1. What is the hash rate?

Hash rate refers to the amount of computational power being used to mine and process transactions on a blockchain network, specifically on proof-of-work (PoW) blockchains. It’s a measure of how many guesses or "hashes" are being generated per second by miners on the network. A hash itself is a hexadecimal number created by a hashing algorithm, and hashing is the process of attempting to match that number by changing specific values.
In essence, hash rate is a measure of how quickly a miner (or group of miners) can generate guesses to solve the cryptographic puzzle that secures the blockchain. The more hashes a miner can generate, the higher their hash rate and the better their chances of solving the puzzle and earning block rewards. Hash rate is also used to adjust the difficulty level of mining a block and gauge the overall security and participation level of a network.
2. How does hash rate work?

Blockchain networks that operate on proof-of-work (PoW) algorithms use hashing functions to generate a hash. When a miner attempts to mine a block, their mining computer performs a series of calculations on the information from the proposed block using a hashing algorithm. The goal is to find a hash that is lower than or equal to a target value, which will "solve" the block.
Each guess made by a miner is counted as a hash, and the hash rate measures how many of these guesses are being made per second. Miners can operate individually or in groups, forming mining pools to combine their hash rates. The more computational power involved in solving the puzzles, the higher the hash rate for the network.
When the network hash rate increases due to more miners joining or faster hardware being used, it becomes more difficult to mine blocks, ensuring that the blockchain remains secure and stable. The block reward is given to the miner or group of miners who solve the puzzle first.
3. Typical hash rate measurements

