1. What is Ripple?
.jpg)
Ripple is a fintech company that was founded in 2004 and is based in San Francisco. Before venturing into cryptocurrency in 2012, Ripple’s core goal was to improve the traditional settlement systems for international transactions. The aim was to make cross-border payments cheaper and faster, offering an alternative to the outdated systems in place at the time.
In 2012, Ripple launched its native cryptocurrency, XRP, and also introduced RippleNet, a global payments network. RippleNet offers real-time gross settlements (RTGS) for financial institutions and other services to simplify, accelerate, and reduce the costs associated with international transactions. RippleNet's primary purpose is to compete with SWIFT, the traditional money transfer network, and provide a more efficient way to move money across borders. Ripple charges a minimal transaction fee (in XRP) to use the network.
2. What is XRP?
.jpg)
XRP is a digital asset that was created in 2012 with the purpose of driving innovation within the financial payments industry. XRP is the native cryptocurrency of the XRP Ledger (XRPL), a decentralized, open-source blockchain maintained by a network of unique nodes (peer-to-peer servers).
XRP’s main use case is to facilitate fast and low-cost transactions across different currencies or networks. It functions as a bridge currency, allowing users to send value between two currencies (or networks) without needing an intermediary, like a bank or payment processor. This peer-to-peer feature enables users to send money across borders in seconds rather than days, making international transactions more efficient and affordable.
Ripple has established a presence in various countries, with banks and financial institutions adopting XRP for its cross-border payment capabilities. It’s particularly popular for "hawala" transfers, a traditional method of transferring money across borders, especially in the Middle East and South Asia.
3.How has XRP performed in recent years?
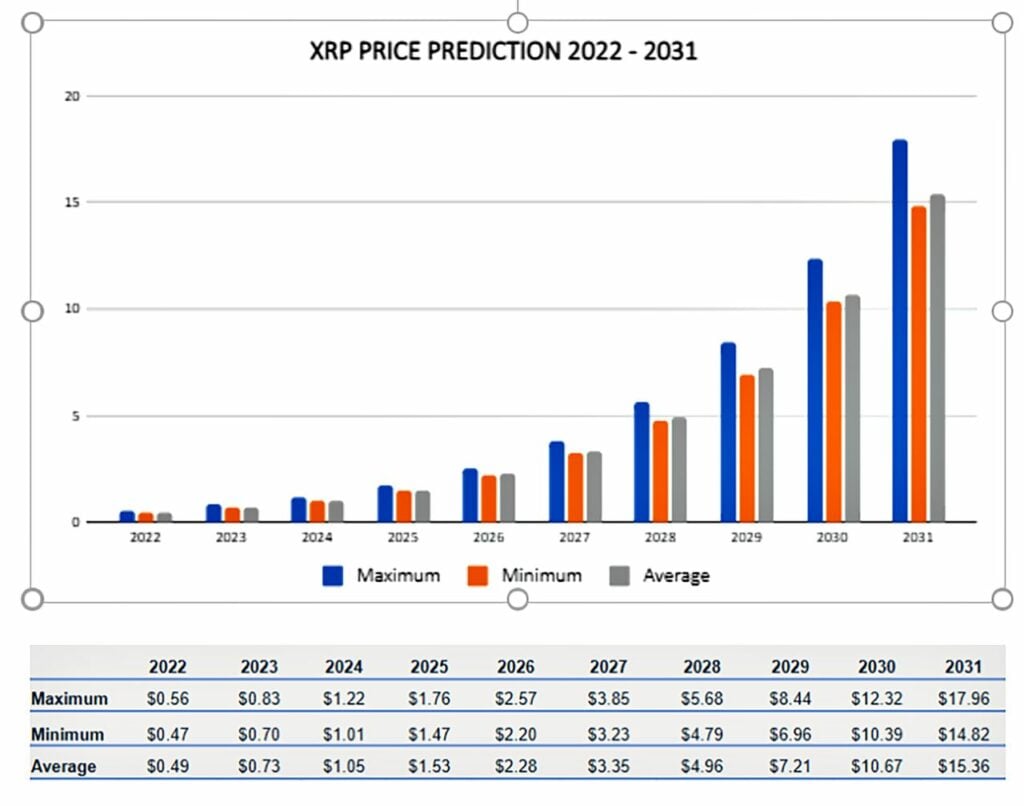
XRP reached an all-time high of $3.4 during the 2017 bull market. However, like many cryptocurrencies, XRP has faced challenges in subsequent years. In mid-2020, its price dipped to as low as $0.15, and by July 2024, it was trading around $0.38. Despite these downturns, XRP has since experienced a significant rebound, gaining nearly 600% in value in the months following its July 2024 low.
This recovery is attributed to multiple factors, including positive market sentiment following the re-election of President Donald Trump in 2024, a growing belief that the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) may lose its case against Ripple, increasing adoption of RippleNet, and the potential approval of an XRP exchange-traded fund (ETF) in 2025. On January 15, 2025, XRP surged to a seven-year high of $3.40, driven by an increase in meme coin trading volume on the network, expectations surrounding Trump’s crypto-friendly policies, and hopes for clarity regarding the SEC case.
Are Ripple and XRP the same?
It’s important to distinguish between Ripple and XRP, as they are often mistakenly used interchangeably.
-
Ripple is the company behind the XRP cryptocurrency. Ripple provides a blockchain-based digital payment network that offers efficient cross-border transaction solutions to financial institutions.
-
XRP is the cryptocurrency that powers RippleNet and is used to facilitate transactions on the XRP Ledger (XRPL).
Ripple Labs, the company, is privately owned, while XRP is a digital asset that operates on a decentralized network. Ripple has continuously evolved and rebranded over the years, acquiring other companies such as Metaco and Fortress Trust in 2023 and 2024 to support its business growth.
4. How does XRP and the XRP Ledger work?

