1. What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology that records transactions across many computers so that the record cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks. This makes it impossible to hack the system, as hackers would need to control more than 50% of the network’s computing power to make any changes.
Each block in a blockchain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. By design, a blockchain is inherently resistant to data modification. Once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks, which requires the collusion of the network majority.
The decentralized structure of blockchain eliminates the single point of failure and the need for trusted third parties to validate transactions. Instead, validation is carried out collectively by the network. This makes blockchains transparent, traceable, and irreversible.
Key features of blockchain technology include:
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the network.
- Security: Cryptographic hashes and consensus mechanisms ensure data integrity.
- Transparency: All transactions are recorded on a public ledger.
- Immutability: Once recorded, data cannot be altered.
In essence, blockchain offers a secure, transparent, and efficient way to record and verify transactions. This has led to its adoption in various industries, including finance, supply chain management, and healthcare.
2. Blockchain Applications: Revolutionizing Industries
Blockchain, a decentralized ledger technology, has found numerous applications across various sectors. Let's delve into some of the most significant use cases of blockchain.
2.1. Blockchain in Cryptocurrency

Blockchain is the underlying technology behind most cryptocurrencies, with Bitcoin being the most well-known example. Here are some key applications of blockchain in the cryptocurrency realm:
- Foundation of Cryptocurrencies: Every cryptocurrency transaction is recorded on a new block in the blockchain, ensuring the integrity and security of the transaction data.
- Decentralized and Peer-to-Peer Transactions: Blockchain enables direct transactions between parties without the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing flexibility.
- Digital Wallets: Blockchain provides digital wallets for securely storing cryptocurrencies. Users have control over their private keys and can conduct transactions without relying on central authorities
- Transparency and Auditability: All transactions are recorded on the blockchain and can be verified by anyone. This enhances transparency and reduces the risk of fraud.
- Enhanced Security: Transactions are secured by robust cryptography. The decentralized nature of the system makes it resistant to cyberattacks.
- Smart Contracts: Blockchain can execute smart contracts, automating agreements and ensuring that terms are met
- Mining and Limited Supply: Miners verify transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain, earning rewards in the process. This process limits the supply of cryptocurrencies, creating scarcity and value.
2.2. Blockchain in Manufacturing and Logistics
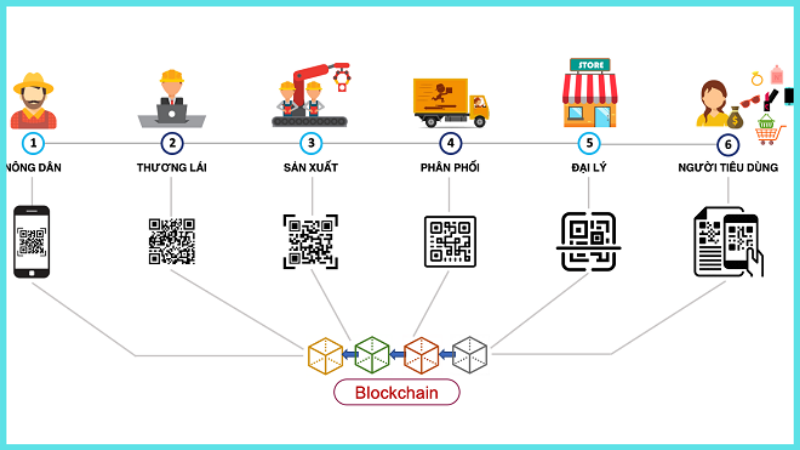
Blockchain can significantly improve efficiency and transparency in manufacturing and logistics:
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain enables tracking and recording the entire journey of a product from origin to consumer, ensuring transparency and reducing fraud.
- Product Information Management: Each product can have a digital passport containing information about its origin, components, and specifications
- Document and Certificate Management: Blockchain can be used to manage certifications, quality certificates, and other product-related documents.
- Production Process Management: Blockchain can record every step of the production process, improving traceability and quality control.
- Enhanced Security: Blockchain provides a secure and decentralized database, reducing the risk of data breaches
- Shipping and Logistics Management: Blockchain can track shipments, store information about routes, storage conditions, and incidents during transit.
- Smart Contracts for Automation: Smart contracts can automate various processes in manufacturing and logistics, ensuring compliance with agreed-upon terms.
2.3. Blockchain in Education

