1. What is a Crypto Ecosystem Map?
.jpg)
A crypto ecosystem map is a visual representation that organizes the numerous elements of the cryptocurrency and blockchain industry into a coherent framework. It helps highlight the roles and relationships of these components, offering users a clearer understanding of the industry.
Key components typically represented in a crypto ecosystem map include:
-
Blockchain networks (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana).
-
Exchanges (e.g., Binance, Coinbase, Uniswap).
-
DeFi platforms (e.g., Aave, Compound, Curve).
-
NFT marketplaces (e.g., OpenSea, Blur).
-
Wallets (e.g., MetaMask, Ledger).
-
Infrastructure providers (e.g., Chainlink, The Graph).
-
Regulatory entities influencing compliance and policies.
This map is essential for understanding the crypto world’s ecosystem and serves as a guide for traders, developers, and investors.
2. Key sectors in the Crypto Ecosystem Map

2.1 Blockchain Networks: The Backbone of Crypto
Blockchain networks are the foundational layer of the crypto ecosystem. They serve as decentralized ledgers that record transactions across peer-to-peer networks.
-
Bitcoin (BTC): The first blockchain and a pioneer in decentralized digital currencies.
-
Ethereum (ETH): The leading platform for smart contracts and decentralized applications.
-
Layer-2 Solutions: Networks like Polygon, Optimism, and Arbitrum reduce congestion and fees on Layer-1 blockchains.
-
Emerging Blockchains: Newer platforms like Avalanche and Aptos aim to improve scalability and interoperability.
These networks form the infrastructure upon which tokens, dApps, and other elements are built.
2.2 Exchanges: The Gateways to Digital Assets
Exchanges enable users to buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies, making them critical components of the ecosystem.
-
Centralized Exchanges (CEXs): Platforms such as Binance, Kraken, and Coinbase provide user-friendly interfaces and high liquidity.
-
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Protocols like Uniswap, SushiSwap, and PancakeSwap operate without intermediaries, granting users greater control over their funds.
-
Hybrid Models: Platforms combining CEX and DEX features, like Binance DEX, aim to bridge the gap between usability and decentralization.
Exchanges facilitate price discovery and liquidity, ensuring the smooth functioning of the market.
2.3 Decentralized Finance (DeFi): The Future of Financial Services
DeFi protocols replicate traditional financial services like lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries.
-
Lending and Borrowing: Platforms like Aave and MakerDAO allow users to earn interest or take loans.
-
Decentralized Exchanges: SushiSwap and Curve Finance facilitate token swaps directly between users.
-
Stablecoins: Assets like USDT, USDC, and DAI provide price stability for transactions within the crypto ecosystem.
DeFi is transforming financial systems, making them more accessible and efficient.
2.4 NFTs: The New Era of Ownership
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have introduced a unique way to represent ownership in the digital world.
-
Art and Collectibles: Platforms like OpenSea and Rarible enable the buying and selling of digital art and collectibles.
-
Gaming: Projects like Axie Infinity and The Sandbox integrate NFTs for in-game items and land ownership.
-
Tokenization of Real Assets: Platforms like RealT tokenize real estate for fractional ownership.
NFTs are reshaping industries ranging from art to real estate by redefining digital ownership.
2.5 Wallets and Security Solutions
Crypto wallets are tools for securely storing and managing private keys, the foundation of cryptocurrency ownership.
-
Hot Wallets: Examples include MetaMask and Trust Wallet, which are software-based and convenient for frequent transactions.
-
Cold Wallets: Hardware wallets like Ledger and Trezor provide enhanced security by storing private keys offline.
-
Multi-Signature Wallets: These wallets require multiple approvals for transactions, adding an extra layer of security.
Wallets ensure user control and safety in managing digital assets.
3. Benefits of Mapping the Crypto Ecosystem

3.1 Simplifying Complexity
A crypto ecosystem map helps users grasp the intricacies of the industry, from technical foundations to application layers.
3.2 Identifying Opportunities
By visualizing the ecosystem, investors and developers can spot underserved sectors or emerging trends.
3.3 Enhancing Decision-Making
Traders and businesses can use these maps to strategize, mitigate risks, and optimize their operations within the crypto world.
4. Guide to use a Crypto Ecosystem Map
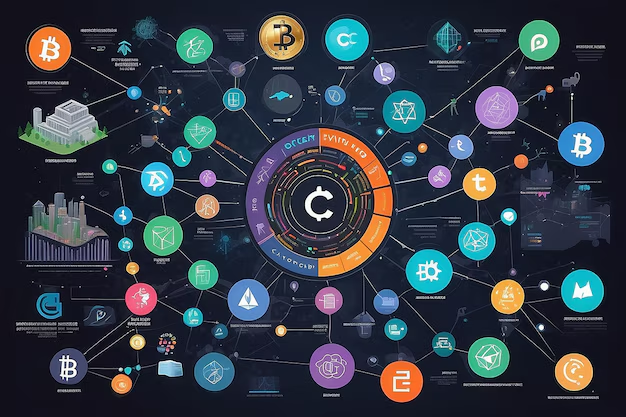
To fully harness the power of a crypto ecosystem map, it’s important to understand how its components interact and evolve. Below are key steps to make the most of this tool:
4.1 Understanding Interconnections
By studying the relationships between components—like how DeFi protocols depend on stablecoins—users can identify critical dependencies and vulnerabilities.
4.2 Identifying Key Players
Mapping helps highlight major industry players, such as dominant exchanges, leading blockchains, or fast-growing dApps.
4.3 Staying Updated
Since the crypto ecosystem evolves rapidly, maps should be updated regularly to reflect new technologies and trends, such as AI tokens or next-generation blockchains.
5. Conclusion
A crypto ecosystem map is more than just a visual tool; it is a gateway to understanding the dynamic and interconnected world of blockchain and cryptocurrencies. By categorizing and analyzing various components, such as blockchains, exchanges, and DeFi protocols, users can navigate this complex landscape with confidence.
Whether you’re an investor, developer, or blockchain enthusiast, a well-constructed crypto ecosystem map offers valuable insights to capitalize on opportunities, mitigate risks, and stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of digital assets.
Read more:


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt.png)
















