1. What is Layer 3?

Layer 3, also called the application layer, is the topmost layer in the blockchain ecosystem. It is built upon Layer 1 (the base blockchain) and Layer 2 (scaling solutions). While Layers 1 and 2 focus on infrastructure, consensus, and scalability, Layer 3 is dedicated to user-facing applications and protocols. This includes decentralized applications (dApps), DeFi platforms, gaming networks, and other blockchain-based services designed to interact directly with users.
2. What problems do Layer 3s solve?
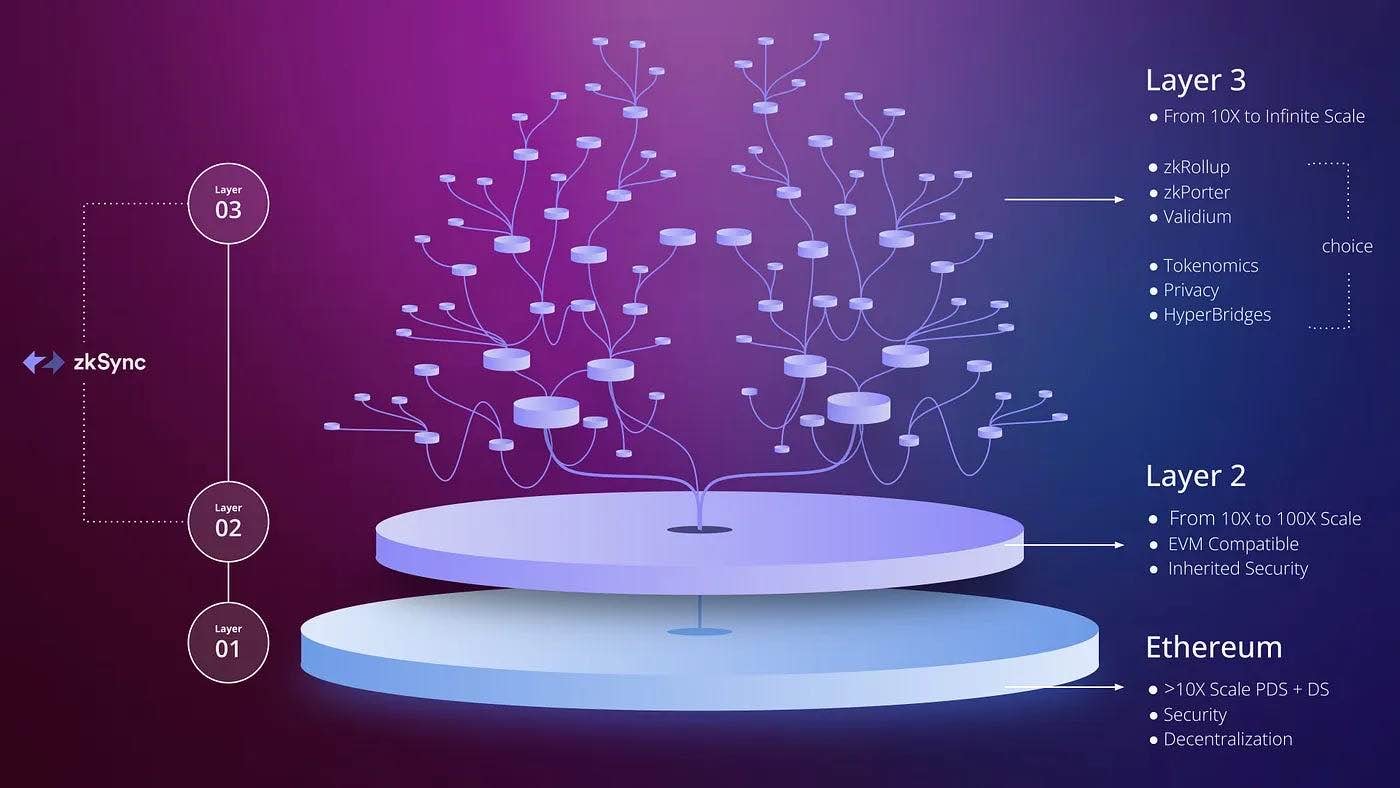
Layer 3 solutions address critical challenges that Layers 1 and 2 cannot fully resolve, particularly in areas such as scalability, interoperability, and the development of advanced decentralized applications (dApps). By building on the foundational and scaling capabilities of lower layers, Layer 3 unlocks the potential for more complex, efficient, and user-friendly blockchain applications.
One of the key problems Layer 3 solves is scalability. While Layers 1 and 2 provide important scaling mechanisms, Layer 3 takes this further by offering a framework that can support a significantly larger volume of transactions and accommodate complex applications. This enhanced scalability is essential for meeting the growing demands of blockchain technology as adoption increases and use cases become more diverse.
In addition to scalability, Layer 3 is designed to support more sophisticated dApps. These applications often require advanced infrastructure to enable features such as improved user interfaces and dynamic interactions. By handling these complexities, Layer 3 makes dApps not only more functional but also more accessible to everyday users. It facilitates the development of intricate smart contract designs and enhances the overall user experience, making blockchain technology more intuitive and engaging.
