1. Introduction to Cross-chain Bridge
Cross-chain Bridge is a cross-chain bridge that helps transfer assets between two or more blockchains to improve interoperability and communication between blockchains.
Cross-chain Bridge plays an important role in enhancing liquidity between blockchains, saving time and costs for users, increasing flexibility for dApps and ensuring safety when transferring assets between blockchains.
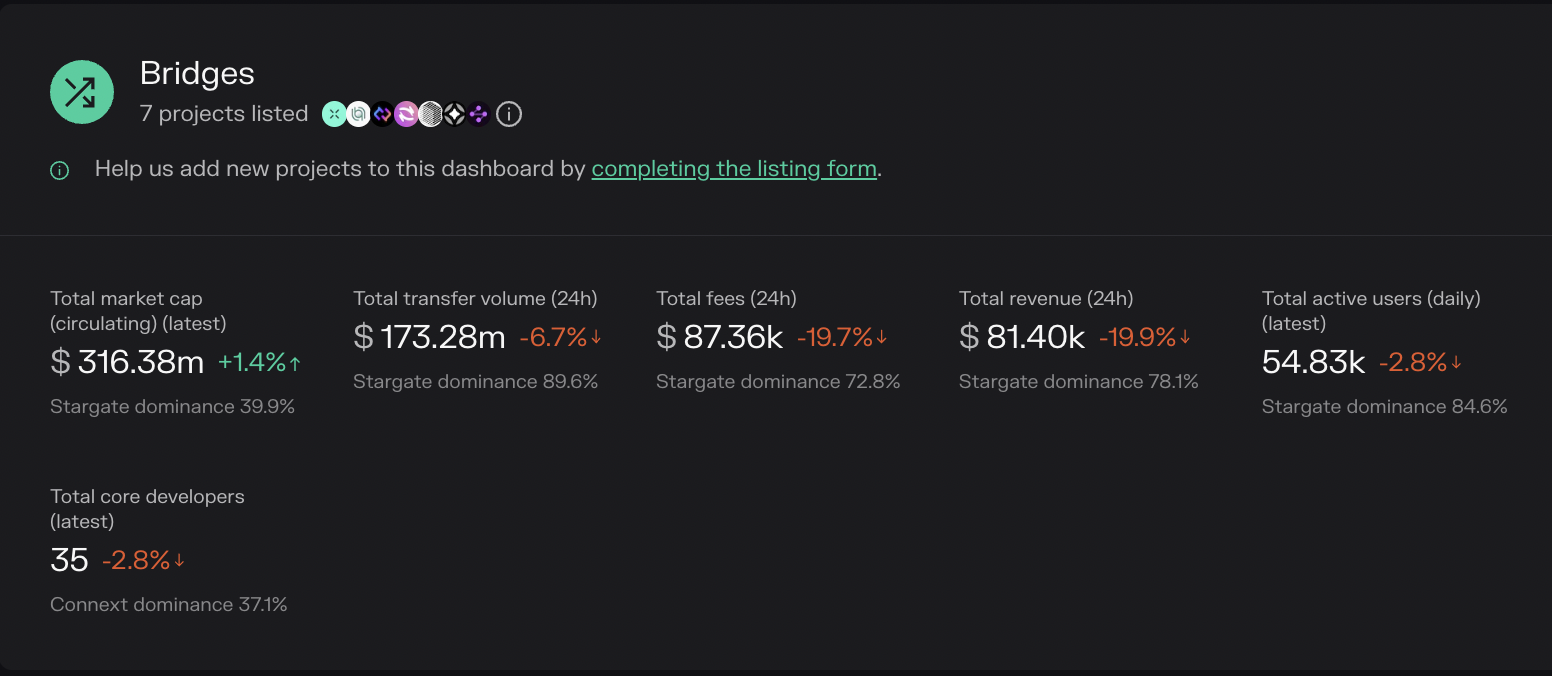
In the article below, I will guide you how to use Cross-chain Bridge to transfer assets between blockchains and notes to protect your assets with these intermediary applications.
