1. What is Crypto Staking?
.png)
In 2012, Sunny King and Scott Nadal introduced the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism as a potential solution to Bitcoin’s high energy consumption. This was followed by the launch of Peercoin in 2013, which became the first cryptocurrency to implement staking as a means of validating blockchain transactions. Fast forward to 2022, when Ethereum completed its transition from Proof of Work (PoW) to PoS, marking a significant milestone in the cryptocurrency industry. As a result, crypto staking has surged in popularity, offering both rewards and a vital role in securing blockchain networks.
Crypto staking is the process by which token holders participate in the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism by locking their cryptocurrency into a staking contract and running the associated validator software. The more tokens a validator stakes, the greater their chances of being selected to verify and add new blocks to the blockchain. In return, validators earn staking rewards, which typically come in the form of the staked cryptocurrency or other rewards native to the blockchain.
Staking plays an essential role in ensuring the stability and security of PoS blockchains. Validators are financially incentivized to act honestly because they risk losing their staked tokens if they validate fraudulent transactions. While the exact rewards and terms vary by blockchain, staking generally offers a chance to earn returns proportional to the amount of crypto staked, and those rewards can increase as the blockchain grows and becomes more popular.
2.PoS vs. PoW: How Crypto Staking Works
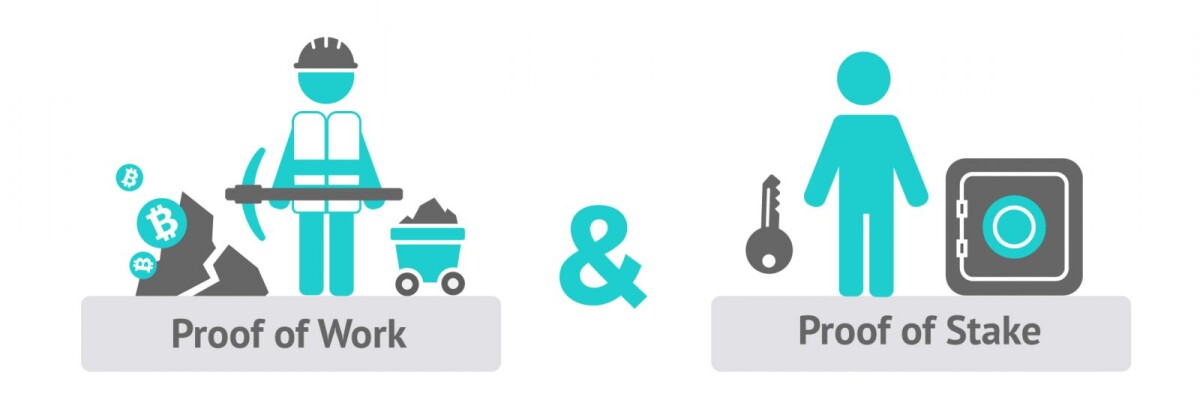
The Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanism differs from the Proof of Work (PoW) model used by Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. Both models serve the same purpose—validating and securing transactions—but they do so in different ways:
-
Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators "stake" their cryptocurrency into a smart contract to secure the blockchain and are randomly selected to create new blocks. In return, they earn block rewards (newly minted coins) and transaction fees. Validators are incentivized to act honestly because any dishonest behavior can result in a penalty, known as slashing, where a portion of their staked coins are forfeited.
-
Proof of Work (PoW): In the PoW model, miners must solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets the right to add a new block to the blockchain and earns both newly minted cryptocurrency and transaction fees. PoW requires a significant amount of computational power, leading to higher energy consumption.
3. Roles in Staking: Validators and Delegators

In PoS, there are two main roles: Validators and Delegators.
-
Validators: These are node operators responsible for verifying transactions and creating new blocks. To become a validator, users must stake a certain amount of cryptocurrency as collateral. For example, Ethereum requires at least 32 ETH to become a validator. Validators are crucial to the security of the network, and their honesty is ensured through the risk of slashing.
-
Delegators: These are individuals who don’t have enough capital to become validators but still wish to participate in the staking process. Delegators lock up their cryptocurrency and delegate it to a validator. In return, they earn a portion of the staking rewards that the validator receives. Delegators have the benefit of participating in staking without the minimum requirements of becoming a full validator.
