart contract is a special program that is programmed and runs on the blockchain, helping transactions to be automated according to specific rules.
An NFT contract is one of the most important factors to help users avoid buying scam (fake) NFT collections on the market, as it reflects the ownership of the holder and stores the transaction history of that NFT.
Additionally, the contract allows users to trade, buy, and sell NFTs, set the characteristics and features of the NFT, or establish royalties for the author.
Before deciding to invest in and trade any NFT collection, users need to use the official social platforms of the project, such as the website, Twitter, Discord, etc., to obtain the official contract of the NFT collection, as announced by the project.
Moreover, users can check and obtain the NFT contract on network explorer sites like Etherscan/BSCscan/… in the ERC-721/BEP-721 section. Alternatively, when clicking on an NFT in their personal wallet, users can see the contract of that collection in the contract address section.
2. Total volume
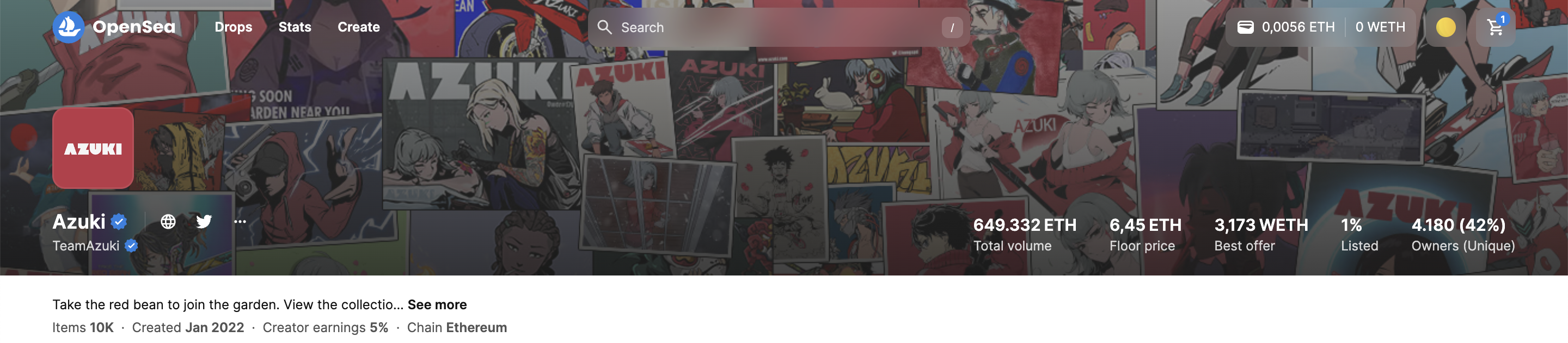
3. Floor price
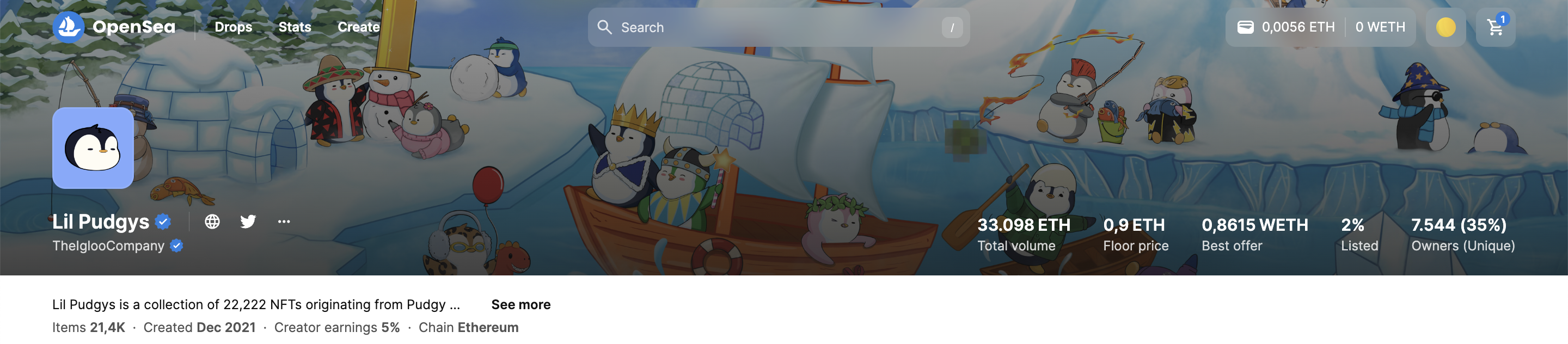
When accessing any NFT collection on OpenSea, users will be able to see the floor price of that collection. This metric indicates the lowest price at which an NFT can be bought or listed on the current market.
The floor price is a measure to evaluate the community's interest in the NFT collection and its value. Typically, the total market capitalization of an NFT collection is calculated by multiplying the floor price by the total supply of NFTs in the project. The higher the floor price, the greater the demand for the NFT collection, and consequently, the higher the project's market capitalization.
Investors often aim to place a bid or offer on an NFT at a price close to the floor price to optimize their entry point.