2. Issues and risks when using Cross-chain Bridge
If you want to use cross-chain bridges effectively, the first thing you need to understand is the operating model of cross-chain bridges and the problems cross-chain bridges often encounter. Below is a summary of some common problems and risks users encounter when using cross-chain bridges.
2.1. Transaction time is slow
The time to deposit & withdraw tokens between blockchains when using Bridge is not fixed, depending on many things. Processing times can fluctuate significantly and affect user experience.
For the use of Cross-chain Bridge , token deposit and withdrawal time periods may vary significantly. While the deposit time can take a few minutes to a few dozen minutes, the token withdrawal time is quite long, ranging from a few hours to 2 - 3 weeks.
This difference can cause inconvenience and trouble for users, especially when they want to make quick transactions.
To save more time, users can handle this problem by depositing & withdrawing tokens back and forth between blockchains using exchanges. However, the limitation of this method is that exchanges usually only support a limited number of prominent blockchains.
For new blockchains, users are required to use an intermediary bridge built by the project or provided by a third party.
2.2. Money missing after deposit to Bridge
There are a number of possible causes of missing funds while using Cross-chain Bridge that users need to pay attention to, including:
- Technical errors : Cross-chain Bridge projects may experience technical problems or errors during the conversion process, resulting in funds being lost during sending or not received on the destination chain.
- Using a scam platform: If you choose to use a Cross-chain Bridge from an untrusted source or an unknown project, there may be a high risk of funds going missing or being scammed.
- Transaction times : Some Cross-chain Bridges may require transaction confirmations from multiple blocks across multiple blockchain chains, which can lengthen transaction times and increase the chance of funds going missing.
- Wrong wallet address error : If you enter the wrong destination wallet address during the conversion process, your funds may be sent to an unrecoverable address and lead to asset loss.
To avoid potential risks, users should consider and choose a reliable Cross-chain Bridge from proven and highly reliable projects. At the same time, please carefully check and confirm the wallet address and transaction information before transferring assets between blockchain chains.
2.3. Transaction execution costs
Cross-chain Bridge helps users easily convert assets between different blockchains, but this also entails quite high costs when performing transactions on these cross-chain bridges.
If a user wants to transfer assets from chain A to chain B via cross-chain bridge, the user will need to pay some fees such as:
-
Network fees: The process of converting tokens through Cross-chain Bridge requires interaction with different blockchain networks, so users need to pay transaction fees corresponding to that network (usually the fee will be based on the original network user sends token). For example, for Bridges related to Ethereum, the fees will be very high.
-
Fees on exchanges: If users use CEX Bridge, they need to pay additional transaction fees from the exchange and depending on the type of exchange and blockchain, the fees will vary. However, depositing and withdrawing tokens between the blockchain through CEX will cost less than using the default bridge.
-
Protocol Fees: Some Cross-chain Bridges may impose conversion rates or flat fees for transferring tokens between different blockchains. This can increase the total cost and reduce the benefits of using Bridge.