4. How Does Staking Crypto Work?
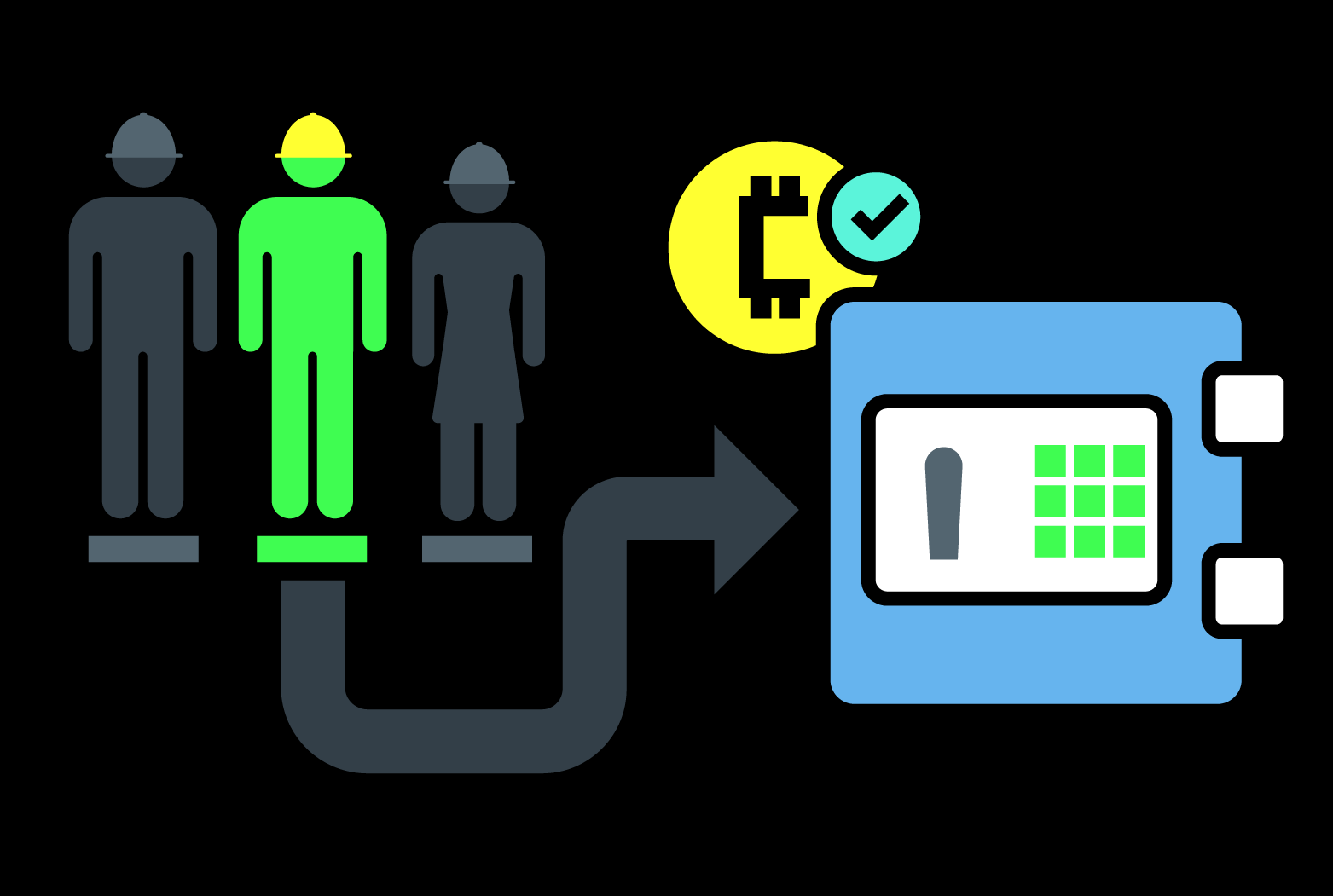
4.1. Selecting a Crypto for Staking
Before diving into staking, it’s important to understand the cryptocurrency you’re investing in, as well as the underlying blockchain project. Factors to consider include:
-
The vision and team behind the project.