Blockchain can revolutionize the education sector:
- Student Record Management: Blockchain can create secure and transparent student records, including degrees, certificates, and academic achievements.
- Credential Verification: Blockchain can verify the authenticity of educational credentials quickly and efficiently.
- Content Sharing: Blockchain can facilitate secure and transparent sharing of educational materials and research.
- Tuition and Financial Management: Blockchain can streamline tuition payments and financial management.
- Smart Contracts for Educational Services: Smart contracts can automate various administrative tasks, such as course registration and grading.
2.4. Blockchain in Healthcare
Blockchain can improve healthcare by enhancing data security, privacy, and efficiency:
- Electronic Health Records: Blockchain can create decentralized and secure electronic health records, allowing patients to control their health data.
- Credential Verification: Blockchain can verify the credentials of healthcare professionals.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can track the journey of medical supplies, ensuring their authenticity and safety
- Clinical Trials: Blockchain can improve the transparency and efficiency of clinical trials.
2.5. Blockchain in E-commerce

Blockchain can enhance trust and security in e-commerce:
- Secure Payments: Blockchain enables direct and secure payments between buyers and sellers
- Product Authenticity: Blockchain can verify the authenticity of products and their origin.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Blockchain provides transparency into the entire supply chain, from manufacturing to delivery
- Customer Reviews: Blockchain can create tamper-proof systems for product reviews, ensuring their authenticity.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Blockchain can be used to protect digital assets and intellectual property
In conclusion, blockchain technology offers a wide range of applications across various industries, revolutionizing the way we conduct business and interact with each other. Its potential to enhance security, transparency, and efficiency is driving its adoption worldwide.
3. Opportunities and Challenges of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain, a revolutionary technology, presents both significant opportunities and challenges. Let's delve into both aspects.
3.1. Opportunities
- Enhanced Transparency: Blockchain offers unparalleled transparency in transactions. Every transaction is recorded on a public ledger, preventing fraud and promoting fairness. This fosters trust among users and encourages responsible business practices.
- Security and Privacy: Blockchain's decentralized nature and robust cryptography make it highly secure. Transactions are protected from cyberattacks, and user data is safeguarded.
- Automation with Smart Contracts: Smart contracts automate agreements and processes, reducing the risk of errors and disputes. This has the potential to revolutionize industries such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain management.
- Efficiency and Cost Reduction: By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain can streamline processes and reduce costs.
3.2. Challenges
- High Implementation Costs: Developing and maintaining a blockchain infrastructure can be expensive, especially for smaller organizations.
- Scalability: As blockchains grow, they can become slower and more expensive to operate. Scaling solutions are still being developed.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory landscape for blockchain is still evolving, creating uncertainty for businesses and investors.
- Security Risks: While blockchain is inherently secure, it is not immune to attacks. Vulnerabilities can be exploited, and the complexity of blockchain systems can make it difficult to detect and address security threats.
- Technical Complexity: Blockchain technology is complex, requiring specialized skills to develop and implement.
- User Adoption: Widespread adoption of blockchain technology requires significant changes in business processes and consumer behavior.
In conclusion, blockchain technology holds immense promise but also presents challenges. As the technology matures and regulatory frameworks evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of blockchain. However, it is crucial to address the challenges associated with blockchain to fully realize its potential.
Key considerations for successful blockchain adoption include:
- Clear understanding of business needs: Identifying specific use cases where blockchain can add value.
- Careful evaluation of costs and benefits: Assessing the return on investment and considering alternative solutions.
- Collaboration with experienced partners: Working with experts in blockchain technology to overcome technical challenges.
- Compliance with regulations: Staying up-to-date with the evolving regulatory landscape.
- Continuous education and training: Investing in the development of a skilled workforce.
By addressing these challenges and capitalizing on the opportunities, organizations can harness the power of blockchain to drive innovation and create new value.
4. Conclusion
It's evident that blockchain technology is reshaping our world through its ability to enhance transparency, security, and automation. From e-commerce to personal finance, blockchain's applications are vast and far-reaching. However, to fully realize its potential, challenges such as standardization and security must be addressed. As we move forward, careful consideration should be given to integrating blockchain into our everyday lives.
Readmore:

 English
English Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt