1. What are Layer 2 Solutions?

Layer 2 solutions are protocols or technologies built on top of a layer 1 blockchain, such as Ethereum, to enhance scalability and reduce congestion. These solutions operate off-chain, meaning they process transactions outside the main blockchain while periodically communicating with it for security and data finality.
A relatable analogy is a busy restaurant: if one chef handled everything from preparing ingredients to serving dishes, service would be slow. Instead, multiple stations focus on specific tasks, increasing efficiency. Similarly, Layer 2s offload tasks from the layer 1 blockchain, enabling faster and cheaper transactions.
2. Why are Layer 2 Solutions Important?

Layer 1 blockchains prioritize decentralization and security, but these features often come at the expense of speed and scalability. For instance, Ethereum can process around 15 transactions per second (TPS), leading to high fees and slow transaction times during peak demand.
Layer 2 solutions address these issues by:
-
Reducing Fees: By bundling multiple transactions into a single batch, Layer 2s significantly lower gas costs.
-
Improving Speed: Higher TPS capabilities ensure faster transaction confirmation.
-
Enhancing Usability: Lower fees and quicker transactions make blockchain technology more accessible to users and developers alike.
3. How do Layer 2 Solutions Work?
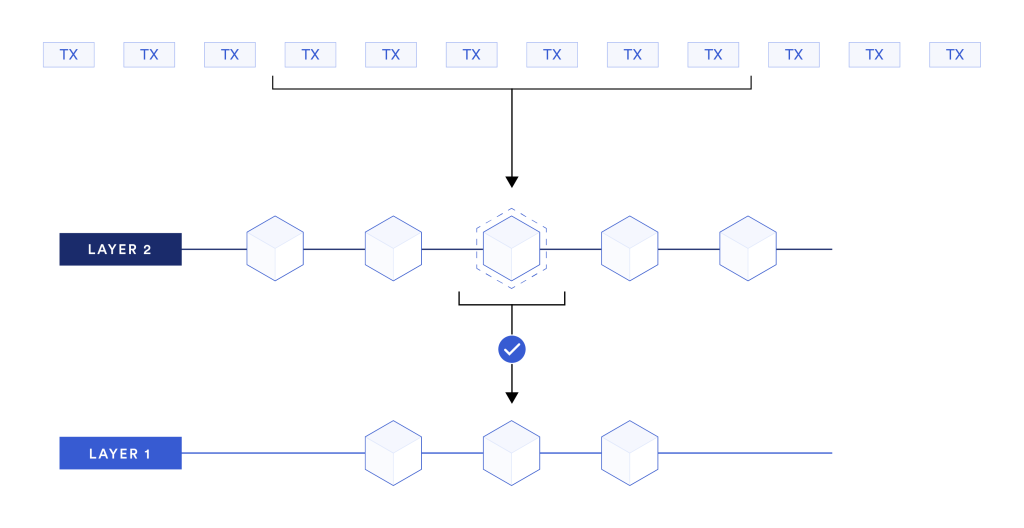
Layer 2 protocols enhance blockchain scalability by creating a secondary framework where transactions are processed independently of the main chain (Layer 1). This offloading reduces the workload on the base layer, enabling faster and cheaper transactions. After processing, Layer 2 applications submit summarized transaction data back to Layer 1, ensuring it is secured within the blockchain's ledger and history.
Accessibility to Layer 2 solutions varies. Some cater to a wide range of applications, while others are tailored for specific projects. Core technologies used in Layer 2 scaling include rollups and sidechains.
3.1 Rollups
Rollups execute numerous transactions off the main chain, compress the data, and then post it to Layer 1 for validation. This approach leverages Ethereum’s security while significantly reducing gas fees, often by 10–100x. There are two main types of rollups: Optimistic Rollups and ZK Rollups.
a. Optimistic Rollups
Optimistic rollups operate in parallel with Ethereum, processing transactions off-chain and periodically posting summaries to Layer 1. Fraud-proof mechanisms allow anyone to challenge suspicious transactions. If fraud is suspected, the rollup re-computes the transaction to verify its validity.
-
Advantages: EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) and Solidity compatibility. Supports all Ethereum-based applications with low fees.
-
Examples: Arbitrum, Optimism, and Boba.
-
Considerations: Exiting funds back to Layer 1 may take longer due to fraud-proof processing, but transactions within the rollup are confirmed quickly.
b. ZK Rollups
ZK (Zero-Knowledge) rollups use cryptographic proofs, such as SNARKs or STARKs, to validate transactions. These proofs are posted to Layer 1, ensuring authenticity without requiring the entire transaction data.
-
Advantages: Faster finality with immediate Layer 1 validation. Highly efficient for applications requiring frequent state updates.
-
Considerations: Limited EVM compatibility. Computationally intensive for certain applications.
-
Examples: zkSync, StarkNet.
c. Sidechains
Sidechains, like Polygon PoS and xDai, are independent, EVM-compatible blockchains that interact with Ethereum via bridges. While they mimic Ethereum’s architecture, they rely on separate consensus mechanisms and are not secured by Ethereum itself.
-
Advantages: Lower transaction costs and higher throughput. Flexibility in governance and customization.
-
Considerations:
Increased security risks due to reliance on external validators.
Not considered true Layer 2 solutions because they lack Ethereum's security guarantees.
d. Validiums
Validiums, such as StarkWare, utilize validity proofs like ZK rollups but store transaction data off-chain. Multiple validium chains can run in parallel, processing up to 10,000 transactions per second.
-
Advantages: High throughput and scalability.
-
Considerations: Limited support for general-purpose smart contracts. Greater reliance on external storage and trust models.
4. Examples of Common Layer 2 Solutions