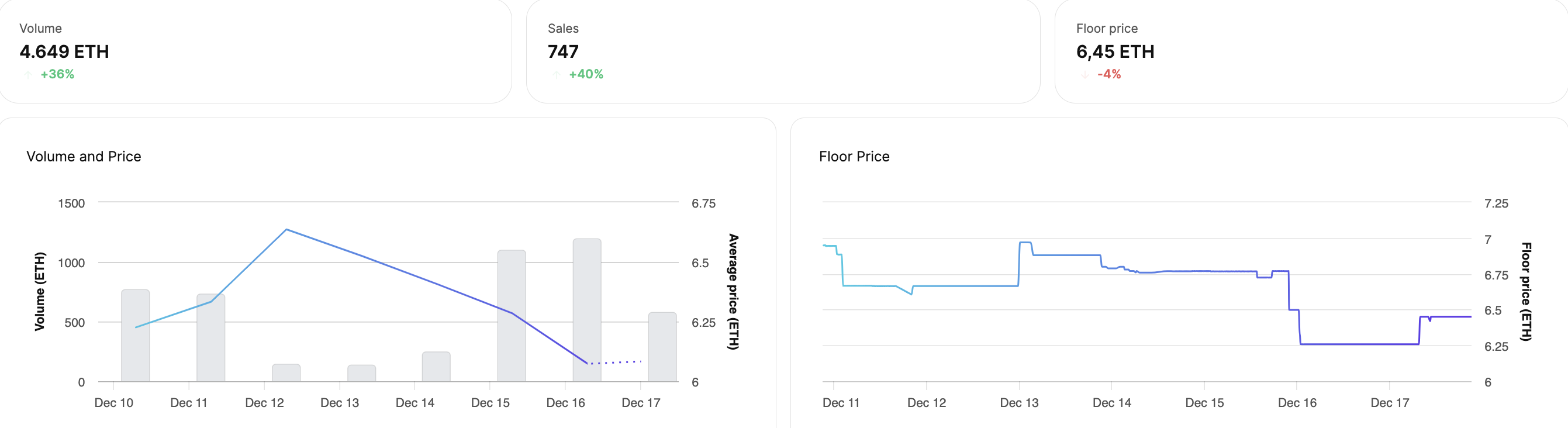
Before purchasing an NFT, users can go to the "analytics" section of NFT marketplaces to assess the price fluctuations and changes of the collection over various time periods (7 days, 30 days, 90 days, since the beginning, etc.) to find the most suitable buying position based on their analysis and preferences.
4. Total supply
The total supply represents the total number of NFTs in the collection. Based on the project's total supply, we can assess its market capitalization and value.
For projects with a high total supply (tens of thousands, hundreds of thousands), there won't be much scarcity created for the project. Collections with a high total supply often have a lower market value per NFT. In contrast, collections with a low total supply usually have a higher value per NFT due to their scarcity.
5. Creator earning/ Royalties Fee
The "Royalties Fee" or "Creator Fee" is part of the smart contract that stipulates whenever an NFT is resold, the creator (often an artist or author) receives a percentage of the sale price as a commission. This royalty fee is established to ensure that content creators continue to receive a portion of the value when their work is transferred.
The royalty fee is typically defined as a percentage of the sale price, and this can vary depending on the agreement between the NFT creator and the initial buyer. Generally, royalty fees range from 5% to 30%, but they can differ based on specific conditions and market dynamics.
This fee represents a significant revenue source for the project, as the creators of the collection are often integral to its success. Therefore, investors should consider this factor carefully, as projects with excessively high royalty fees can impact investor profitability.
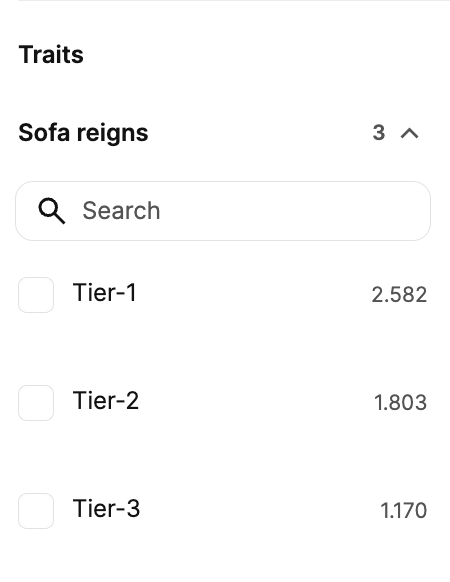
6. Rarity
The concept of "rarity" in NFT collections refers to the level of uniqueness and specialness of each item within the collection. Rarity is evaluated based on factors such as availability, uniqueness, and specific attributes of each NFT. The goal is to create NFTs with high rarity to enhance the value and attractiveness of the collection.
Not all NFT collections categorize items into different levels of rarity and uniqueness.
7. Conclusion
Here are the 6 fundamental criteria and metrics for initial evaluation of NFT projects for new investors stepping into the NFT market. Of course, during the investment process, investors will need to research and understand many other factors to make decisions on whether to invest in a project. However, these are considered the core and most important factors for starting to analyze and evaluate a project.
I hope this article provides useful information about projects to users. The content is informational and not investment advice. Investors should conduct their own research (DYOR - Do Your Own Research) and make their own evaluations before deciding to invest in any project.
Read more:

 English
English Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
