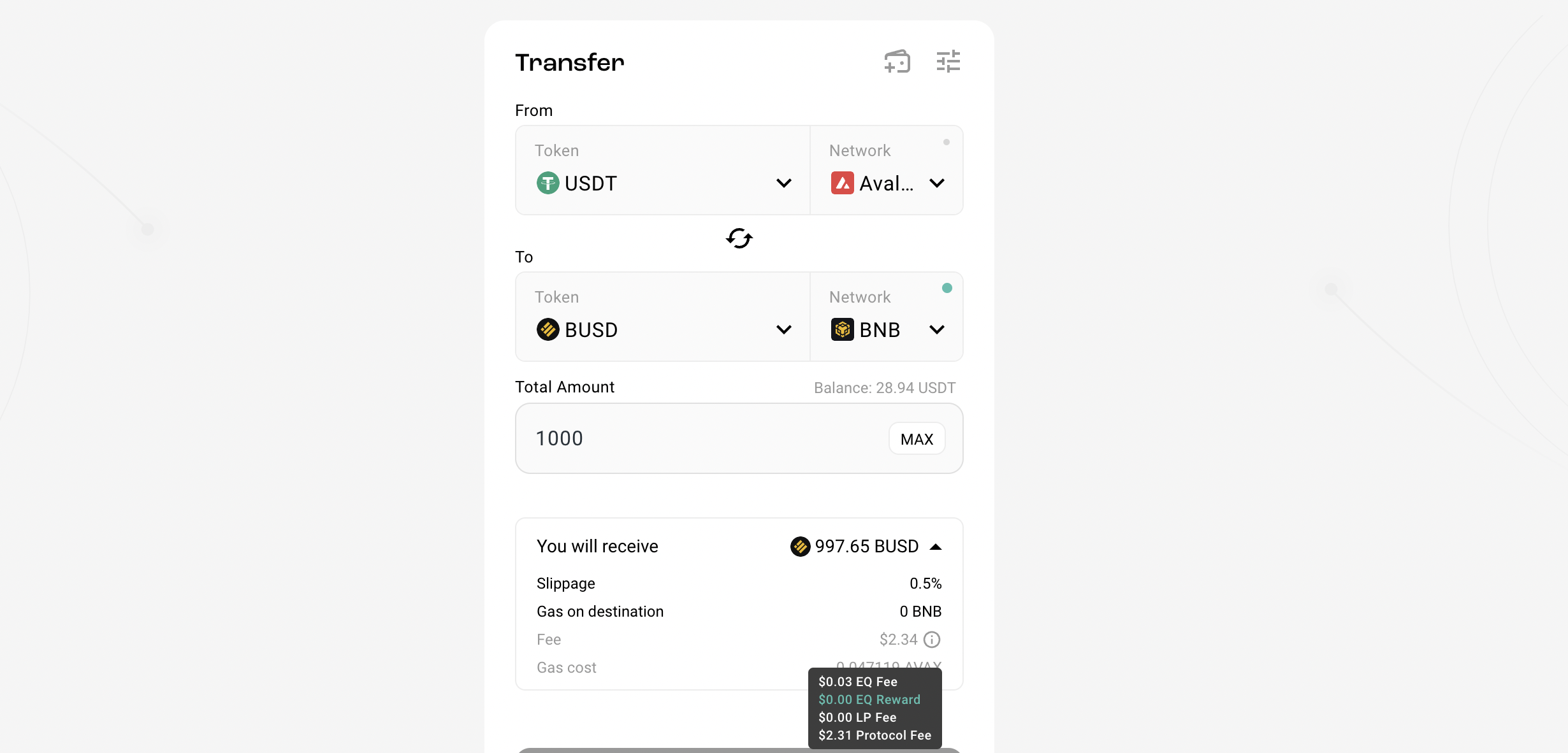
2.4. Security risks
In the context that cross-chain bridge technology is not really complete and has many potential risks of security holes, users of cross-chain bridges when transacting cannot completely avoid the risk of losing money.
Cross-chain bridges are often the focus of million-dollar hacks in DeFi because they are the largest concentration of TVL. Typical examples include some classic hacks of Poly Network (600 million USD) , Ronin (Axie Infinity), Wormhole ,...
Previously, cross-chain bridges often operated based on the Lock-Mint-Burn model design. If a user wants to transfer tokens from blockchain A to blockchain B, they must lock their tokens to the bridge. After that, the bridge will mint an amount of wrapped tokens corresponding to the number of tokens sent in chain A on blockchain B. If you want to transfer back, the number of wrapped tokens in chain B will be burned and the tokens in chain A will be burned. will be unlocked.
Hackers took advantage of some vulnerabilities in the smart contract to unlock tokens on Chain B without locking the corresponding tokens on Chain A. From there, the assets on the cross-chain bridge "went flying".