Another critical issue addressed by Layer 3 is blockchain interoperability. Acting as a bridge between different blockchain networks, Layer 3 ensures seamless data and transaction flow across platforms. For instance, a Layer 3 application can enable connectivity between Ethereum and Solana, allowing users and developers to leverage functionalities from multiple blockchains simultaneously. This interoperability is a game-changer for the blockchain ecosystem, fostering collaboration and breaking down silos between various networks.
Customization is another area where Layer 3 shines. Developers can tailor their applications to specific needs, incorporating features such as private transactions, unique governance models, or the use of native tokens. For example, Arbitrum Orbit allows developers to customize transaction fee tokens, implement permissioned systems, and launch their own blockchain networks with specific functionalities, such as Nitro-powered compatibility and enhanced governance mechanisms. This flexibility makes Layer 3 applications highly adaptable to a wide range of industries and use cases.
Layer 3 also significantly improves cost efficiency. By processing certain operations off-chain, it reduces network congestion and, consequently, transaction fees. This reduction in costs lowers the barrier to entry for both developers and users. A notable example is the Xai Network, a Layer 3 solution built on Arbitrum. Designed for Web3 gaming, the Xai Network leverages parallel processing to increase scalability while minimizing expenses, making it an ideal platform for cost-sensitive industries like gaming.
3. Benefits of Layer 3