Layer 2 solutions are designed to work seamlessly within the Ethereum ecosystem, offering diverse options for developers and end-users. These systems complement each other, with the strengths of one layer 2 addressing the limitations of another. Below is a detailed overview of commonly used layer 2 solutions, divided into general-purpose and application-specific categories.
4.1 General-Purpose Layer 2 Solutions
General-purpose layer 2s replicate the core functionalities of Ethereum’s mainnet but with significantly lower transaction costs (gas fees). These solutions prioritize scalability and compatibility, making them versatile for various use cases.
Optimism
Optimism is an EVM-equivalent layer 2 solution that employs Optimistic rollups to enhance transaction speed, simplicity, and security. While its fraud-proof system is still evolving, Optimism provides users with a fast and cost-effective environment for deploying Ethereum-based applications.
Arbitrum One
Arbitrum is another Optimistic rollup that mirrors Ethereum’s mainnet while significantly reducing transaction fees. It is known for its robust developer tools and high compatibility with Ethereum applications.
Boba Network
Initially a fork of Optimism, Boba Network is an Optimistic rollup focused on further reducing fees, increasing transaction throughput, and expanding smart contract capabilities. Boba aims to create a more efficient and scalable ecosystem for Ethereum developers.
4.2 Application-Specific Layer 2 Solutions
Application-specific layer 2s are tailored for specific sectors or use cases, providing specialized performance enhancements for niche markets.
Loopring
Loopring is a ZK rollup designed to offer Ethereum-level security with enhanced scalability. It boasts throughput improvements of up to 1,000x compared to Ethereum mainnet and reduces transaction costs to just 0.1% of those on Layer 1. Loopring is particularly well-suited for decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and payment systems.
zkSync
zkSync, developed by Matter Labs, is a ZK rollup already live on the Ethereum mainnet. It supports a variety of use cases, including payments, token swaps, and NFT minting. Trusted by platforms like Binance, zkSync offers a blend of high security, scalability, and low transaction fees, making it a popular choice for projects needing fast and reliable Ethereum integration.
5. FAQs
Q1. What is the main benefit of Layer 2 solutions?
Layer 2 solutions improve blockchain scalability by enabling faster transactions and lower fees without compromising security.
Q2. Are Layer 2s secure?
Yes, most Layer 2 solutions inherit the security of their layer 1 blockchain by periodically syncing data for validation.
Q3. How do I choose the right Layer 2 solution?
Consider your use case. For example, Optimistic rollups are great for general scalability, while ZK rollups are ideal for projects requiring high security and throughput.
6. Conclusion
By integrating Layer 2 solutions, blockchain networks can overcome scalability challenges and unlock their full potential. If you’re interested in exploring more about blockchain technology, stay tuned to our website for the latest insights!
Read more:

 English
English Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt

.png)







.jpg)