Currently, the cross-chain bridge model has had many innovations and changes to enhance security and users can also feel more secure when using it. Some of the most prominent cross-chain bridge model designs being applied include:
- LayerZero's Omnichain (typically Stargate Finance is applying)
- Circle's CCTP
- Chainlink's CCIP
3. Solution to use cross-chain bridge effectively
Below are some experiences for newbies who want to use cross-chain bridges effectively and avoid the risk of losing assets.
3.1. Learn carefully about Bridge before using it
- Learn about the Cross-chain Bridge project: Read documents, websites and related information about the Bridge project to understand how it works and its basic features or search for the keyword “cross-chain bridge ” on Theblock101 website to learn about the most potential cross-chain bridge projects.
- Talk to the community: Find out what other users have to say, join communities on social platforms or forums to ask and discuss using Bridge.
- Use a demo account: If available, test Bridge on a test environment or use a demo account to get familiar with the migration process.
3.2. Check the costs and transaction fees involved
- Understand costs: Identify the fees and costs associated with using a Cross-chain Bridge. This includes deposits, withdrawals, conversions and other fees that may arise.
- Compare with other methods: If applicable, compare the costs of using Cross-chain Bridge with converting tokens through exchanges (CEX) or other ways. This helps you optimize Bridge usage.
3.3. X confirms the wallet address correctly
- Copy and paste wallet address: When making a transaction, copy and paste the wallet address correctly to avoid errors and sending tokens to the wrong address.
- Verify twice before sending: Before sending tokens, confirm the wallet address twice to ensure accuracy.
3.4. Note the transaction time and successful confirmation
- Track transaction time: Track transaction time from sending the token until it is received on the destination chain. This helps you know how fast the conversion process is.
- Confirm success: Once the transaction is complete, confirm the success status and ensure that the number of converted tokens is as expected.
3.5. Wallet security
-
Do not click on malicious links to avoid losing money in your account.
-