Layer 3 introduces several key advantages that enhance the functionality and usability of blockchain systems:
-
Enhanced User Experience
Layer 3 prioritizes creating intuitive interfaces and seamless interactions between users and blockchain-based applications, making blockchain technology more accessible to non-technical users. -
Interoperability
Many Layer 3 solutions are designed to work across multiple blockchains, enabling smooth communication and data exchange between different platforms. This fosters collaboration and connectivity in the blockchain ecosystem. -
Scalability
While scaling is a primary function of Layer 2, Layer 3 applications leverage these solutions to manage high transaction volumes and support complex processes without sacrificing performance. -
Security and Compliance
Layer 3 can integrate advanced security protocols and compliance tools, helping applications meet regulatory requirements while protecting user data. -
Customization
Developers can build highly specialized applications tailored to unique industry needs or specific use cases, adding features like private transactions, custom governance models, or unique token mechanisms.
4. Use Cases of Layer 3s

Layer 3 solutions offer a diverse range of applications by building on the foundational and scaling capabilities of Layers 1 and 2. Here are some prominent use cases where Layer 3s demonstrate their potential:
4.1. Blockchain Gaming
One of the most promising use cases for Layer 3 technology is in blockchain gaming. Gaming applications often require high-speed transaction processing to maintain seamless gameplay. By leveraging Layer 3, developers can create dedicated blockchains optimized for gaming, capable of handling a significantly higher volume of transactions at faster speeds.
This scalability is crucial for ensuring a smooth in-game experience, particularly for multiplayer or massively interactive games where delays can negatively impact user engagement. Additionally, gaming applications frequently involve microtransactions—small, rapid payments for in-game assets or upgrades—which can become costly on Layers 1 or 2. Operating on Layer 3 allows developers to reduce transaction fees, ensuring that users benefit from a cost-effective gaming experience.
An example is the Xai Network, a Layer 3 solution designed for Web3 gaming, which utilizes parallel processing to enhance scalability while minimizing costs. This makes Layer 3 an ideal framework for the gaming industry, where speed, efficiency, and low costs are paramount.
4.2. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Applications
Layer 3 is also well-suited for decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. DeFi platforms require high levels of customization to cater to specific financial use cases, such as lending, borrowing, trading, and yield farming. Layer 3 enables developers to tailor their applications by customizing privacy settings, governance mechanisms, and token economics to meet the unique needs of their users.
The scalability of Layer 3 is another key advantage for DeFi. With the ability to process large volumes of transactions quickly, Layer 3 ensures that time-sensitive activities such as real-time trading and automated market-making are not hindered by network congestion. Moreover, Layer 3 promotes interoperability, allowing DeFi platforms to connect with various blockchain networks seamlessly. This cross-chain functionality empowers users to transfer assets and execute transactions across multiple blockchains, enhancing liquidity and accessibility.
For instance, a DeFi application operating on Layer 3 could facilitate instant token swaps between Ethereum and Solana, enabling users to interact with diverse financial ecosystems without leaving the platform. This interoperability is a significant step toward creating a more unified and efficient DeFi landscape.
5. Examples of Layer 3 Projects

While Layer 3 solutions are a relatively recent development in the blockchain space, several notable projects have already begun exploring this innovative concept. Below are some key examples:
5.1 Orbs
Orbs is a pioneering Layer 3 blockchain designed to address the scalability limitations of Ethereum and other Layer 1 platforms. Described as an "Enhanced Execution" layer, Orbs operates as a decentralized serverless cloud, enabling developers to write and deploy smart contracts without managing the underlying network infrastructure. This eliminates the need for physical servers, offering a seamless development experience.
Orbs integrates with multiple Layer 1 and Layer 2 protocols, including Ethereum, BNB Chain, Avalanche, and Polygon. By collaborating with these networks, Orbs extends scalability and enhances the execution of decentralized applications. Its focus on developer-friendly solutions makes it a significant player in the Layer 3 space.
5.2 Arbitrum Orbit
Released by the Arbitrum Foundation in 2023, Arbitrum Orbit introduces Layer 3 functionality built on the Arbitrum Nitro platform. This feature allows developers to create self-managed, specialized blockchains tailored to their unique project requirements.
With Arbitrum Orbit, developers benefit from even lower transaction costs and enhanced scalability. The platform empowers them to implement customized governance models, tokenomics, and privacy features, all while leveraging the robust infrastructure of the underlying Arbitrum ecosystem. Arbitrum Orbit exemplifies how Layer 3 technology can provide developers with unprecedented flexibility and efficiency.
5.3 zkSync Hyperchains
zkSync Hyperchains represent an innovative Layer 3 framework developed by the zkSync team. These Hyperchains utilize Layer 2 solutions for settlement and are powered by zkEVM, an advanced zero-knowledge proof engine. Importantly, all ZKP circuits in zkSync Hyperchains remain consistent across deployments and inherit the security guarantees of the underlying Layer 1 blockchain.
One of the standout features of zkSync Hyperchains is their ability to facilitate rapid communication and interoperability between Layer 3 chains that settle on the same Layer 2. This interconnected architecture streamlines messaging and enhances the usability of decentralized applications within the broader zkSync ecosystem
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, the development of Layer 3s marks an exciting and promising innovation in the cryptocurrency space. By combining the strengths of Layer 1 and Layer 2 — enhancing scalability while maintaining security — Layer 3 solutions take blockchain technology to the next level. However, it is important to recognize that each layer plays an integral role in the blockchain ecosystem, with no competition between them. While Layer 3 is still in the developmental phase, it is clear that it will play a pivotal role in the future of blockchain, enabling the network to handle high transaction volumes more efficiently and paving the way for more advanced, user-friendly decentralized applications.
Read more:

 English
English Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt.png)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)