Hash rate is typically measured in the number of hashes generated per second, with different units depending on the scale of the operation. Here are some common measurements of hash rate and the networks or devices that generate them:
-
Kilohash per second (KH/s): 1,000 hashes per second. This is considered very slow and typically associated with early or less powerful devices.
-
Megahash per second (MH/s): 1 million hashes per second. This is typically achieved by GPUs or CPUs and is also considered quite slow by modern standards.
-
Gigahash per second (GH/s): 1 billion hashes per second. This is generally the hash rate of a solo miner using faster equipment.
-
Terahash per second (TH/s): 1 trillion hashes per second. This is common in ASIC miners or small mining pools.
-
Petahash per second (PH/s): 1 quadrillion hashes per second. This is typically seen in medium to large mining pools.
-
Exahash per second (EH/s): 1 quintillion hashes per second. This level is typical of large mining pools or entire networks.
-
Zettahash per second (ZH/s): 1 sextillion hashes per second. No blockchain network has reached this level yet, but it represents the future potential of hash rates.
4. Why is hash rate important?
Hash rate is an important indicator of several aspects of a blockchain network:
-
Security: A higher hash rate means more miners are competing to solve blocks, making it harder for a single entity to take control of the network and conduct attacks like a 51% attack.
-
Mining difficulty: As the hash rate increases, the difficulty of mining a block also increases. The network automatically adjusts the difficulty to ensure that blocks are mined at a consistent rate, preventing any one group of miners from dominating the process.
-
Network power: A high hash rate reflects a powerful network with significant computational resources backing it. This can give investors confidence in the network’s stability and security.
-
Energy consumption: As the hash rate increases, so does the energy consumption of the network. This is one of the reasons why hash rate is used to estimate the energy usage of a blockchain.
5. What happens when the hash rate increases or decreases?
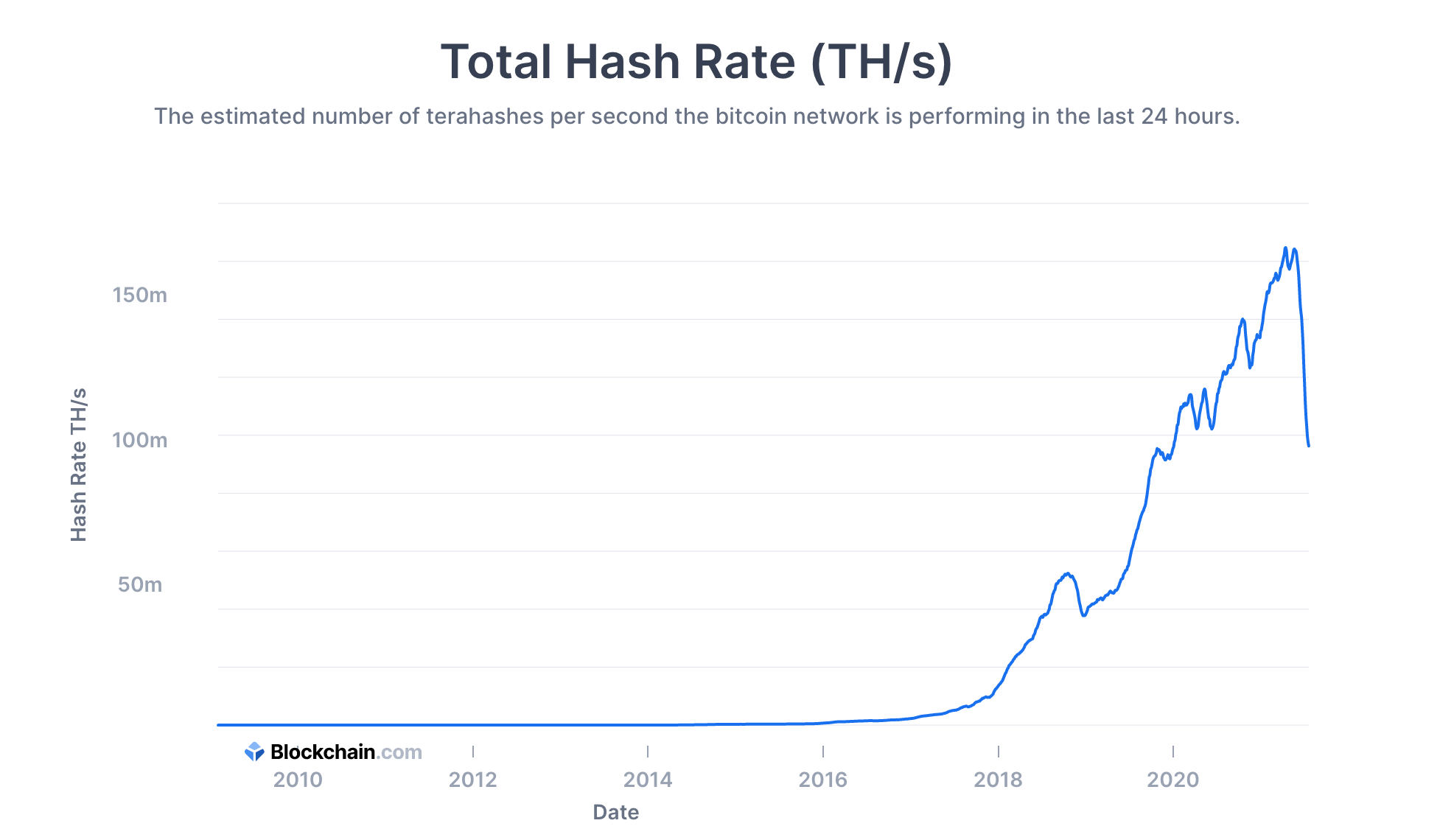
The hash rate of a blockchain can fluctuate due to several factors, such as changes in the number of miners, improvements in mining hardware, or shifts in market conditions. Here’s what happens when the hash rate increases or decreases:
-
When the hash rate increases:
-
More computational resources are being used to mine blocks.
-
Increased energy consumption from mining operations.
-
The network becomes more secure as it is harder for a small group of miners to overpower the network.
-
The protocol adjusts to require more hashes to be generated, keeping the mining difficulty in check.
-
When the hash rate decreases:
-
Fewer miners are competing to add blocks to the blockchain.
-
The network becomes less secure and more vulnerable to attacks, as fewer resources are dedicated to protecting it.
-
Mining power consumption decreases, which may be seen as a positive for energy efficiency.
-
The protocol adjusts to require fewer hashes to be generated, reducing the mining difficulty.
6. The Importance of Hash Rate on Bitcoin Price
The hash rate, a key metric in Bitcoin's mining network, represents the computational power used to process transactions and secure the blockchain. It is a critical factor that directly influences the stability, security, and overall performance of the Bitcoin network. While the hash rate itself doesn't directly control Bitcoin's price, it plays a significant role in shaping market sentiment and can have indirect effects on Bitcoin's value.
6.1. Security and Network Stability
A higher hash rate means more miners are participating in the network, making the blockchain more secure and resistant to attacks, such as the 51% attack. Increased security boosts confidence in Bitcoin, making it a more attractive investment for traders and institutional players. When security is enhanced, it often results in positive sentiment, driving the price up.
6.2. Mining Difficulty Adjustment
Bitcoin’s mining difficulty adjusts approximately every two weeks to ensure that a new block is mined approximately every 10 minutes. If the hash rate increases, the difficulty increases to maintain this consistent block time. A rising difficulty often signals increased competition among miners, and this is generally seen as a bullish signal for Bitcoin, as it shows that more people are betting on Bitcoin’s future. This can lead to upward pressure on the price.
6.3. Miner Behavior and Price Correlation
The hash rate and Bitcoin price have a cyclical relationship. When Bitcoin prices rise, miners are incentivized to allocate more computational power to mining because the rewards (in BTC) are more valuable. Conversely, when Bitcoin’s price falls, miners may struggle to cover operational costs (especially electricity), leading to a decrease in hash rate as some miners shut down operations. This reduction in hash rate can affect the security of the network and may result in increased volatility, which often negatively impacts the price.
6.4. Investor Confidence
When hash rate rises steadily, it signals a healthy and robust network to investors, enhancing their confidence in Bitcoin’s long-term viability. Conversely, a decline in hash rate can signal weakness in the network, causing concerns about Bitcoin's future and driving down market prices. Investors closely monitor hash rate data as part of their decision-making process, making it an important variable in Bitcoin’s price action.
In summary, while the hash rate itself is not a direct cause of Bitcoin's price fluctuations, it is an important indicator of the network’s health, security, and future potential. Higher hash rates typically correlate with higher security and greater miner confidence, both of which can drive positive price movements. Conversely, decreases in hash rate can signal potential challenges for Bitcoin’s price, affecting investor sentiment and market behavior.
7. Conclusion
Hash rate is a vital metric in the cryptocurrency world, measuring the computational power behind a blockchain network. It plays a critical role in determining the security, efficiency, and sustainability of the network. Whether you’re a miner or an investor, understanding hash rate is crucial for gauging the strength of a blockchain and its ability to withstand malicious attacks. By monitoring changes in hash rate, participants can gain insights into the overall health of the network and make informed decisions about their involvement in crypto projects.
Read more:

 English
English Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt.png)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)




