1. What is Proof-of-Stake (PoS) in Crypto?
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) is a blockchain consensus mechanism used to validate transactions and secure a blockchain network. Consensus mechanisms are methods by which a decentralized network agrees on the validity of transactions and maintains the integrity of the blockchain without relying on a central authority.
PoS is a more energy-efficient and scalable alternative to Proof-of-Work (PoW), which is traditionally used by cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. The key difference between PoS and PoW is the way blocks are validated and transactions are confirmed. While PoW relies on computational power and energy-intensive mining, PoS uses staking as the mechanism for securing the network and selecting validators.
2. How Proof-of-Stake Works
In Proof-of-Stake (PoS), blockchain security is maintained by participants who stake their cryptocurrency to become validators. The process of staking is where users lock up their coins as collateral, committing to act honestly in the validation process. Validators who stake their tokens are responsible for validating transactions and creating new blocks in the blockchain.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how PoS works:
-
Staking: Users who want to become validators must "stake" a certain amount of cryptocurrency. The more tokens a participant stakes, the higher their chances of being selected to validate a block.
-
Validator Selection: Unlike PoW, where miners compete based on computational power, in PoS, validators are selected in a pseudo-random manner. This means that while the number of coins staked gives users a higher probability of being chosen to validate a new block, validators are not chosen based on their computational ability. Instead, the selection process often considers factors such as the amount of cryptocurrency staked, the validator's history, and randomization.
-
Block Validation: Once selected, validators are responsible for confirming transactions within a proposed block. They verify that all transactions are legitimate and adhere to the blockchain's rules. If the transaction is deemed valid, the validator signs off on the block and adds it to the blockchain.
-
Rewards: Validators are rewarded for their role in securing the network. These rewards usually consist of transaction fees or new tokens issued by the blockchain. The more tokens a validator has staked, the more they can earn in rewards.
-
Slashing: To ensure that validators act honestly, PoS networks implement a penalty system called slashing. If a validator behaves maliciously, such as by attempting to validate fraudulent transactions or creating invalid blocks, they lose a portion of their staked tokens. This incentivizes validators to act in good faith and protect the network’s integrity.
3. Advantages of Proof-of-Stake

PoS offers several advantages over PoW, making it an appealing choice for modern blockchain networks. These advantages include energy efficiency, improved scalability, and greater decentralization. Below are the main benefits of PoS:
3.1. Energy Efficiency
-
One of the primary criticisms of PoW is its high energy consumption. PoW mining requires vast amounts of computational power, which in turn consumes enormous amounts of electricity. In contrast, PoS does not require energy-intensive mining hardware. Validators only need to lock up a certain amount of cryptocurrency as collateral, significantly reducing the network’s overall energy consumption.
-
For instance, after Ethereum transitioned from PoW to PoS (with its upgrade known as “The Merge”), the network's energy consumption was reduced by 99.84%. This makes PoS much more environmentally friendly and sustainable in the long term.
3.2. Lower Costs and Accessibility
-
PoS eliminates the need for specialized, expensive mining hardware. In PoW, miners must invest in high-performance computing equipment (like ASIC miners), as well as pay for electricity to run the machines. This creates a barrier to entry, as only those who can afford significant upfront costs can participate.
-
In PoS, however, anyone with the required amount of cryptocurrency can participate in the validation process. This makes PoS more accessible to a wider range of users, enabling more people to contribute to securing the network without the need for costly equipment.
3.3. Scalability
-
PoS allows for faster transaction processing and higher scalability compared to PoW. Since PoS does not rely on time-consuming cryptographic puzzles, blocks can be validated and confirmed more quickly. This leads to improved throughput and lower transaction fees.
-
PoS networks are generally more scalable because they don’t suffer from the same bottlenecks that occur in PoW networks, where miners must compete for block rewards by solving difficult mathematical puzzles.
3.4. Security
-
PoS is designed to be secure even with a higher degree of decentralization. While PoW networks can be susceptible to 51% attacks (where an attacker gains control of more than 50% of the mining power and manipulates the blockchain), PoS prevents this threat by making it extremely expensive to control 51% of the staked cryptocurrency.
-
In PoS, validators must stake their tokens, and if they attempt to cheat the system, they risk losing those staked tokens. This makes PoS highly secure because malicious behavior becomes financially unfeasible.
-
Slashing is an important security feature in PoS. If a validator is found to be acting maliciously or irresponsibly, a portion of their staked tokens can be forfeited, making it less likely for anyone to try to compromise the network.
3.5. Decentralization
-
PoS encourages decentralization because it removes the need for specialized mining equipment, which can be expensive and concentrated in specific regions or entities. This ensures that the network is more distributed, allowing smaller participants to participate in the validation process.
-
As a result, PoS helps to ensure that blockchain networks remain decentralized and resistant to centralization, where large mining pools or entities could otherwise gain control of the network.