-
The use cases the crypto serves.
-
The project’s community and development support.
-
The staking requirements, such as the minimum amount of tokens needed to stake, and the associated rewards.
For instance, to become a validator on Ethereum, you must stake at least 32 ETH, while on Polkadot, delegators (known as nominators) must stake a minimum of 502 DOT to participate.
4.2. Acquiring Crypto for Staking
To stake crypto, you first need to acquire it. There are several ways to do this:
-
Centralized Exchanges (CEX): The easiest option for beginners. Exchanges like Binance or Coinbase provide wallets and user-friendly interfaces for purchasing and staking crypto.
-
Crypto ATMs: While limited to certain tokens like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH), some ATMs allow you to purchase crypto and transfer it to your wallet.
-
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX): Requires a bit more expertise, as users must secure their wallets and interact directly with the blockchain.
-
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Services: Allows users to buy directly from other individuals.
4.3. Participating in Staking Pools
If you don’t have enough tokens to meet the minimum requirements for a validator, you can participate in a staking pool. These pools combine the stakes of multiple users, allowing each participant to earn a share of the rewards proportional to their contribution.
5. Benefits of Crypto Staking

-
Passive Income: Staking allows you to earn rewards (usually in the form of interest) on your crypto holdings. This creates a source of passive income, where rewards are typically paid out periodically (e.g., daily, weekly, or monthly).
-
Network Security and Stability: Staking strengthens the security of PoS blockchains. Because validators have a financial stake in the network, they are incentivized to act honestly, making attacks on the network more difficult and costly.
-
Supporting the Ecosystem: By staking your tokens, you’re directly contributing to the growth and security of the blockchain ecosystem, helping to validate transactions and ensure the network operates smoothly.
-
Potential for Capital Appreciation: Many tokens have the potential to appreciate in value over time. By staking these tokens, you can earn rewards while holding a long-term position that could increase in value.
6. Risks of Crypto Staking
While staking offers rewards, it also carries inherent risks:
-
Illiquidity: Staking typically involves locking up your tokens for a period of time, which can limit your ability to sell or trade them if needed. If the market price of the staked asset falls during the lockup period, you could face a potential loss.
-
Slashing: Validators are penalized for dishonest behavior, such as trying to validate false transactions. If a validator behaves maliciously or fails to perform their duties, they risk losing a portion of their staked tokens. This risk applies to both validators and delegators who rely on them.
-
Token Devaluation: The value of staked tokens can drop, leading to a loss of value in your holdings. Since the rewards are paid in the staked crypto, this can offset any potential gains from staking.
-
Counterparty Risk: If you choose to stake your tokens via a staking pool, you are dependent on the operator's trustworthiness and reliability. Poor decisions by the pool operator can result in losses for participants.
-
Network Vulnerabilities: Staking is not immune to network attacks, smart contract bugs, or technical failures. These issues can prevent the staking process from completing or lead to loss of funds.
-
Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory status of staking remains unclear in many countries. Depending on the jurisdiction, staking might be subject to taxes or other legal complexities.
7. The Future of Crypto Staking
As the cryptocurrency ecosystem evolves, staking will likely become a more integral part of blockchain infrastructure. With the success of Ethereum’s transition to PoS and the growing market demand for sustainable blockchain solutions, staking could play a critical role in supporting decentralized finance (DeFi) and the broader Web3 ecosystem.
Moreover, the rise of liquid staking (where users can stake their tokens and still maintain liquidity) is expected to reduce the risks of illiquidity, making staking more appealing to a broader audience. As more blockchains adopt PoS, and as the regulatory landscape becomes clearer, staking may emerge as a mainstream way to earn rewards and participate in blockchain governance.
8. Conclusion
Crypto staking offers an exciting opportunity for crypto enthusiasts to earn passive income while contributing to the security and decentralization of blockchain networks. However, it’s essential to understand the mechanics, rewards, risks, and the crypto ecosystem before participating. Whether you’re a validator or a delegator, staking can be a profitable and engaging way to deepen your involvement in the world of digital assets. As the market grows and evolves, staking will likely continue to offer new opportunities and challenges, making it an area to watch closely in the coming years.
Read more:

 English
English Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt.png)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)