The XRP Ledger (XRPL) operates using a consensus model that differs from traditional proof-of-work (PoW) systems like Bitcoin’s. Rather than relying on miners to validate transactions, XRP utilizes a network of trusted servers (referred to as "unique nodes") to reach consensus on the validity of transactions. If 80% of the nodes agree on a transaction, it’s validated and recorded on the ledger.
One of the significant advantages of this consensus mechanism is that it is far less energy-intensive than Bitcoin’s PoW model, making XRP a more environmentally sustainable option. Additionally, XRP transactions are typically faster and cheaper than those on other networks like Bitcoin or Ethereum.
4.1 XRP – The Native Token
The total supply of XRP is capped at 100 billion tokens, which were created and distributed at the launch of the XRP Ledger. Unlike cryptocurrencies that are mined (such as Bitcoin), XRP was pre-mined. A smart contract regulates the release of future XRP tokens into circulation.
RippleNet uses XRP for "on-demand liquidity" services, which allow users to make payments without needing to pre-fund an account. XRP acts as an intermediary, helping to bridge two currencies with different methods of transfer, enabling liquidity in the process.
4.2 XRP vs. Bitcoin: Key Differences
XRP and Bitcoin have some fundamental differences:
-
Consensus Mechanism: Bitcoin uses Proof of Work (PoW), which requires miners to validate transactions, whereas XRP uses a consensus protocol across trusted nodes to validate transactions by reaching an agreement on their validity.
-
Energy Efficiency: XRP’s consensus model requires less computational power, making it more energy-efficient compared to Bitcoin’s PoW mechanism.
-
Mining: Bitcoin is mined, while XRP was pre-mined, and future releases are controlled by a smart contract.
-
Ownership: XRP is managed by Ripple, a privately-owned company, while Bitcoin is decentralized and not owned by any individual or entity.
5. Advantages and Disadvantages of XRP
5.1 Advantages
-
Low Fees: XRP transactions have extremely low fees, often less than $0.01, compared to the high fees charged by traditional banking systems for cross-border payments.
-
Fast Transactions: XRP can handle up to 1,500 transactions per second, and each transaction is settled in under 5 seconds, making it much faster than Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
-
Partnerships with Banks: Ripple has built partnerships with major financial institutions like Santander, American Express, and Mitsubishi UFJ, which use XRP and RippleNet for cross-border payments.
-
Eco-Friendly: XRP’s consensus protocol uses significantly less energy than PoW-based networks like Bitcoin, and Ripple is committed to achieving carbon neutrality by 2030.
5.2 Disadvantages
-
Centralization: XRP has been criticized for being more centralized than other cryptocurrencies. Ripple controls over 55% of the total XRP supply, which gives the company significant influence over the market.
-
Regulatory Concerns: The SEC’s ongoing legal case against Ripple over whether XRP is a security has led to some uncertainty regarding its future. The outcome of this case could impact XRP’s value and its legal status.
6. The SEC v. Ripple Case

In 2020, the SEC filed a lawsuit against Ripple, accusing the company of selling XRP as an unregistered security. The case has been ongoing, and in 2025, there is growing optimism that the legal battle may soon come to an end. A U.S. judge ruled in 2023 that Ripple did not violate securities laws by selling XRP on public exchanges, which caused XRP’s price to surge. However, the case is still not resolved, with the SEC appealing parts of the decision and continuing to press charges related to institutional sales of XRP.
With potential changes in leadership at the SEC and the appointment of crypto-friendly figures in President Trump’s administration, the regulatory environment for XRP may shift in a favorable direction, contributing to the token’s growth.
Conclusion
XRP is a unique cryptocurrency that offers faster, cheaper, and more efficient cross-border payments. It’s backed by a strong company, Ripple, which has partnered with several leading banks and financial institutions. While it has faced challenges, particularly legal battles with the SEC, its potential for growth remains high, especially with increased adoption and potential regulatory clarity. Whether XRP will continue to thrive depends on its ongoing legal struggles and the future development of the crypto industry as a whole.

 English
English Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt.png)