4. Proof-of-Stake vs Proof-of-Work
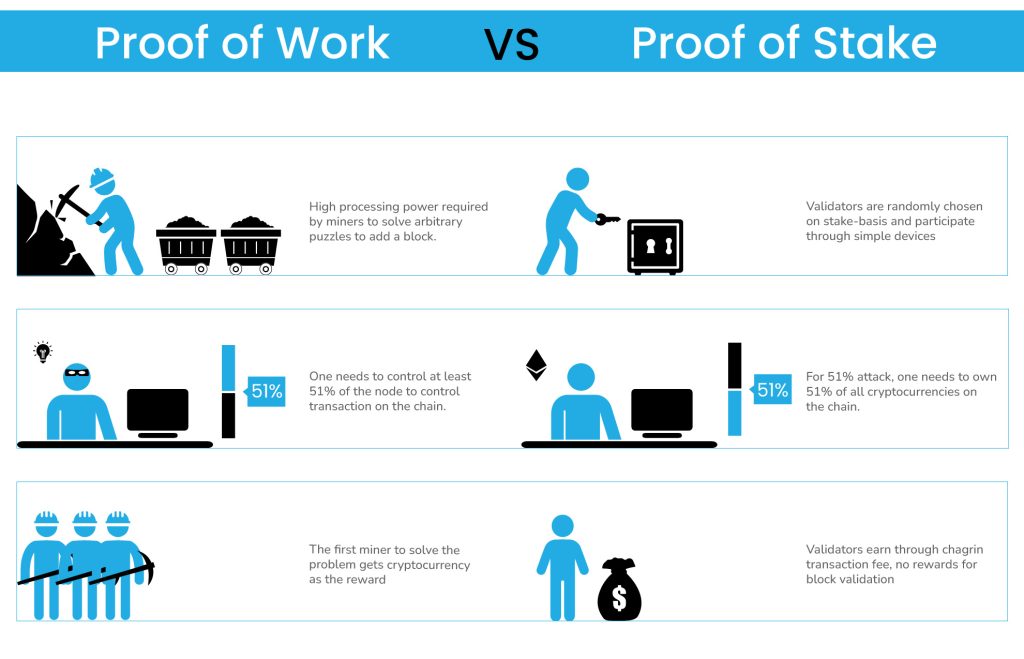
Proof-of-Stake and Proof-of-Work both serve the same fundamental purpose: to secure the blockchain and validate transactions. However, they operate in very different ways. Here’s a detailed comparison between PoS and PoW:
| Feature | Proof-of-Stake (PoS) | Proof-of-Work (PoW) |
| Block Creators | Validators (selected based on staked coins) | Miners (competing to solve computational puzzles) |
| Validation Process | Validators are chosen to confirm transactions based on staked tokens and randomization. | Miners solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions. |
| Energy Efficiency | Low energy consumption. No need for powerful hardware. | High energy consumption due to the need for specialized hardware. |
| Hardware Requirements | Low (just need to own tokens and stake them) | High (requires powerful mining rigs and hardware). |
| Security | Security is provided by staked tokens and slashing penalties. | Security is provided by the computational difficulty of mining. |
| Reward System | Validators earn transaction fees and sometimes new tokens. | Miners earn block rewards (newly minted coins) and transaction fees. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with faster transaction processing. | Less scalable due to mining bottlenecks. |
5. Popular cryptocurrencies using Proof-of-Stake
Several major cryptocurrencies have adopted Proof-of-Stake as their consensus mechanism, offering users the ability to stake their coins and participate in the validation process. Some notable PoS-based cryptocurrencies include:
-
Ethereum: Ethereum transitioned from PoW to PoS with the upgrade known as "The Merge." This shift has greatly reduced the blockchain's energy consumption while enhancing scalability.
-
Tezos: A blockchain platform that uses a liquid PoS model, enabling users to delegate their tokens to validators without giving up ownership of the tokens.
-
Cardano: A PoS-based blockchain that focuses on security, scalability, and sustainability, with a focus on academic rigor and peer-reviewed research.
-
Solana: A high-performance blockchain that uses a combination of PoS and Proof-of-History (PoH) to provide fast and scalable decentralized applications.
-
Polkadot: A multichain network that uses PoS for securing the relay chain and enabling the creation of interoperable blockchains.
-
Algorand: A PoS blockchain that aims to create a decentralized and secure network with a focus on scalability and performance.
6. Conclusion
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) is seen as a more efficient, secure, and scalable alternative to Proof-of-Work (PoW). By replacing energy-intensive mining with staking, PoS offers greater accessibility, lower energy consumption, and enhanced decentralization. With higher scalability and a reduced environmental impact, PoS is increasingly becoming the consensus mechanism of choice for modern blockchain networks. As more projects adopt PoS, it is likely to continue shaping the future of decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain technology.'
Read more:

 English
English Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt.png)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)