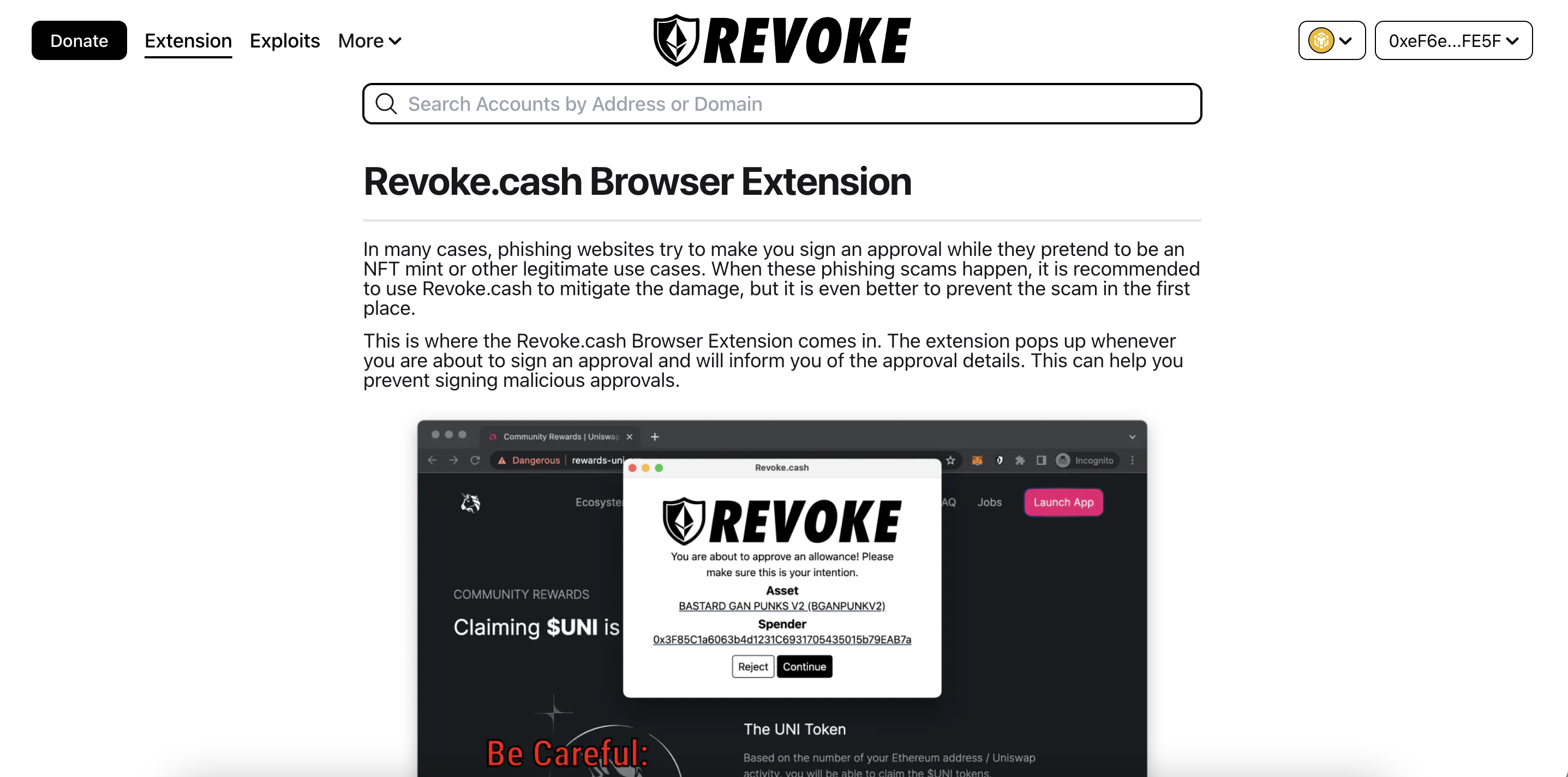
Regularly update information about blockchain hacks to avoid using unreliable platforms. You can use https://revoke.cash/exploits to check and stay informed about these hacks.
-
Normally, wallets when using cross-chain bridges will be wallets related to the main network such as Ethereum, Solana, Aptos,... in addition to CEX Bridges, please revoke the wallet to avoid the wallet being attacked. Note that these are user-side protections and they cannot protect you if the platform itself is hacked.
4. Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
4.1. Which Cross-chain Bridges should be used?
Prominent Cross-chain Bridge projects that are receiving attention and large transaction volume in the bridge market today include: Synapse, Stargate Finance, Hop Protocol, Li.Fi , Orbiter,... Choosing the type of bridge Which to trade depends on personal needs and goals as well as the network the project supports.
4.2. How to transfer tokens with the least fees?
The cost of transferring tokens depends on the blockchain network you want to interact with and the transaction fees from the protocol. You can test on several similar platforms to convert tokens and see which side's implementation cost is more optimal.
However, for some bridges related to Ethereum, high fees are inevitable. Layer 2 solutions will be more economical in terms of transaction fees.
4.3. Is cross-chain bridge safe?
Previously, due to technological limitations, cross-chain bridge projects were hacked a lot, leading to users doubting their safety. At present, although many new technologies have been developed to fix it and no hacking incidents have taken place, the bridge is still one of the places most at risk of being attacked by hackers.
Depending on your needs and understanding as well as your level of risk tolerance when participating in the DeFi market, you should consider your usage. Prioritize choosing reputable, transparent platforms with good backers to increase your safety level.
Read more:
What is Stargate Finance (STG)? New generation cross-chain protocol on LayerZero
What is a wormhole? Cross-chain bridge "rebounded" after being hacked for 326 million USD
What is LI.FI Protocol? Comprehensive cross-chain bridge solution for the blockchain ecosystem

 English
English Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt